Laser cutting has become an increasingly popular method for cutting materials such as metal, plastic, wood, and glass. A wide variety of industries, including the automotive and medical device sectors, use laser cutting because it offers a high degree of accuracy and precision. Each of these industries has different requirements and uses laser cutting in different ways. The automotive industry, for example, uses laser cutting to manufacture car parts and precision components. The medical device industry creates medical devices and implants with laser cutting.
The following article will discuss the eight laser-cutting uses and their importance:
1. Automotive Industry and Laser Cutting
The automotive industry has embraced the advantages offered by laser cutting to produce a range of components. Tolerances in the automotive industry are extremely tight, and laser cutting is well-suited to meet them. Laser cutting’s flexibility and capability to create complex shapes and designs make it a popular technology for producing car parts. In the past, car parts were created with stamping and die-cutting methods. However, these methods are not as accurate, nor can they create complex shapes and designs like laser cutting. The automotive industry primarily uses fiber lasers for cutting sheet metal due to their speed, precision, and ability to handle reflective materials like aluminum and stainless steel. Materials that are laser cut in the automotive industry include, but are not limited to, car parts, components, die-castings, forgings, and stampings.
2. Medical Device Industry and Laser Cutting
The medical device industry utilizes laser cutting to produce a variety of products, including pacemakers, stents, and catheters. The laser beam melts, vaporizes, or burns away the material, leaving a clean, precise cut. Laser cutting is often used to create products with intricate designs, such as those intended for use within the human body. The type of laser cutting used will depend on the material being cut and the desired final product. For example, some medical devices are made from stainless steel, which is typically cut using fiber or ultrafast lasers for improved precision and reduced heat-affected zones. Other materials, such as plastics, can be cut with a fiber laser.
3. Jewelry Industry and Laser Cutting
The jewelry industry is one of the most ancient industries in the world, with a long and rich history. In recent years, however, it has undergone a major transformation, thanks to the advent of laser-cutting technology. While traditional methods of jewelry making relied on manual labor and simple tools, laser cutting has allowed for a much more precise and intricate level of design. As a result, jewelry made with laser cutting is often more intricate than its traditional counterpart. Laser cutting in the jewelry industry is typically used to create detailed patterns and designs in metal, as well as to cut gemstones. It can also be used to engrave text or images onto jewelry pieces. Jewelry products that are commonly made with laser cutting include rings, pendants, earrings, and bracelets. The use of laser cutting in the jewelry industry has revolutionized the way that jewelry is made and has allowed for a whole new level of creativity and design.
4. Ceramic Manufacturing and Laser Cutting
Ceramic manufacturing is the process of shaping and firing ceramic materials to create products. Ceramics can be made from clay, glass, metal, or synthetic materials. Laser cutting can be used in the ceramic manufacturing process to create precise shapes and designs in the material. This type of cutting is often used to create intricate patterns and decorative elements in products. Common examples of products made with laser cutting include tiles, pottery, and sculptures. In ceramic manufacturing, ultrafast lasers such as femtosecond lasers are often preferred for technical ceramics due to their precision and minimal thermal damage, though CO₂ lasers can be used for softer ceramics or decorative applications. This method offers high precision and supports the creation of complex designs. CO₂ laser cutting is also relatively fast, making it ideal for use in the ceramic manufacturing process.
5. Silicon Industry and Laser Cutting
When it comes to the silicon industry, laser cutting is a vital process. Silicon manufacturing refers to the production of silicon wafers—thin discs of semiconductor material that are used in the fabrication of various electronic devices. The silicon industry typically uses ultrafast or solid-state lasers (e.g., femtosecond or Nd:YAG lasers) for precision dicing and patterning of silicon wafers. It is used to create the small-scale features found on silicon wafers. There are a variety of different products that are produced in the silicon industry, including integrated circuits, solar cells, and semiconductor chips. CO₂ laser cutting is used to create intricate patterns on these products, which are then used in a variety of electronic devices.
6. Packaging Industry and Laser Cutting
Packaging refers to the process of enclosing products or items for protection and handling. Laser cutting is utilized in the packaging industry to create various packaging products, such as boxes, containers, and lids. Two main types of laser-cutting technology are used in this industry: fiber lasers and CO₂ lasers. CO₂ lasers are typically utilized to cut cardboard, paper, and thin plastics. Fiber lasers are more commonly used for cutting metals and are less typical in packaging; CO₂ lasers remain the standard for cutting paper, cardboard, and thin plastics.
7. Metalworking Industry and Laser Cutting
Metalworking is the process of shaping and forming metal into desired shapes using various tools. Laser cutting is often employed in the metalworking industry to cut metal into desired shapes. Some common products that are produced are: beams, columns, pipes, tubing, and sheet metal. These products can be used in a variety of industries, such as construction, automotive, and aerospace.
8. Woodworking Industry and Laser Cutting
The woodworking industry is a sector of the manufacturing industry that produces wood products. These products can be used for construction, furniture making, or other purposes. Laser-cutting technology is often utilized in this industry to create precise and intricate designs in wood. Some commonly produced items are: furniture, cabinets, and decorative items. The type of laser cutting used in the woodworking industry is typically a CO₂ laser. This type of laser uses a beam of infrared light to cut through wood. The CO₂ laser can create very complicated designs due to the high level of precision that it offers.
What Is the Importance of Using Laser Cutting?
The importance of laser cutting lies in its highly accurate and consistent method of cutting a wide variety of materials, including but not limited to sheet metal. It is also an effective alternative to traditional etching for certain applications, particularly where precision and repeatability are required. Laser cutting has several advantages over other methods of sheet metal cutting, including:
- Higher level of precision
- Ability to cut complex designs
- Cost-effectiveness
- Less workpiece contamination
- Less human error
- Uses less energy
For these reasons, laser cutting is now the preferred method of sheet metal cutting for many applications.
How Does Laser Cutting Work?
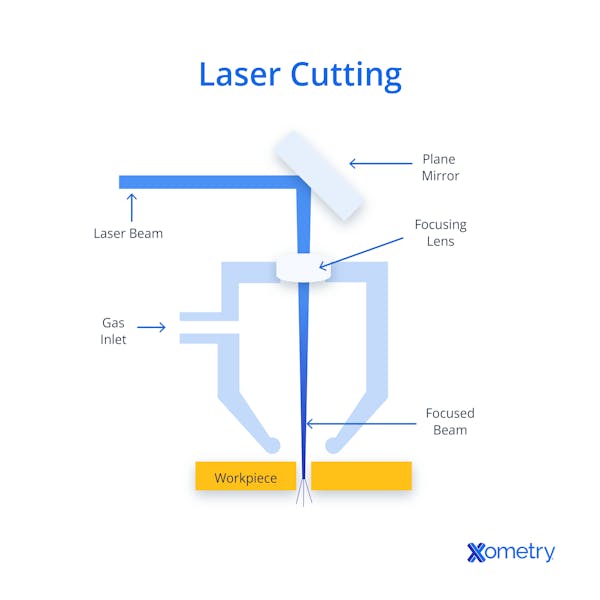
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to cut materials. The laser beam is focused on the material, and depending on the type of material and laser, it may be vaporized, melted, or burned away. As the laser beam moves across the material, it can cut through it. Laser cutting is a very precise process and can be used to cut through a variety of materials, including sheet metal, steel, and other metals.
What Are the Best Laser Cutting Machines?
Below are the best laser-cutting machines available on the market today:
- Epilog Zing 16 30-Watt CO₂ Laser: The Epilog Zing 16 is a compact CO₂ laser cutting machine with a maximum material height capacity of 4.5 inches, but it can typically cut through materials up to about 0.25 inches thick in a single pass, depending on the material.
- Trotec Speedy 300 30-Watt CO₂ Laser: The Trotec Speedy 300 is another powerful laser cutter that can handle materials up to 0.5 inches thick.
- Full Spectrum Hobby Series 20-Watt CO₂ Laser: The Full Spectrum Hobby Series is a great option for those who need a powerful laser cutter but don’t need a large cutting area. It can cut through materials up to 0.25 inches thick.
How Does Laser Cutting Differ for Different Materials?
Laser cutting differs for different materials in that each material has different physical and chemical properties that require different laser settings and processes. For example, metals are generally good reflectors of light, so they require higher-power lasers and special cutting techniques. Plastics, on the other hand, can be cut with lower-power lasers, but the edges of the cut can be very jagged and require post-processing. Glass is a transparent material, so it can be more difficult to cut with a laser. Special techniques, such as using a lens to focus the laser beam, are required to cut glass cleanly.
What Materials Can Be Laser Cut?
There are several materials that can be laser cut, including metal, plastic, and glass. However, the materials that can be laser cut depend on the type of laser used. For example, some laser cutters can only cut certain materials, while others can cut a wide variety of materials. If a CO₂ laser cutter is used, a variety of materials can be cut, including wood, plastic, glass, and metal. A fiber laser cutter, on the other hand, can cut stainless steel, aluminum, and brass. If you are unsure about what type of laser cutter you have or what materials it can cut, consult the user manual or contact the manufacturer.
What Materials Cannot Be Laser Cut?
The materials that cannot be laser cut are: highly reflective materials, such as mirrors, thin materials that can easily warp or melt, and materials that are dangerous to cut, such as asbestos or explosives.
Is It Easier To Laser Cut Metal Than Plastic?
No, in general, it is easier to laser-cut plastic than metal. Plastics absorb CO₂ laser energy more efficiently and melt or vaporize at lower temperatures. Metals, especially reflective ones like aluminum or copper, require higher laser power and often specialized equipment, such as fiber lasers, to cut effectively.
Summary
This article presented the eight different laser cutting uses, explained what they are, and discussed the importance of each. To learn more about the uses of laser cutting, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including sheet cutting and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


