Custom Online 3D Printing Service
Get instant online 3D printing service quotes on custom parts in dozens of plastic and metal materials. Order 3D printed items and get free shipping on all US orders. International prototype pricing includes tariffs. ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, IATF 16949:2016, and AS9100D certified. ITAR registered.
High-Quality Rapid Prototyping and Production 3D Printed Parts
Xometry offers industry-leading 3D printing online services. Whether you need prototypes or production parts, we can make them on demand. We are your one-stop shop for accurate, precise, custom 3D-printed parts at an affordable price. Upload your 3D CAD file to get a 3D printing quote and lead time within seconds. We print everything from single prototypes to thousands of production-grade parts.
We use the latest additive manufacturing technology to build affordable, high-quality products in over 60 metals and plastics. Xometry offers eight high-quality 3D printing processes, including selective laser sintering, fused deposition modeling, stereolithography, direct metal laser sintering, PolyJet, Carbon DLS, metal binder jetting, and HP Multi Jet Fusion. We use commercial and industrial-grade printers such as Stratasys Fortus 900mc and Fortus 450 FDM, EOS Polymer Laser Sintering (SLS) and DMLS, Concept Laser, SLM Solutions, 3D Systems, ExOne, and more. For a great introduction to additive manufacturing, please visit our Complete Guide to 3D Printing.
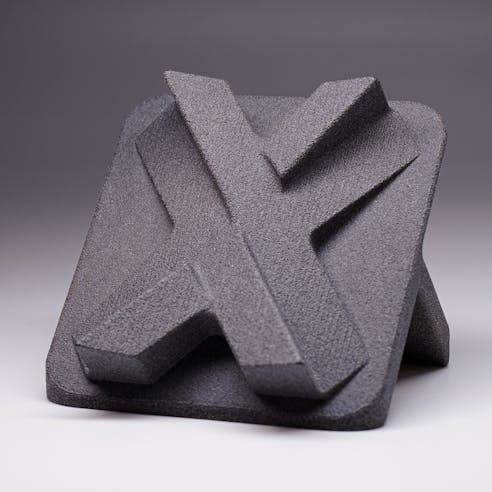

Thermoplastic 3D Printing

Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D Printing Service

HP Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) 3D Printing Service

Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D Printing Service
Resin 3D Printing

PolyJet 3D Printing Service

Stereolithography (SLA) 3D Printing Services

Carbon Digital Light Synthesis™ (DLS™) 3D Printing Service
Metal 3D Printing

Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) 3D Printing Service

Metal Binder Jetting 3D Printing Service
The Best 3D Printing Material Selection

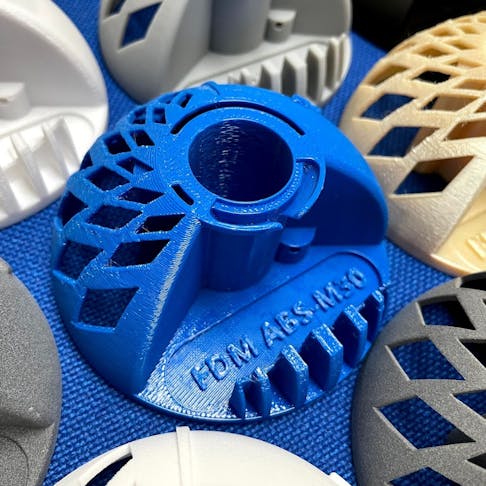
Nylon is one of the most versatile options for 3D print services with great feature detail and performance.

ABS and ASA 3D prints have a variety of colors and are a staple to 3D printed plastics.
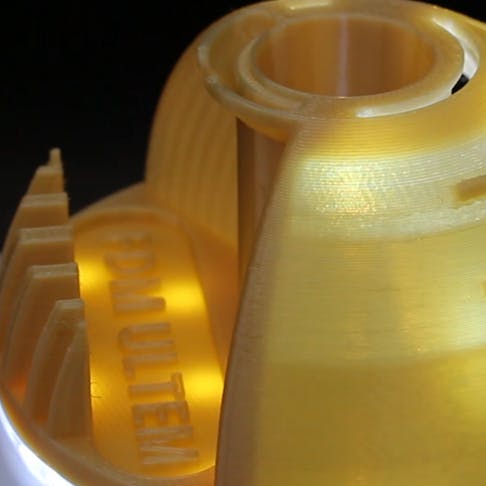

Tough, heat resistant, and durable ULTEM is engineered to withstand the most rigorous environments.

3D printed TPE and silicone-based elastomers give rubber parts without the need for tooling.
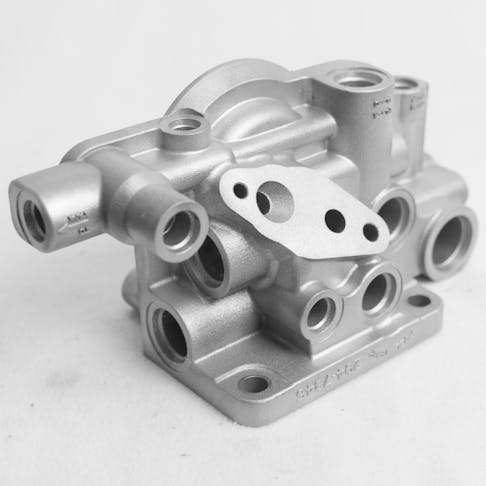

3D printed metal parts can achieve complex geometries without a sacrifice in performance.
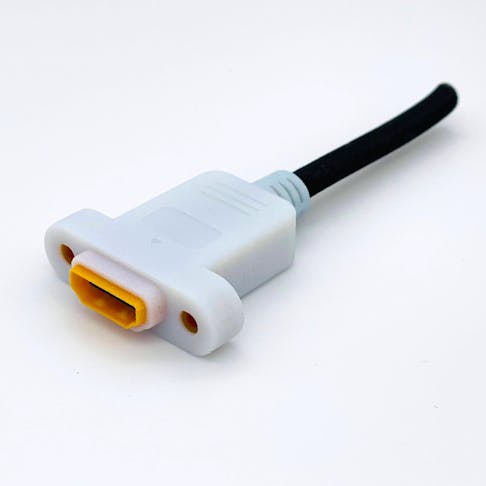

PolyJet 3D can combine multiple properties for overmolds and other cosmetic features and print in hundreds of thousands of hues, all in a single print.
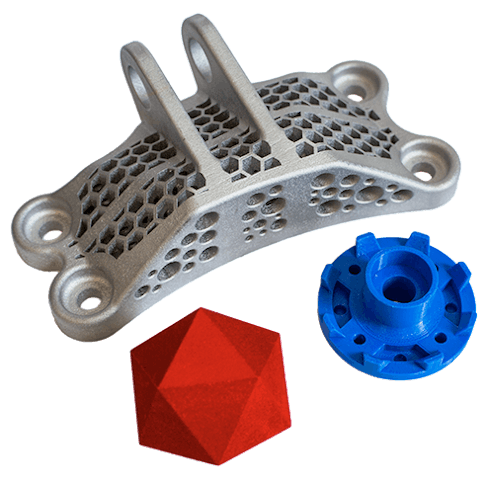
Xometry has the widest variety of industrial 3D custom printing materials available for instant quoting.
Flame Retardant Plastic 3D Printing
Xometry's 3D Print Service offers a variety of polymers that are flame retardant and qualify for UL-94 V-0 and FAR 25.853 60 second burn test. This includes FDM ULTEM 9085, FDM ULTEM 1010, and SLS Nylon 12, Flame Retardant. These polymers are perfect for aviation and aerospace applications. Learn more about 3D Printed Flame Retardant Plastics.

Ready to start making custom 3D printed parts?
Free shipping available for domestic 3D printing orders ; learn more!
Applications of 3D Printing

Concept Models
The speed and versatility of custom 3d printed items lets product developers create physical snapshots of their designs through the iterative process.

Rapid Prototyping
3D Printing can be used to create fully-functional prototypes, complete with moving parts, as well as all-in-one assemblies.

Direct Digital Manufacturing
The high accuracy and consistency of 3D printing makes it an ideal way to build production quantities of discrete or customized parts.
Advantages of 3D Printing

Parts can typically be shipped in as little as 1 day, allowing for faster design iterations and speed to market.
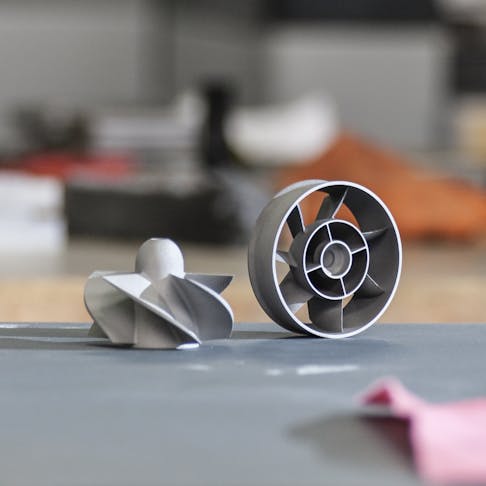

3D printing can offer great impact strength, medium flexibility, and high resistance to environmental factors.
Geometries can be built more easily due to the 3D printing process, adding complexity without additional cost.
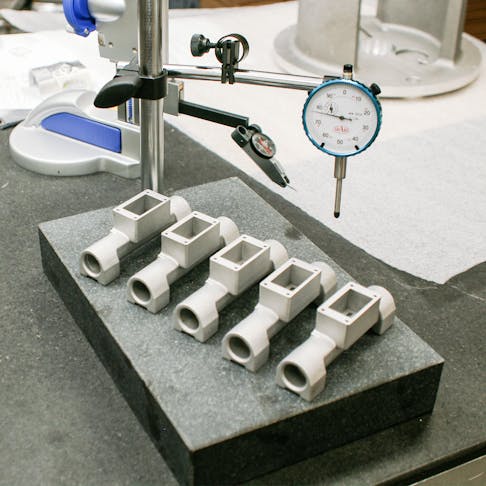

3D printing can achieve precise parts and feature details.
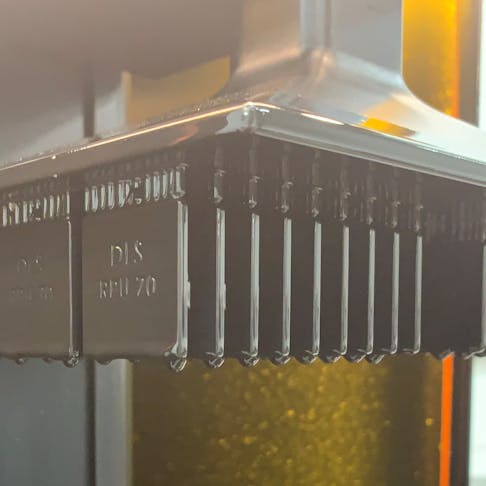

3D printing with Xometry helps you produce end-use parts on-demand, increasing throughput.
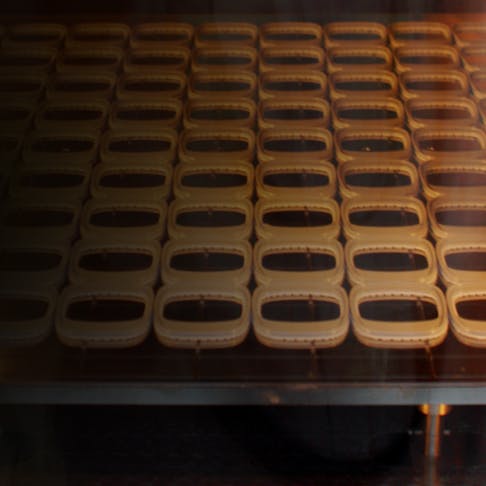

With 3D printing, you can make a single part or component as easily as dozens of production pieces.
3D Printing General Tolerances
| Description | Tolerance Notes |
|---|---|
Description Part Size | Tolerance Notes Xometry can accommodate 3D printing up to 24" x 36" x 36" without the need to split and bond parts. |
Description Minimum Feature Size | Tolerance Notes 0.030" - 0.060" is typical. |
Description Minimum Wall Thickness | Tolerance Notes 0.020" - 0.060" is typical. |
Description Clearance Between Features | Tolerance Notes At least 0.030" |
General tolerances apply before secondary finishing or post-processing unless otherwise specified. Please check out Xometry's Manufacturing Standards for more information on tolerances per process.
What is 3D Printing?
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process where materials are joined together to make objects from 3D model data (CAD). Typically, 3D printing is a layer-by-layer process where part geometries are “grown,” fusing with the previous layer. 3D printing processes can build objects in plastics, photopolymers, reaction polymers, composites, metal, glass, and other materials.

Instant Quote Demo
See how fast and simple it is to get a quote for 3D printing using the Xometry Instant Quoting Engine®.
Why Choose Xometry for 3D Printing?

Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.

Easy to Use
Get your parts delivered right to your door without the hassle of sourcing, project management, logistics, or shipping.

Quality Assurance
We are ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, IATF 16949:2016, and AS9100D certified.

Become an additive expert with our Complete Guide to 3D Printing
3D Printing Services Available at Xometry

Color 3D Printing Service by Xometry

Large Scale 3D Printing Service on Xometry

Rubber 3D Printing Service on Xometry
