A CO2 laser cutter is a cutting tool that makes use of a focused beam of coherent light to precisely cut a wide range of flat materials into intricate designs. These materials can be anything from paper to steel plates. CO2 lasers are one of the most popular laser technologies, with many entry-level and industrial machines making use of the technology.
A CO2 laser can cut most metals, plastics, wood, and paper, but does struggle with highly reflective materials. CO2 lasers require regular maintenance and the laser tube needs to be replaced every so often. This article will describe what a CO2 laser is, what it is made from, and how to use it.
What is Inside a CO2 Laser?
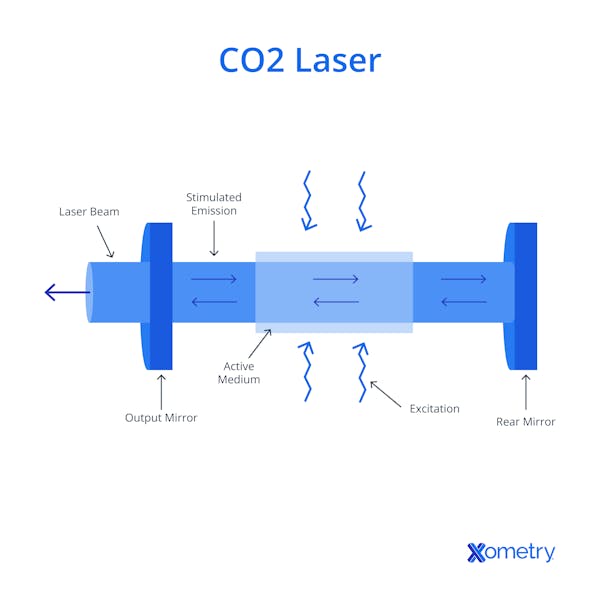
There are several important components inside a CO2 laser. The most important part is its laser tube, which is typically fixed to the frame of the laser cutter. A power supply is needed to ionize the CO2 gas molecules while also supplying power to the drive motors. Mirrors are used to direct the beam to the moving cutting head and ultimately into the focusing lens. The tube is kept at an optimal temperature using a cooling system. The cutting head is mounted on a gantry and is moved horizontally across the cutting base using stepper or servo motors. Some laser cutters have a pressurized air or gas supply piped into the cutting head to assist with the cutting process. Some smaller laser cutters have a ventilated enclosure with a door that helps keep fumes inside the machine.
What is the Difference Between a CO2 and a Fiber Laser?
Fiber lasers can cut many of the same materials as CO2 lasers, but unlike CO2 lasers, they can cut highly reflective materials like stainless steel and aluminum.
A CO2 laser makes use of a tube filled primarily with CO2 gas molecules. A strong electric field is used to ionize the CO2 molecules which cause the electrons to move up to a higher energy level. This ionization causes the CO2 molecules to emit photons when their electrons fall back into a stable state. When these photons pass near another excited molecule, it causes another photon to be released. This process creates a cascading effect. These photons then bounce back and forth between two mirrors in the tube, one reflective and the other semi-reflective. Once the light in the tube reaches a certain threshold, it passes through the semi-transparent mirror and is directed to the focusing lens via a series of precisely placed mirrors.
A fiber laser, on the other hand, is a solid-state laser. Instead of a gas-filled tube, it has a fiber optic filament dosed with neodymium. Light is directed into this filament, and once it reaches the dosed section it excites the neodymium electrons, which release photons of a specific wavelength. When these photons pass near other excited neodymium atoms, they cause the excited electrons to drop down into a stable state and new photons are emitted. A fiber laser makes use of Bragg gratings, which have the same function as the mirrors in a CO2 laser. The Bragg gratings cause photons to bounce back and forth to ultimately increase their total energy. The light then travels back and forth in the filament until it reaches a high enough energy level to pass through the grating and down the length of the filament until it reaches the focusing mirror.
CO2 lasers require regular maintenance whereas fiber lasers do not. Fiber lasers are also cheaper to purchase and operate when compared to CO2 lasers.
What Can a CO2 Laser Cut?
A CO2 laser can cut a wide range of different materials, which makes it an excellent general-purpose cutting tool. Some typical materials that are suitable for cutting with a CO2 laser are listed below:
- Wood
- Foam
- Rubber
- Paper
- Plastic
- Cork
- Carbon fiber
- Fabric
- Cardboard
- Steel
It must be noted that CO2 lasers are not generally suitable for highly reflective materials like aluminum or stainless steel.
How Much Do CO2 Lasers Cost?
A CO2 laser can cost anywhere from $5,000 to $1,000,000. The main determining factor in this cost is the machine's bed size and its laser power, which can vary from several hundred watts to several thousand watts. Higher-cost lasers are typically used for industrial applications like cutting metal, whereas cheaper CO2 lasers are better suited to materials like wood, paper, and plastic.
How Long Do CO2 Lasers Last?
The weak point of a CO2 laser is the laser tube which is typically the first component to fail and is quite expensive to replace. A laser tube can last anywhere from a few months to many years. However, the exact duration depends on numerous factors including (but not limited to): tube quality, tube cooling effectiveness, operating power, cleanliness of the optical path, and the usage rate of the laser cutter.
Where Are CO2 Lasers Typically Used?
CO2 lasers are used in a wide range of applications. They are one of the most popular technologies for cutting steel sheets and plates. Most entry-level laser cutting machines also make use of CO2 lasers and are used to cut wood, plastic, and paper for artistic applications.
What is the Pulsed Power That a CO2 Laser Produces?
An entry-level CO2 laser typically has a power rating of 150 W, whereas an industrial CO2 laser typically operates in the 4 to 6 kW range.
What is the Wavelength That a CO2Laser Produces?
A CO2 laser produces a wavelength of 10,600 nm. This wavelength is very specific to the CO2 gas molecule that is used to generate the laser energy.
How to Use a CO2 Laser
To use a CO2 laser, the desired design file, such as a raster or vector image, must be loaded into a suitable laser-cutting software package. Most hobbyist laser cutters will have a proprietary software package specifically tuned to the laser cutter to help users get optimal results. Once the file is ready, it can be loaded onto the laser cutter via wifi, ethernet, or a flash drive. Next, the material to be cut must be loaded into the laser cutter. Then, the cutting can commence. Once the parts are ready they can be removed and post-processed if required.
Is It Safe to Use CO2 Lasers for Wood Cutting?
Yes, it is safe to use CO2 lasers for cutting wood. CO2 lasers are often used to cut and engrave wood. However, lower-powered CO2 lasers (up to 150 W) are preferred for cutting wood, to eliminate the risk of fire.
Is it Safe to Use CO2 Lasers for Paper Cutting?
Yes, it is safe to use CO2 lasers for cutting paper. CO2 lasers are often used to cut paper into intricate designs. However, lower-powered CO2 lasers (up to 150 W) are preferred for this. Paper can burn easily and, as such, optimal settings such as short focal lengths must be followed and paper must be perfectly flat during cutting.
Can CO2 Lasers Cause a Fire?
Yes, CO2 lasers can cause fires. CO2 lasers are cutting tools that use extremely high temperatures to melt and burn materials. Some materials, especially wood and paper can easily catch fire. However, this risk can be mitigated by using the correct power, speed, and beam focus settings for the material. Transfer masks that stick onto the sheet can also be used to avoid the potential for fire as they prevent burning on the cut edges.
Summary
This article presented the CO2 laser cutter, explained what it is, and discussed what it's used for. To learn more about CO2 laser cutters, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including sheet cutting and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Copyright and Trademark Notices
- Glowforge is a trademark of Glowforge Inc. CORPORATION DELAWARE.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.

