Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D Printing Service
High-Quality Large Format FDM 3D Printing
1-Day Expedites Available. Free Shipping on All US and International Orders.
International prototype pricing includes tariffs.
What is FDM 3D Printing?
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is an additive manufacturing technology widely known for its speed, accuracy, and competitive cost. FDM machines precisely extrude melted material to create a part. FDM parts can be made in as fast as one day.
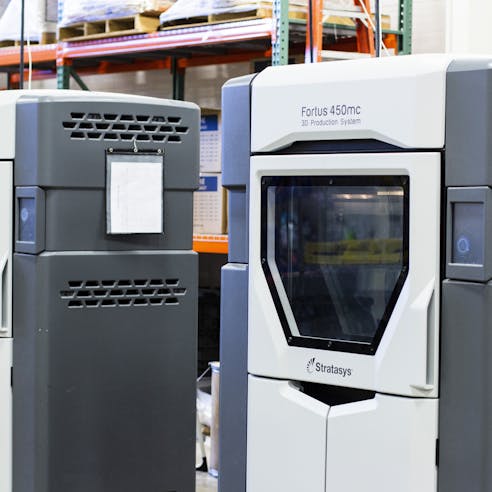
Xometry's FDM 3D printing service offers large build volumes up to 24″ x 36″ x 36″ on Stratasys Fortus platforms. Economical, general-purpose, material options are also available, utilizing various FDM or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) printers. FDM 3D printing offers the most extensive variety of colors and selection of production-grade thermoplastics of any 3D printing process. Materials range from general-purpose ABS or ASA to high-performing polycarbonate and heat-resistant ULTEM.

General Purpose Materials
| Material Name | Color(s) | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) | Data Sheets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Material Name ABS (General Purpose) | Color(s) Black, Blue, Dark Grey, Ivory, Red, White | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 33 MPa-28 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 10.5%-4.7% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 87 °C | Data Sheets ABS Data Sheet (Reference Only) |
Material Name PLA (General Purpose) | Color(s) Black, Blue, Red, White | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 50 MPa-37 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 2.9%-1.9% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 55 °C | Data Sheets PLA Data Sheet (Reference Only) |
Material Name ASA (General Purpose) | Color(s) Black, Dark Blue, Dark Gray, Light Gray, Green, Ivory, Orange, Red, White, Yellow | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 37 MPa-31 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 9.2%-4.6% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 100 °C | Data Sheets ASA Data Sheet (Reference Only) |
Material Name Stratasys ABS-M30 | Color(s) Black, Blue, Dark Grey, Ivory, Red, White | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 32 MPa-28 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 7%-2% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 96 °C | Data Sheets |
Material Name Stratasys ASA | Color(s) Black, Dark Blue, Dark Gray, Light Gray, Green, Ivory, Orange, Red, White, Yellow | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 27 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 9%-3% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 98 °C | Data Sheets |
Stratasys material properties are achieved by running OEM materials and parameters on OEM Fortus equipment. Due to a broad material and equipment allowance, general ABS, ASA, and PLA material properties and colors may vary slightly, and datasheets are for reference only. International options are available for general-purpose ABS, ASA, and PLA.
High Performance Engineered Materials
| Material Name | Color(s) | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) | Data Sheets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Material Name Stratasys Nylon 12 | Color(s) Black | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 49.3 MPa-41.8 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 30%-6.5% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 91.9 °C | Data Sheets |
Material Name Stratasys PC | Color(s) White | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 57 MPa-42 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 4.8%-2.5% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 138 °C | Data Sheets |
Material Name Stratasys PC-ABS | Color(s) Black | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 41 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 6% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 110 °C | Data Sheets |
Material Name Stratasys ULTEM 1010 | Color(s) Amber (Natural) | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 64 MPa-41 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 3.3%-2.0% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 216 °C | Data Sheets |
Material Name Stratasys ULTEM 9085 | Color(s) Black, Tan | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 47 MPa-33 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 5.8%-2.2% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 153 °C | Data Sheets |
Properties apply to US-based production (Stratasys Fortus FDM).
Speciality Materials for Medical or Electronics
| Material Name | Color(s) | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) | Data Sheets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Material Name Stratasys ABS-ESD7 (Static Dissipative) | Color(s) Black | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 35.4 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 3.4% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 101.4 °C | Data Sheets |
Material Name Stratasys ABS-M30i (Biocompatible) | Color(s) Ivory | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 36 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 4.0% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 96 °C | Data Sheets |
Material Name Stratasys PC-ISO (Biocompatible) | Color(s) Translucent Natural, White | Tensile Strength, Yield (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) 57 MPa | Elongation at Break (XZ%-ZX%) 4% | HDT @ 66 psi (°C) 133 °C | Data Sheets |
Properties apply to US-based production (Stratasys Fortus FDM).
General Purpose ABS, ASA, or PLA
Our available materials include General-Purpose ABS, ASA, and PLA. These low-cost, rigid thermoplastics are typically produced via Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) using an array of 3D printers. These materials can also access our global manufacturing network, providing significantly reduced pricing compared to branded Stratasys materials.

Available Finishes for FDM Parts
Standard
FDM parts are built with support material that is removed during post-processing. The part surfaces are left with fine layer lines.
Custom
Xometry can provide additional processing such as painting or vapor smoothing to meet your needs.

Ready to get started on your 3D printing quote?
Free shipping available for domestic 3D printing orders ; learn more!
Video: Quick Tips: FDM 3D Printing
FDM Applications

Concept Models
The speed and versatility of FDM lets engineers create physical snapshots of their designs.

Rapid Prototyping
An FDM machine can be used to create durable prototypes that withstand thermal, chemical, and mechanical stress.

Manufacturing Tools
High-performance materials make FDM ideal for producing jigs, fixtures, and production tooling.
Benefits of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)


We use the most advanced industrial FDM printers designed to meet tolerances of +/- a single build layer thickness (e.g. 0.010") for the first inch and +/- .002” for every inch thereafter.

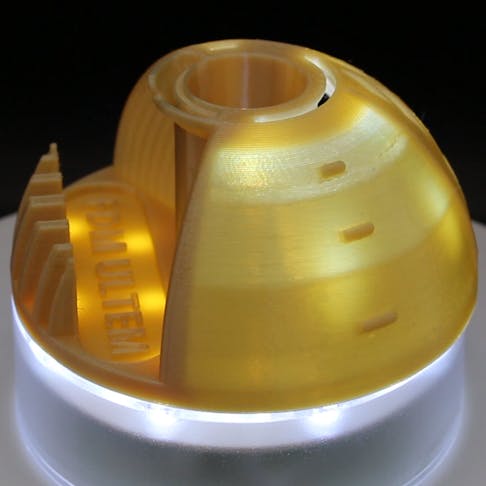
FDM printed parts are available in a variety of high-performance plastics for applications that require resistance to the elements.

Xometry can produce FDM parts with large build volumes up to 24″ x 36″ x 36″
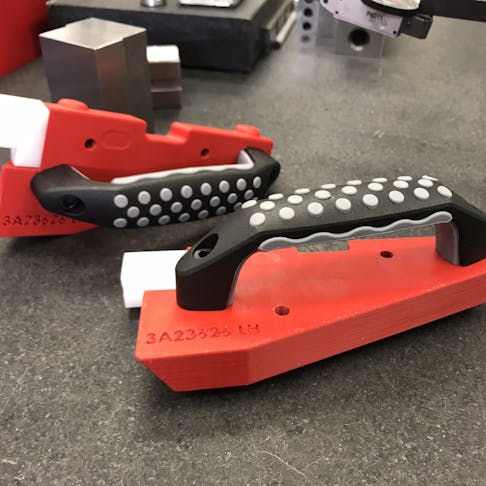

FDM parts do not require tooling which reduces the manufacturing lead time from weeks to days.
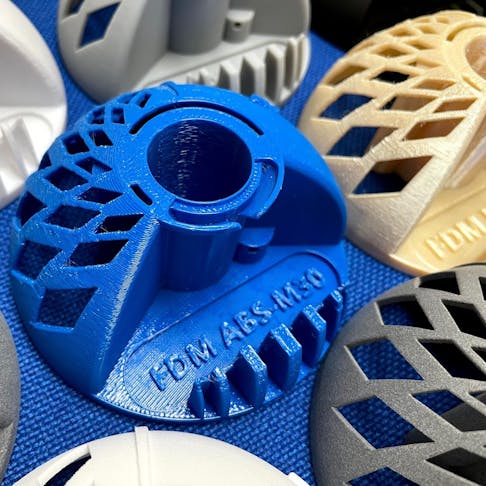

FDM has the highest variety of real engineered thermoplastics.
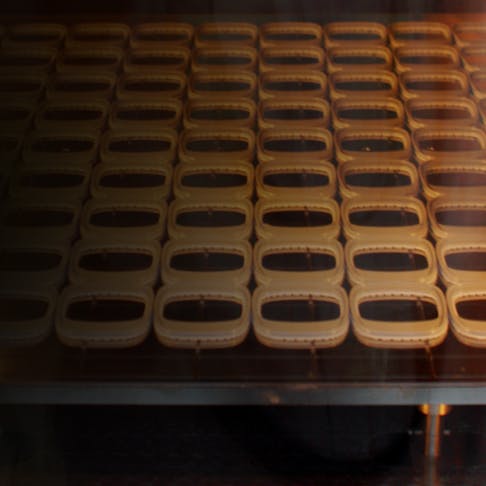

An FDM printer is capable of producing end-use parts on-demand, increasing throughput and helping you get to market faster.
FDM General Tolerances
| Tolerance Note | Description |
|---|---|
Tolerance Note General Tolerance | Description +/- a single build layer thickness for the first inch and +/- .002” for every inch thereafter. |
Tolerance Note Build Size | Description Up to 24" x 36" x 36" |
Tolerance Note Layer Height, less than 16" | Description 0.010" Layers (0.008" for PLA) |
Tolerance Note Layer Height, greater than 16" (up to 36") | Description 0.013" Layers |
Tolerance Note Minimum Wall Thickness | Description 0.047"(less than 16"), 0.060" (greater than 16") |
FDM 3D printed parts can be built up to 24" x 36" x 36". Stratasys Fortus 400/450-series machines will produce parts up to 16", and Stratasys Fortus 900MC or F900 platforms are used for parts larger than 16". General-purpose ABS, ASA, and PLA can be built on desktop equipment, using generic materials, or both. General tolerances apply before secondary finishing or post-processing unless otherwise specified. To learn more tips about FDM 3D printing, check out our Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Design Guide. Applies to US-based production only.
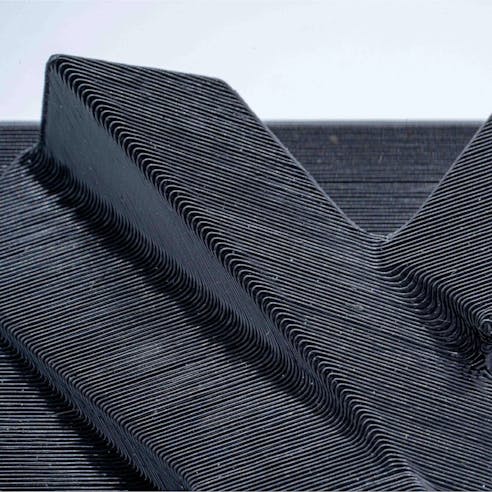
Feature Details - FDM


The dark grey ABS-M30 part was made using Stratasys Fortus equipment, with a .010" layer height as the default setting. Note that the text and small feature resolution are coarse.
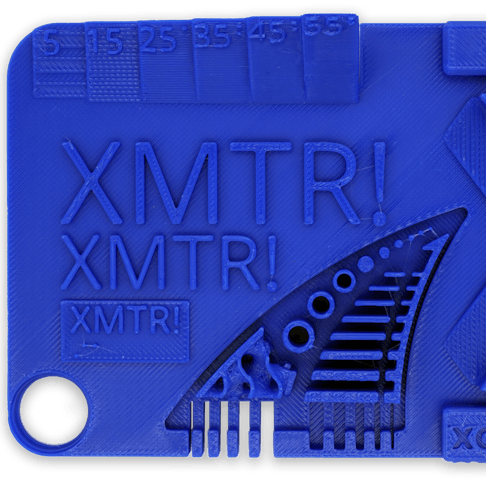
The desktop 3D printed FFF model in blue Prototyping PLA overall had better feature resolution, failing at walls thinner than 0.5 mm, pegs to 0.75 mm, and text below 5 mm.
FDM Infill Options

Solid

Light

Ultralight
What is Infill?
Infill is a characteristic unique to the FDM process. In FDM, an extruder nozzle deposits material along the toolpath, fusing it to previous layers to build a 3-dimensional body. The interior of the volume can be printed as “solid,” but it does not necessarily have to be. The pattern printed inside the contours is referred to as “infill.”
Infill can reduce material consumption and weight and allow for the production of confined volumes. An in-depth article on infill can be read here.
Need to Compare Printing Processes?
Our quick reference guides let you quickly compare different 3D printing processes!
An Overview of the FDM Process
How Fused Deposition Modeling Works
With FDM technology, a spool of the chosen feedstock is introduced to a typical fused deposition modeling system via an extruder, which regulates the feed movement of the polymer to the heater where it melts. This molten polymer is extruded through a nozzle and deposited onto the print bed, also known as the build platform. The extruder, heater, and nozzle are all contained in a printhead which is attached to a gantry above the flat build platform. This is designed to offer relatively high freedom of motion in the X and Y axes as the material is deposited.
The fused deposition modeling system uses innovative printer software to separate a 3D computer-aided design (CAD) file into individual slices, or cross-sections. Each slice in the file is converted into machine code, which essentially uses the Cartesian coordinate system to determine the path the printer head must follow across the X and Y axes to deposit the first layer of material onto the build platform. Once the bottom layer is complete, the build platform descends by a small amount – relative to the deposited layer thickness – and the printhead repeats the process to deposit the second layer. This procedure is repeated in sequential layers until the part is finished.

Most FDM systems have a two-nozzle system that can selectively extrude sacrificial support structures as they part prints. Depending on the feedstock, this support may be soluble in a sodium hydroxide (NaOH) bath, leaving only the printed part after processing. The support structure can also be removed manually without damaging the printed part.
The benefits of this technique are manifold, particularly when it comes to the development of concept models and rapid prototypes for research and design (R&D) processes.

Why Use FDM For Your Parts?
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) is among the most easily accessible and recognizable additive manufacturing technologies worldwide. Available to both 3D printing hobbyists and large-volume manufacturers alike, it is known for its speed and precision in generating three-dimensional polymeric structures using a choice of feedstock materials. The range of filaments available for fused deposition modeling include:
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS-M30, ABS-M30i, ABSi)
Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA)
Polycarbonates (PC, PC-ABS and PC-ISO)
High-performance plastics (PPSF, Ultem 1010, Ultem 9085, and Nylon-12)
Benefits Of Fused Deposition Modeling
FDM printing is a cost-effective additive manufacturing process, especially for rapid prototyping or low-volume production. Since FDM prints require little post-processing and use more readily available materials, leads times from quote to print and delivery are fast.

Why Choose Xometry for FDM 3D Printing?

Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.

Easy to Use
Get your parts delivered right to your door without the hassle of sourcing, project management, logistics, or shipping.

Vetted Network
We are ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, and AS9100D certified. Only the top shops that apply to become Suppliers make it through our qualification process.