Jigs and fixtures may be small and inexpensive compared to other manufacturing aids, but without them, parts wouldn’t be as consistent, functional, accurate, or even as aesthetically pleasing. Often confused for one another, jigs and fixtures are manufacturing aids that most times work together, but are very different.
Let’s take a look at exactly what these manufacturing aids are, how they’re used, and how you can design your own for your manufacturing needs.
What Are Jigs?
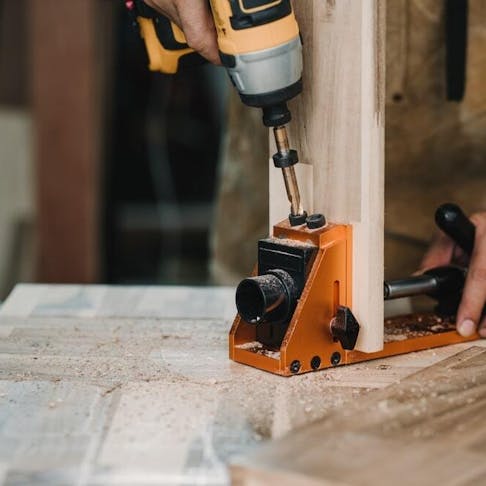
A jig is a typically lightweight aid designed to guide a tool so that it can repeat a specific task in the same manner every time. It’s used mainly in manual jobs like drilling and tapping. It provides a sort of template that makes sure the tool does always the same thing. For instance, if you want holes that are evenly spaced out on a part, a jig will show the tool where to drill and prevent it from drilling outside of the designated spot. Jigs can also save you some money. If you want to drill a hole at an angle (that isn’t just a simple up and down) without a jig, a 3-axis machine won’t be able to do it because it doesn’t have the ability to tilt either the tool or the part. The hole would simply just have to be drilled straight in. You could do this with a 5-axis machine since these can tilt and move as required, but these machines are notoriously expensive. The lowly jig is a very simple and cost-cutting solution to this problem. Take a look at the picture below to get an idea of what a jig could look like:

What Are Fixtures?
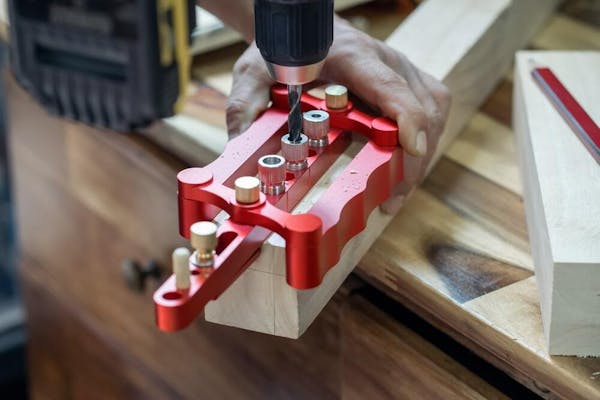
A fixture has one task, and that is to hold a material or workpiece in the right place to allow the tool to do its job. Without the fixture, there’s a good chance of the material moving and you could end up drilling or cutting in the wrong place. They’re fixed in place and more about supporting and positioning each workpiece in the exact same way so that the tool will drill or cut it (and all following pieces) consistently. Although they’re not exactly clamps, they can be actuated so that they do clamp onto a material when it’s in the correct position. A good example is a robotic arm. Fixtures are used in processes like milling, turning, broaching, grinding, and fabrication, and can look something like this:
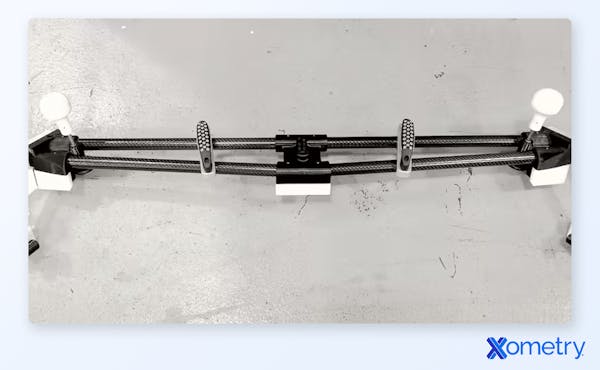
Jigs vs. Fixtures
Jigs are the Bonnie to fixtures’ Clyde, and vice versa. As mentioned, jigs guide the tools, and fixtures align and hold the parts or materials that will be worked on securely in place. Together, they offer just about the most precision you can get in manufacturing — especially when it comes to mass production of an item — without having to resort to using (or investing in) a CNC machine. Here’s a visual representation of their differences:
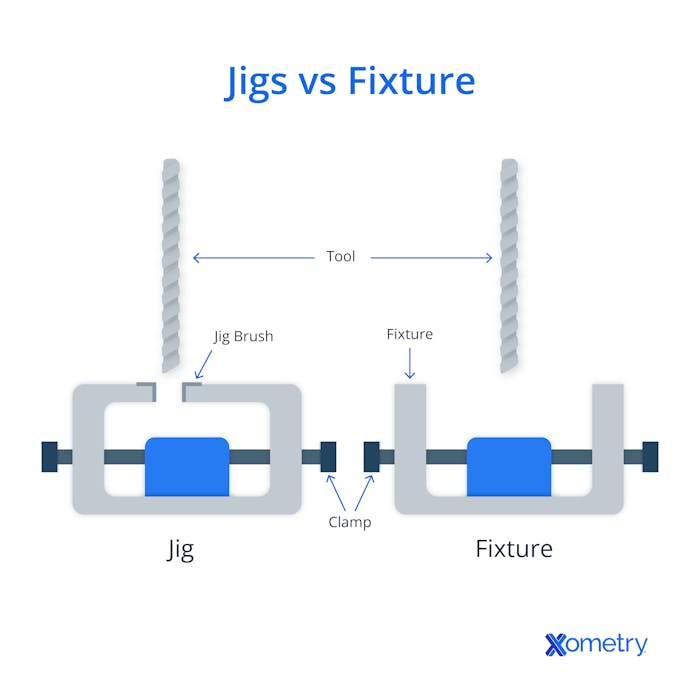
There are many reasons why jigs and fixtures belong together. They allow for much better precision by eliminating the chance of human error, by keeping both the tool and the workpiece steady. When properly aligned, the process is quick and easy for the worker who will know exactly where to drill or cut thanks to the provided “template.” Without these, only someone incredibly skilled would be able to pull off acceptable results. They also help to keep costs down by speeding things up so that one person is able to do the job of many and by reducing the chance of wasted parts caused by silly mistakes.
Both jigs and fixtures can come in all shapes and sizes and can be custom-made according to your exact manufacturing needs.
Designing Jigs and Fixtures
Jigs and fixtures are available to buy as ready-made products, but if you have specific manufacturing needs, it’s best to get your own designed and made. When it comes to designing them, there are a few important things to think about:
- Orientation: To reduce the likelihood of making a mistake, there should be no wrong way to use a jig or fixture — just one way, the correct one.
- Multi-uses: If you can, making a jig or fixture that can do more than one job, i.e., holding a part in place for both drilling and milling, could save you costs, but we understand that this might not always be possible.
- Material: To get plenty of use out of it, your jig or fixture should be made from a hardy and durable material.
- Handling: The parts should be designed in such a way that they’re easy to hold and manage with just one hand.
- Constraining: While it’s important for the fixture to hold the part in place, “over-constraining” could make it distort, bend, or misalign. You’ll have to find just the right balance.
- Force analysis: You’ll also have to work out the amount of force the aids are expected to receive to ensure they have the ability to withstand such forces.
- Tolerances: The jig or fixture should be a little flexible in that it can tolerate a slight variation of the piece it’s holding, i.e., if the part that needs to be worked on hasn’t yet been squared off properly, the fixture should still be able to hold it securely and accurately.
How Xometry Can Help
A quick and easy way to make your jigs and fixtures is by having them 3D printed — and we can help you out with this because it’s one of the services we offer. The process could save you a lot of money (especially if you have more complex designs), because it uses less material (it builds instead of subtracts), and is generally a more affordable manufacturing method. For high-precision parts to make, it’s better to go for CNC machining instead. You can also get your free, no-obligation quote for 3D printed jigs and fixtures, or any other manufacturing need you have, including CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, and metal stamping.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


