Brass Laser Cutting Services
Xometry offers the highest quality brass laser services and can assist in the production of parts with intricate and complex geometries and excellent surface finishes.
Xometry offers the highest-quality brass laser cutting services, which are able to create precise and attractive components for a multitude of applications. Brass is a versatile material that is easy to cut, bend, and machine. It has good wear resistance and corrosion resistance but also looks very appealing.
As a result, brass is used in many architectural components and finishes, such as: door handles and hinges, plumbing fittings and valves, and electrical outlets and switch plates. Laser cutting of brass sheets can accurately produce components for each of these areas. Laser engraving of brass is another manufacturing approach, which provides other opportunities for using brass for decorative purposes or commemorations on plaques and awards.
What Is Brass Laser Cutting?
Brass laser cutting is a method of processing brass into specific shapes by cutting it with a precise laser. Brass in large sheets (available in various thicknesses) is placed on a table, and a computer-controlled laser moves across the surface of the sheet, using the energy in a focused laser beam to melt the brass in precise patterns. In this way, a design can be manufactured rapidly and repeatedly from brass.
Brass can also be engraved using a laser. In this case, the brass sheet is not cut, but rather a designed pattern is engraved on the metal’s upper surface. There are different types of laser cutters, with the common types being fiber lasers and CO2 lasers. A CO2 laser is commonly used to lightly mark brass, whereas a fiber laser is necessary to engrave or cut brass.
Applicable Laser Cutting Processes for Brass
Laser cutting can be applied to brass in different ways. Below are two ways to use a laser cutter with brass, together with some examples of applications:
- Laser Cutting
- Laser Engraving

Laser Cutting
Laser cutting of brass uses a focused laser to heat a specific point on a brass sheet to melting temperature. An assist gas is then used to blow the melted brass away, creating the cut. In order to melt the brass, the laser needs to transfer sufficient energy to the metal to raise its temperature to the melting point. Brass is a reflective metal and therefore does not readily absorb the optical energy from lasers. For this reason, a fiber laser is used. The fiber laser uses light with a shorter wavelength of 1.06 μm which is better absorbed than the light from a CO2 laser at 10.6 μm. A fiber laser can transfer more optical energy than a CO2 laser, so it is more capable of heating brass to its melting point. The reflectivity of brass also drops significantly in its molten state—so once a cut is started, so long as it is maintained, the cutting of brass with a laser is relatively easy (on sheets up to approximately 0.25 inches thick).
Laser Engraving
Laser engraving brass is also carried out with a fiber laser. However, with engraving, a lower laser power is sufficient to penetrate a limited depth into the brass surface. The reflectivity of the brass still limits other types of lasers from engraving it—a fiber laser is necessary. Engraving brass is popular for details such as nameplates for trophies, and decorative or promotional items. The shine and golden color of the brass make it attractive for this application.
Advantages of Brass Laser Cutting
Listed below are the advantages of brass, as well as the process of laser cutting it:
- Malleable
- Rust Free
- Decorative
- Corrosion Resistant
- High Precision

Listed below are the advantages of brass, as well as the process of laser cutting it:
Malleable
Brass has a number of useful properties, such as its malleability. As a result, it is easy to bend and form. Further to this, it is easy to machine. Brass therefore allows quick and easy manufacturing (with resultant lower costs) compared to other materials.
Rust Free
Brass is rust-free, as it is a non-ferrous metal (it has no iron), but also because it generally does not easily corrode. Specifically in wet environments, brass does not readily oxidize. This is a major advantage for longevity in plumbing applications, but also for cleanliness and smoothness in applications with gears or bushings.
Decorative
Brass is an attractive material that can be used in a decorative way. In particular, laser cut brass decorations are popular as they can have intricate and interesting designs, and will have an appealing golden shine.
Corrosion Resistant
Brass is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and therefore is used in various applications within corrosive environments. This includes water services (plumbing) and components that may be exposed to the elements, such as: door hinges, locks, and handles.
High Precision
Laser cutting is a highly precise method of shaping brass. The laser is focused to a fine point, and the kerf width (the thickness of material lost due to cutting) is predictable and can be kept to a minimum, particularly for thinner sheets. Modern laser cutters are controlled by computer numerical control (CNC), making the process highly accurate, repeatable, and less prone to errors.
Disadvantages of Brass Laser Cutting
Brass does have some disadvantages to its use, including when laser cutting. These disadvantages are listed below:
- Tarnishing
- Maintenance
- High Reflectivity

Tarnishing
Although brass is rust-free due to its good corrosion resistance, it can still be discolored and made dull by tarnishing. The tarnish on brass is a passive oxide film that builds up over time purely due to exposure of the brass surface to air. The tarnish removes the shine and affects the appealing golden-yellow color of brass. Therefore, brass does need regular attention in order to polish off the tarnish and keep it at its best.
Maintenance
Although brass is fairly low maintenance, the fact is that it still requires some maintenance, particularly for aesthetic or decorative pieces. These need to be polished at regular intervals to maintain the brass’s shine and attractive color. The frequency of this maintenance will depend on how exposed the brass is to the environment. A brass component outside in the elements will need much more attention than one inside an air-conditioned room.
High Reflectivity
Brass is a reflective metal, so can be difficult to laser cut as it reflects some of the optical energy from the laser. Due to this high reflectivity of brass, it cannot be cut well using a CO2 laser, but rather a fiber laser is required.
In need of custom brass laser cutting services?
Brass Laser Cutting Applications
Brass is a versatile material that is frequently used in wet environments due to its excellent corrosion resistance. It is also easy to machine but has good wear resistance. As a result of these properties, brass has many popular applications.
- Locks
- Hinges
- Gears
- Bearings
- Zippers
- Plumbing Fittings, Hose Couplings, and Valves
- Electrical Sockets
- Electrical Plugs
Locks
Brass is a common material for locks, as locks are typically exposed to the elements, and brass weathers this environment well. It is also relatively easy to machine, leading to lower manufacturing costs. Elements of the internal mechanism of door locks are also commonly made of brass.
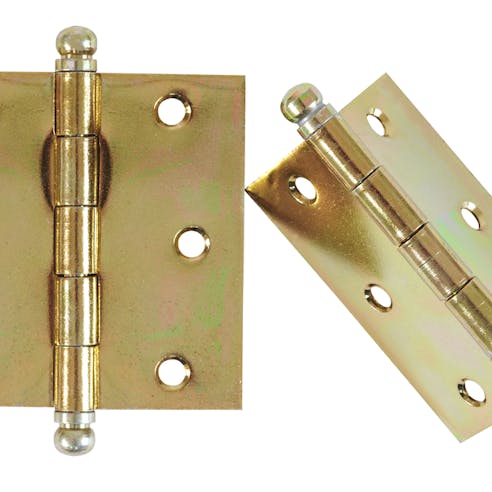
Hinges
Brass is a popular choice for door hinges as it is corrosion-resistant and aesthetically pleasing. It is a ductile material that is easy to cut, drill, and machine, but still has sufficient strength to support loads such as doors. Hinges can be laser cut from a brass sheet, particularly small, decorative hinges.
Gears
Brass is widely used for small, accurate gears. This is because it has a reasonably high tensile strength, but is easily machinable into accurate and intricate dimensions. It also has good corrosion resistance and wear resistance, so brass gears are able to operate for extended periods without failure.
Bearings
Brass is used in bearings and bushings because it is rust-free and easy to machine. Particularly because of its corrosion resistance, brass is a good selection for underwater applications. However, brass is softer than alternatives like bronze, so brass bushings and bearings are not used in applications with very high loads.
Zippers
Brass has historically been used to manufacture zippers for clothing. Although other lighter and cheaper materials are often used today, brass zippers are still used for heavy-duty applications like: jackets, bags, and tents.
Plumbing Fittings, Hose Couplings, and Valves
Brass plumbing fittings are ubiquitous, mainly due to their excellent resistance to corrosion in wet environments. Brass is also easy to machine and cut, and as such is well suited to manufacturing the small details of plumbing fittings and hose couplings. These properties also make it ideal for both valve bodies and finer valve internals.
Electrical Sockets
Brass can be used for electrical sockets to provide an attractive aesthetic look. It is reasonably priced but has a pleasing golden shine, or otherwise can be weathered to give an antique effect. The wear resistance of brass is also useful for switch plates, which will be touched hundreds or thousands of times over years of service.
Electrical Plugs
Brass is used for electrical plug pins as it has a favorable combination of low cost, good conductivity, and wear resistance. Brass is conductive as its main alloying element is copper. The wear resistance is necessary for plug pins in particular due to plugs being pushed into and removed from sockets.
Alternatives to Brass Laser Cutting
Xometry offers alternatives to laser cutting for creating profiles from brass such as:
- Waterjet Cutting
- Plasma Cutting

Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet cutting is an alternative method of cutting sheets, including materials such as brass. Waterjet cutting works by using a pump to create very high-pressure water. This water is directed at the material to be cut, as a very focused, high-impact stream. For tougher materials, an abrasive can also be added, such as small grains of garnet, which are entrained along the high-pressure jet of water. Waterjet cutting does have the benefit over laser cutting in that it does not create a heat-affected zone. However, laser cutting is faster, more precise, and has no liquid waste.
Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting uses an electrical voltage to create an electric arc between a plasma torch and the material to be cut. The material to be cut must therefore be conductive—this is therefore applicable for brass. This electric arc forms ionized particles in a plasma stream. When this comes into contact with the material to be cut, it reaches very high temperatures and melts the material very quickly in order to cut it. Plasma cutting is generally cheaper than laser cutting, but it cannot achieve the precision and detail that a laser cutter can.
Why Choose Xometry for Brass Laser Cutting Services?

Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.

Easy to Use
Get started with our easy-to-use platform and let our experts take care of managing the project from locating the right manufacturing partner to delivery logistics.

Vetted Network
We are ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, and AS9100D certified. Only the top shops that apply to become Suppliers make it through our qualification process.