Custom Die Casting Services
High Quality Die Cast Metal Parts.
Die Casting Process
Die casting is the manufacturing process of choice when producing high volumes of relatively complex metal parts and is widely used due to its versatility, reliability, and accuracy. Die casting eliminates all or most secondary operations needed to make a metal part; however, post-machining is common to meet tighter critical-to-function tolerances. Die casted parts can also be post-processed in any finish their respective CNC machined counterparts can.
Like injection molding, die casting requires the fabrication of a mold tool--called a die--that can have one or multiple cavities. The process works for softer alloys, including aluminum and zinc alloys, due to their relatively lower melting temperature. Die casting works by injecting molten metal into a die cavity, which takes the shape of the part and hardens into place before removal. Depending on the project scope, die casting can be low- or high-pressure, using a ladle or plunger to deposit metal. Die casting can produce highly complex, tight-tolerance parts in a repeatable manner at very high production volumes. Modern die casting methods such as squeeze casting and semi-solid metal casting produce high-quality parts for nearly every industry. Die casting companies will often specialize in casting aluminum or zinc, with aluminum making up roughly 80% of die cast parts.
Our project managers and experts personally review and manually quote each die casting project to ensure we meet your unique needs while providing a fast and easy manufacturing experience. Learn more about the process and our capabilities in the sections below.
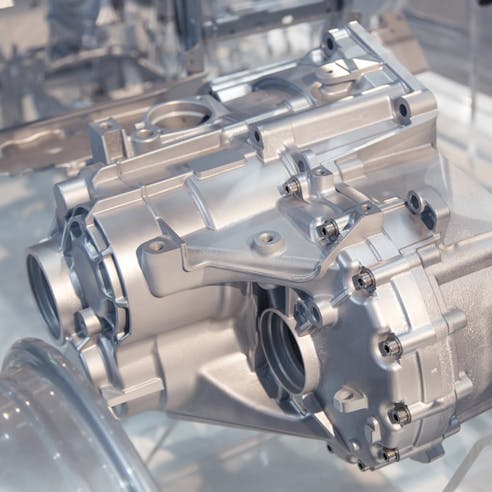

Xometry's Die Casting Service

Start A Quote
Upload your files to the Xometry Quote Engine and configure your project. Our team will consult with you to ensure your specifications, lead time, and price fit your project needs. We will provide a DFM report for approval before kicking off tooling.

Sample Approval
Once your project is kicked off we will build a high-quality die. After the tooling is created we will send out part samples, called T1s, for approval.

Production Begins
Once satisfied with your samples, we move forward with production and deliver the parts. Rest easy knowing Xometry is handling supplier management and logistics throughout the process. You own your tooling and can easily re-order as needed to meet demand.
Die Casting Services Available from Xometry
Xometry partners with die casters that utilize the latest die casting machines and technology to deliver high-quality, on-demand parts to a wide variety of industries. Our offering focuses on the two leading types of die casting: hot chamber casting and cold chamber casting. Both types can produce parts with complex geometry, close tolerances, and robust mechanical properties.
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Also known as gooseneck casting, the hot chamber die casting process is the most popular die casting process. It is optimal for working with lower melting point alloys such as zinc, magnesium, and lead. A holding pot is filled with metal and heated with hot chamber die casting until molten by an attached or built-in furnace. A feature of the hot chamber system referred to as the gooseneck forms a holding chamber within the pot and a nozzle-like pathway that connects to the injection cavity of the fixed half of the die. A plunger that sits above the chamber allows it to fill with molten metal from the holding pot. When the chamber is loaded, the plunger lowers and forces molten material up the gooseneck into the die cavity. The mold is held together under pressure while the metal cools and solidifies in the mold. Once the metal is cool enough, the dies open, and the casted piece ejects via ejector pins.
Cold Chamber Die Casting
With the cold chamber die casting process, the chamber remains at room temperature and does not have a holding pot of molten metal. Metal is melted in a separate furnace and deposited into the shot chamber through a pouring hole by hand with a ladle. In cold chamber die casting, the mold is connected directly to the shot chamber and does not utilize a plunger system. Instead, a ram forces molten metal into the mold and held under high pressure while the metal solidifies. This type of die casting is suitable for comparatively higher melting temperature materials such as aluminum.
Metal Materials for Die Cast Parts
Several different metal materials are available to choose from when manufacturing using die casting. The material you choose will depend on your intended use for the product. For instance, cast aluminum parts are common in aerospace or automotive applications where corrosion resistance and weight reduction are essential factors. You can learn more about the main types of die casting materials we offer in the sections below. If you have a specific material request, just let us know!
Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum alloys are the most widely used for die cast parts. Aluminum die casting suppliers benefit from the total recyclability of the material and its ease of use. Due to the comparatively higher melting point, aluminum die casting may require a cold chamber casting process. Engineers use cast aluminum parts primarily for their great strength to weight ratios, dimensional stability, and diverse finishing options. Some of the other common characteristics of cast aluminum alloys are:
- Withstand high operating temperatures
- Corrosion Resistance
- Good stiffness
- High thermal and electrical conductivity
Engineers and designers can choose from a wide range of alloys for their aluminum casting parts. Xometry offers the most popular aluminum die casting alloys, including:
- A360.0
- A380.0
- A383.0 (ADC12)
- A413.0
Zinc Die Casting
Zinc is the easiest to cast material among the die casting metals and is typically used in hot chamber processes. Molten zinc has exceptional casting fluidity and a lower melting point. Its strength and stiffness allow it to produce parts with thinner walls and highly detailed features and maintain tight tolerances. The low melting point of die casting zinc alloys means the zinc die cast components cool off and solidify more quickly, which results in the fastest production rates of the die casting materials. Zinc is an all-around well-performing material due to its balance of mechanical and physical characteristics, which include:
- Impact strength
- High hardness
- Great stability
- High-quality surface finish and easily plated
- Low melting point
Xometry offers the most popular types of Zamak and ZA die casting zinc alloys. More specifically, those alloys include:
- Zamak 2 (ZA-2)
- Zamak 3 (ZA-3)
Available Die Casting Finishes
Standard (As-Cast)
Zinc and aluminum zinc parts can be left as-cast and retain reasonable corrosion resistance. Aluminum parts must be coated to achieve corrosion resistance. Cast parts are typically broken away from the casting sprue, leaving rough marks at the gate locations. Most castings will also have visible marks left by the ejector pins. The surface finish for as-cast zinc alloys is commonly 16-64 microinch Ra.
Bead Blasted
The part surface is left with a smooth, matte appearance.
Anodized (Type II Or Type III)
Aluminum is typically anodized. Type II anodizing creates a corrosion-resistant oxide finish. Although suppliers can anodize parts in different colors, the surface of a die cast part does not facilitate a cosmetic finish with anodizing. Type III is a thicker finish and creates a wear-resistant layer in addition to the corrosion resistance seen with Type II. Anodized coatings are not electrically conductive.
Powder Coating
All die cast parts can be powder coated. This is a process where powdered paint is electrostatically sprayed onto a part, then baked in an oven. Powder coating creates a strong, wear- and corrosion-resistant layer that is more durable than standard wet painting methods. A wide variety of colors are available to create the desired aesthetic.
Wet Painting
All die cast parts can be wet painted in a wide variety of paint formulations and colors.
Plating
Die cast parts can be plated with electroless nickel, nickel, brass, tin, chrome, chromate, Teflon, silver and gold.
Chemical Film
Suppliers can apply a chromate conversion coat to protect aluminum from corrosion and improve the adhesion of paints and primers. Chemical film conversion coatings are electrically conductive.
Media Tumbled
Die cast materials are subjected to vibratory media tumbling to remove sharp edged and smooth surfaces.
Custom
Don't see the finish you need? Submit an RFQ and our partner shops will look into a finishing process for you.

Ready to get started on your Die Casting quote?
Applications of Die Casting
The versatility and high production potential of die casting enable it for various applications and industries. Die casting products that are small to medium in size with complex features are typically well suited for the process. Examples include consumer and industrial products, automotive parts, aerospace components, and parts for medical devices. Die casting products is a great option when you need high-volume metal parts that may be too large for similar high-volume processes such as Metal Injection Molding (MIM).
- Aerospace & Automotive Components
- Connector Housings
- Pumps and Plumbing Fixtures
- Outdoor lighting
- Gears
- Appliances and Lighting
Die Casting Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Die Casting
Complex Geometry
Die casting can reliably produce custom die cast parts with thin walls and challenging geometry that is durable and dimensionally stable.
Strength
Metal die castings are typically stronger than plastic injection molded parts and more resistant to high temperatures. Metals such as aluminum offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios.
Precision
Die casting offers typical tolerances ranging from +/-0.003″ – 0.005″ per inch but can go as tight as +/- .001” depending on your specifications, part geometry, and material.
Custom Finishes
Metal finishers can produce cast parts with smooth or textured surfaces, paints, and plating finishes. Finishes can protect from corrosion and improve cosmetic appearance.
Disadvantages of Die Casting
Tooling Cost
While the per piece cost of die cast parts is relatively low, the tooling dies and maintenance costs can require a high initial investment.
Not for Low Quantities
Due to the higher upfront tooling costs, die casting is not economical for low-volume runs. We recommend only considering die casting for quantities greater than 1000.
Lead Times
Before production, many steps must be accomplished first, often taking multiple weeks to execute. These steps include addressing DFM concerns, tool design, manufacturing the tools, and creating samples. The upfront checks and validations make die casting one of the slower manufacturing processes to ramp up compared to others.
Our team of experts will be working with you closely throughout the process and offer suggestions and options to provide you with the best possible turnaround while working to meet your unique needs.
Why Choose Xometry for Online Die Casting Services?

Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.

Easy to Use
Get started with our easy-to-use platform and let our experts take care of managing the project from locating the right manufacturing partner to delivery logistics.

Vetted Network
We are ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, and AS9100D certified. Only the top shops that apply to become Suppliers make it through our qualification process.
Built-In Tool Management
Xometry's platform has built-in features that make managing tooled projects a breeze, giving customers greater transparency into production. Find all your tooling quotes and orders in one space with your Tool Library. From there, you can explore their Tool Details page, which covers the current status, milestones, tool specifics, and activity related to that tool. You can also easily find and contact the Xometry team member assigned to your project, no matter the project's current phase.
Our Tool Library and Tool Details pages provide multiple benefits, such as:
- Better Management of Tooled Quotes & Orders
- Tool Organization & Categorization
- Detailed Status Updates & Tooling Information
- Easily Connect with Experts
- Project Transparency
