Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing—Which Is Best for You?
Learn more about the differences between these two 3D printing methods and when it’s best to use each one.
At Xometry, we offer a number of resin-based processes, such as SLA, PolyJet, and more. Likewise, we offer fused deposition modeling (FDM), which uses materials in the form of filaments. Although all these processes can be used to create custom 3D printed parts for our customers, there are some key differences between 3D printing with resin and filament-based processes and materials.
Both of these methods have their pros and cons, and the best one for you will depend on the type of project you’re doing. You’ll also have to factor in your budget and any tight deadlines. Let’s have a closer look at the differences between resin and filament 3D printing, their strengths and weaknesses, and how they can best be used.
What is Resin 3D Printing?
Resin 3D printing uses liquid photopolymer resin materials that are cured, layer by layer, using some type of UV source that’s inside the printer itself, like a laser or a projector. Some types of resin 3D printing are stereolithography (SLA) or digital light processing (DLP). Although they both use resin, these have their differences. SLA uses a UV laser to trace the shape of the item onto the resin’s surface, while DLP projects a UV light pattern onto the entire resin layer, curing it all simultaneously. As it prints, the build platform lowers to allow room for subsequent layers, and the process repeats until the print is complete. Once done, post-processing typically involves the print being washed and cured, with any extra resin being removed.

Resin 3D Printing—Advantages
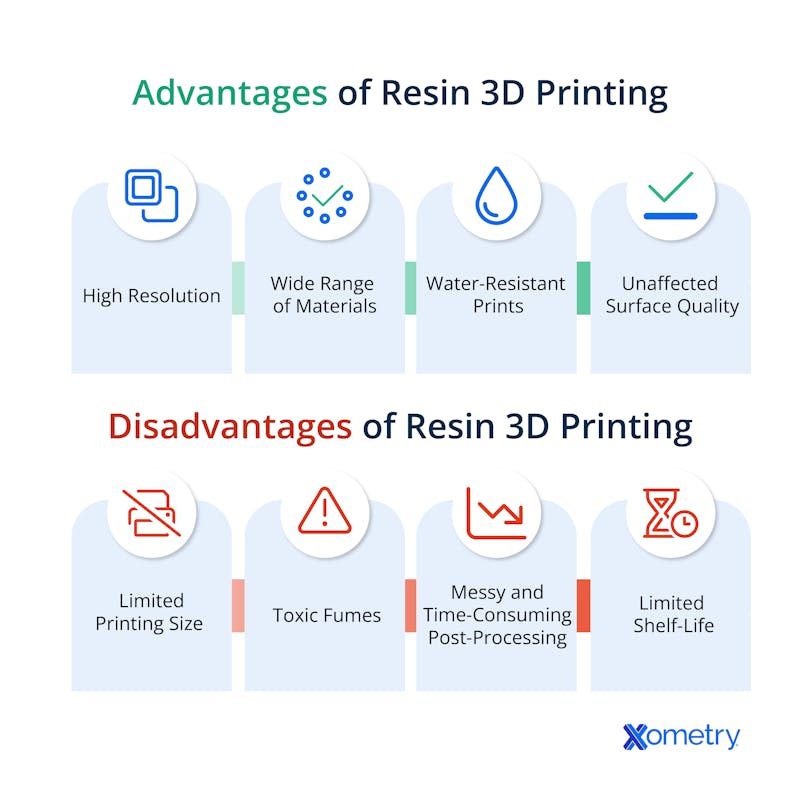
3D printing with resin is popular thanks to its many perks. It is considered the go-to 3D printing method for those who want their complex designs made into detailed and high-resolution prints with smooth surfaces. There is a wide range of resins, including flexible, engineering-grade, and even dental composite resins.
Unlike plastics or powdered materials, resin is water resistant, and continues to be after its hardened. It won’t absorb moisture, making it an excellent choice for creating watertight prints. Another benefit of resin 3D printing is that its surface finish is typically smoother out of the machine due to the high level of accuracy that can be achieved with the UV curing methods commonly used in resin printing. Our PolyJet and SLA processes can all easily achieve layer heights of 50 microns or below.
Resin 3D Printing—Disadvantages
There are a few disadvantages to resin 3D printing, including a limited printing size, which is typically smaller than that of filament printers, and its lengthy process. It takes a lot of time and effort to wash, cure, and sand support knubs from the print, and it can also get quite messy. When 3D printing with resin, it’s important to have good ventilation as this method produces toxic fumes that shouldn’t be breathed in. Resin has a limited shelf life with a best-before date. If you use an expired resin, the prints may be compromised. Finally, resin prints are easily prone to degradation from UV, environmental and other factors.
Software Used for Resin 3D Printing
Chitubox, Lychee Slicer, Formlabs PreForm, and Autodesk® Meshmixer are just some of the popular software options for resin 3D printing. These programs allow you to prepare, slice, and send 3D models to printers, as well as make any modifications and adjustments to the print-quality settings, such as the layer height, exposure time, and support structures. Not all software is compatible with all 3D printer models, so check the manufacturer’s recommendations to make sure you get the right one for your needs.
What is Filament 3D Printing?
Filament 3D printing, also known as fused deposition modeling (FDM), is another 3D printing method that allows users to create 3D objects by extruding a continuous flow of filament or thermoplastic material, one layer at a time, to build a part. This is a widely used type of 3D printing thanks to its adaptability and availability from the hobbyist market up to the industrial level.

How Filament 3D Printing Works
A filament 3D printer works by feeding a large piece of plastic filament from a spool into a nozzle. This is heated, melted, and liquefied before it passes through the extruder and nozzle, and released onto the build plate or subseqeuent layers. The nozzle extrudes the filament as it moves in a pre-set pattern one layer at a time until it’s finished printing the object. As the printed layers are deposited, the filament will start to cool and solidify. Since FDM is a relatively straightforward process it can easily be scaled up, allowing for very large pieces to be printed. For example, our machines at Xometry have a build volume of up to 36x”36”24”!
Filament 3D Printing—Advantages
Filament 3D printing has many advantages which make it an incredibly versatile and accessible 3D printing method. This type of printing is beginner-friendly—much easier than printing with resin—but is also suitable for professional services like Xometry, as it can make durable, strong, and wear-resistant pieces.
With this method, you can print with a wide variety of thermoplastic materials. Xometry, for example, can print in materials like PLA, ABS, nylon, polycarbonate, ULTEM, and more. These materials have a wide range of characteristics and properties that can be chosen to fit your project's specific needs. Industrial FDM printers like the ones we use at Xometry are very reliable and can print very large parts in a single build, making them advantageous for creating life-size prototypes like prosthetics.
Filament 3D Printing—Disadvantages
There are a few things to keep in mind when it comes to filament 3D printing. For starters, FDM prints often have prominent layer lines which can be unsightly. Although it does not require as many post-processing steps as resin-based processes like SLA, it can still be a slow building process, especially for large parts.
It’s also worth noting that support structures will need to be printed alongside the main model to keep it intact. You’ll have to then remove and throw away the supports, making the whole process longer, and also a bit wasteful. Perhaps the most frustrating thing, however, is its tendency for parts to warp while printing unless you have all the correct settings and conditions dialed in, which will likely take some trial and error to get just right. This is why Xometry uses industrial FDM platforms which are optimized for printing a wide range of materials with high reliability and quality.
How Xometry Can Help
At Xometry we offer nine different 3D printing processes, including FDM and resin-based processes like SLA! We have dozens of materials to choose from to fit your project's unique requirements. Best of all, we offer instant quoting on all of our 3D printing processes. You can start by uploading your 3D CAD files to the Xometry Instant Quoting Engine® and get instant pricing and lead times today!
Copyright and Trademark Notices
- Autodesk® is a registered trademark of Autodesk, Inc., and/or its subsidiaries and/or affiliates, in the United States.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.

