Xometry Resources
Webinar Recording - Trimming Costs, Keeping Quality: Smart Design Tips for CNC Machining

Case Study: Ryvid’s Anthem EV Bike Races Through Production With Xometry's Horizontal Supply Chain
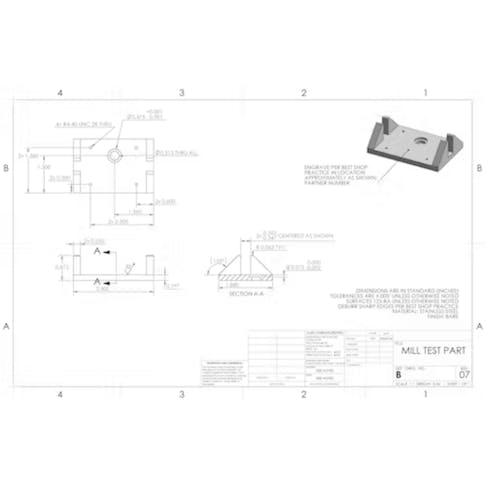
eBook: How to Make a Good Technical Drawing

Industry Design
View All Industry Design ContentDesign tips for our top industries like aerospace and defense, automotive, energy, medical and dental, robotics, supply chain, and more.
Case Studies
View All Case Studies ContentExamples of Xometry's work with customers across various industries and manufacturing processes.
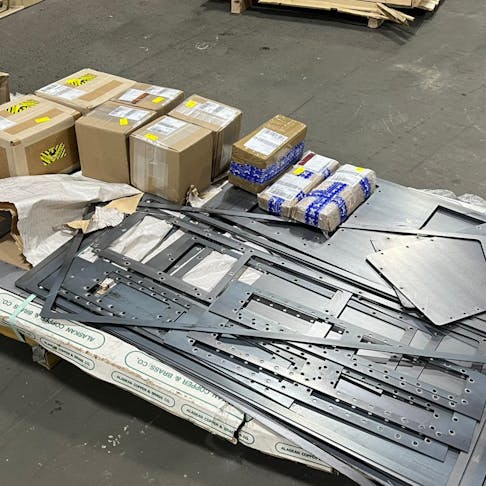

Case Study: Xometry’s Precise Laser Tube Cutting Helps Sea Box Build, Scale Up a Big Project for a Defense Customer
Case Study: KPM Analytics Turns to Xometry’s Instant Quoting Engine for a Quick and Affordable Custom Part

Case Study: Working with Xometry Helps 557 Form Keep All its Parts in Motion

Case Study: Danley Sound Labs Prototypes Products With Perfect Pitch Thanks to Xometry 3D-Printed Parts
Supplier Shop Tips
View All Supplier Shop Tips ContentTips for machine shops, fabrication shops, 3D printing bureaus, and manufacturers in Xometry's Partner Network.




3D Printing Design
View All 3D Printing Design ContentThe latest news, trends, and manufacturing design tips for additive manufacturing.



Machining Design
View All Machining Design ContentThe latest news, trends, and manufacturing design tips for custom machined and fabricated parts.




Design Guides
View All Design Guides ContentIn-depth design guides full of best practices for all of Xometry's manufacturing processes.
Blog
View All Blog ContentThe latest Xometry product updates, news, and trends in manufacturing.


Xometry at IMTS: Commercial Supply Chain Solutions, Laser Tube Cutting Quotes, and More


Materials
View All Materials ContentInformation about common materials used in manufacturing processes.




Injection Molding
View All Injection Molding Content
Overmolding Materials: Definition, Importance, and How the Process Works


Metal and Plastic Extrusion
View All Metal and Plastic Extrusion ContentThe latest technical guides and articles related to extrusion processes.


eBooks Library
View All eBooks Library ContentExplore our eBooks, rich with insights and practical information to help you better comprehend the manufacturing industry.

eBook: 9 Benefits of Reshoring


eBook: Injection Molding Tolerances and How to Optimize Them

eBook: How to Make a Good Technical Drawing
Casting
View All Casting Content

Plaster Casting: What It Is, How It Works, Uses, Process, and Advantages

Tube
View All Tube ContentThe latest news, trends, and manufacturing design tips for laser tube cutting, tube bending, tube rolling, and more.

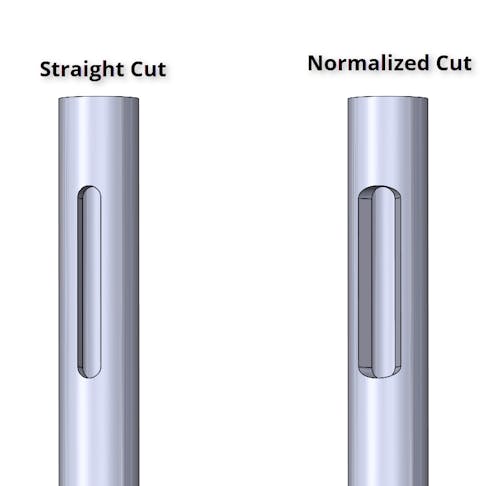
Sheet
View All Sheet ContentThe latest news, trends, and manufacturing design tips for sheet metal, stamping, laser and waterjet sheet cut parts.