When it first entered the scene, 3D printing seemed a little futuristic and was met with some skepticism, but it very quickly became a mainstream manufacturing method. These machines build parts and products one layer at a time and can handle even complex and intricate designs with a lot of detail. You can make pretty much anything you can dream up with 3D printers, and it’s a much easier process than some other more traditional methods. You don’t need copious amounts of training or any particular expertise as the machine does everything for you.
Xometry now has thousands of 3D printing customers and instantly quotes nine different 3D printing processes. From advanced aerospace components and medical implants to tools and equipment to home decor, the applications of 3D printing we see here at Xometry are nearly endless. This article will review 10 applications of 3D printing and briefly discuss other topics related to 3D printing innovation.
Prosthetics
3D printing has transformed the process of creating prosthetics, refining more and more, and making it simpler and efficient to make custom prosthetics for the patient. To make prosthetics, CAD, or computer-aided design, software easily designs them, and then they're manufactured by 3D printing. If there is something wrong with the 3D-printed prosthetic, updating the CAD software and reprinting all that needs to be done.
Replacement Parts
For replacement parts, 3D printing is useful for consumers because there are no long lead times or running around to pick up parts. 3D printing lets consumers and businesses maximize the value of their purchases and focus on more important things.

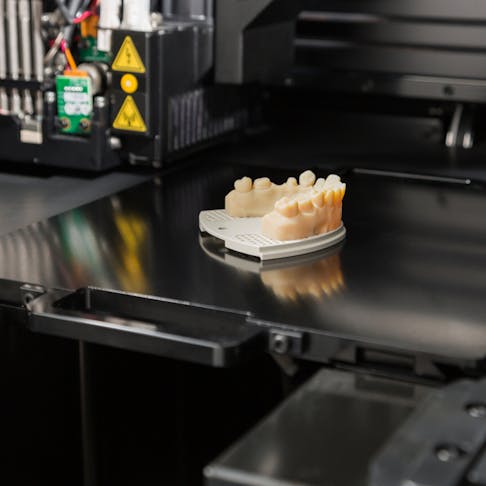
Implants
Like with prosthetics, 3D printing allows creators to better tailor implants to the patients. It improves patient outcomes when parts with complex shapes are printed quickly. Items like maxillofacial and tooth implants, knee replacements, and heart valves can all be 3D printed. Those in the medical industry are looking forward to the 3D printing of organs which could change many people’s lives, and reduce waiting times. Below is a picture of a 3D-printed dental implant.
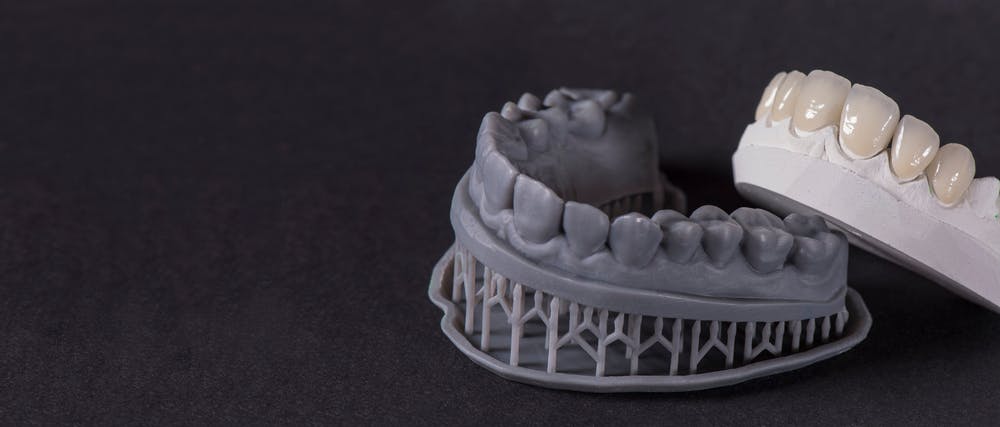
3D-printed dental implant.
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com/Eduard Tanga
Pharmaceuticals
Drugs of different shapes and sizes can distribute both active and inactive ingredients in the body, and 3D printing can create these drugs. The 3D-printed drugs can have special delivery profiles created to match a patient’s specific needs. So far, only one drug has been 3D printed: Spritam®, a levetiracetam produced by Aprecia Pharmaceuticals. But 3D printing can result in on-demand, locally made drugs in the future.
Emergency Structures
Natural disasters happen and can be very detrimental for the affected populations. 3D printing houses, hospitals and other structures can help the crisis situation and assist the victims and emergency responders. It also does this much faster than it would take to build these structures the traditional way.
Aeronautics and Space Travel
Humans are always working to expand our presence in space. 3D printing allows for the on-demand creation of tools, equipment, and entire structures in space and extraterrestrial environments. Back on Earth, 3D printing can make advanced aerospace components like airframes, avionics housings, and more. Overall, 3D printing can help make space travel more cost-effective and thus help create a more sustainable human presence.

Custom Clothing
The fashion industry generates all kinds of waste generated by the fashion industry, especially when people buy an outfit to wear once and throw them away. 3D printing helps reduce some of that waste by letting people create custom clothing. Letting customers print clothing that fits their measurements and style on demand gives them what they want while creating less waste.
Custom-Fitted Personal Products
Lots of everyday objects are designed for the average body type and size. Chairs, clothes, keyboards, and desks are all made for a person of average build. This makes things hard for anyone outside of that average size, leading to discomfort and even disability. 3D printing gives people the option of custom-fitted personal products for better ergonomics, comfort, and safety.
Educational Materials
3D printing gives students tactile objects that they can use to boost their learning process. Things like topographical maps help students better understand the topics they’re learning about. 3D printing can help boost creativity, improve learning habits, and foster collaboration.
Food
This one is quite hard to believe, but even food can be 3D printed. Labs are already growing meat and vegetables using stem cells. In the future, scientists can use 3D printing to create enough quantities of fruits, vegetables, and meat to feed the growing population and reduce the land used for livestock and agriculture.
3D Printing Technologies
There are a variety of 3D printing technologies, and you’ll have to choose which one will suit you best based on your needs and preferences. Here are some of the most commonly used technologies we offer here at Xometry, and how they work.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM technology uses a melted plastic filament expelled by a heated nozzle to 3D print parts.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): This type of 3D printing uses a strong laser to melt polymeric powders and fuse them together.
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): Similar to SLS, this method of 3D printing uses metal powders in place of polymeric powders.
- Stereolithography (SLA): This technology uses an ultraviolet (UV) lamp to build continuous layers of UV-curable photopolymers into parts and products.
PolyJet: This is similar to SLA and DLP, but instead it deposits and cures photopolymers simultaneously using a UV lamp. Check out a great PolyJet part below:

How Xometry Can Help
Xometry offers a variety of manufacturing capabilities, including injection molding, CNC machining services, and nine processes for custom 3D printing services for prototyping and production. Get your instant quote today.
Copyright and Trademark Notices
- Spritam® is a trademark of APRECIA PHARMACEUTICALS, LLC
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


