We are quite familiar with zinc here at Xometry. We primarily offer it as a metal plating option for other metals to give parts a corrosion-resistant layer, but we also make parts directly from zinc alloys through the die casting process. Our customers in the automotive and construction industries often use zinc in their projects. If you’re interested in custom die-cast parts, you can review our die casting service page.
In this article, we’ll look at the makeup, types, qualities, and other aspects of zinc.
What is Zinc Metal?
Zinc is a chemical element. You can find it on the period table by its symbol “Zn” and its atomic number of 30. Zinc is an element unto itself, so the material is made of zinc atoms. These atoms exhibit metallic properties, like electrical conductivity and malleability. It’s bluish-white in color and has a low melting point of 420℃. Zinc is naturally resistant to corrosion, making it popular in applications where that is a concern. You may also be surprised to find out its also a necessary trace element for the human body and other biological processes.
A Brief History of Zinc Metal
Humans have worked with zinc for at least 2,500 years because it’s a critical alloying element in brass. Zinc itself, however, wasn’t recognized as a distinct element until much later. In India in the 1400s, calamine (ZnCO3) and wool were heated to generate metallic zinc. Andreas Sigismund Marggraf discovered zinc again in 1746 when he heated calamine with charcoal. This traditional method is different from the electrolysis of aqueous zinc sulfate (ZnS04) used in modern zinc production.
Historically, the word “spelter” was used interchangeably with “zinc,” though technically spelter is a zinc-lead alloy. It’s also known by other terms like “galvanizing metal,” “blende,” and “calamine.”
Processing Zinc Metals
There are two common extraction processes used for zinc; smelting and electrolysis. In both cases, sulfur must be removed through exothermic oxidation before extraction.
In the case of electrolysis, concentrates are heated in fluidized-bed roasters to lower the sulfur concentration in preparation for electrolytic production. Then you create a zinc sulfate solution, purify it, and apply a regulated overvoltage so the zinc gathers on the cathode.
Smelting uses a blast furnace to extract zinc-bearing gas and liquid from sintered concentrates and coke. After that, the impurities are extracted through distillation fractionating operations.
Need Zinc Metal Plating On Custom Parts?
Zinc Metal Advantages
There are a number of benefits to using zinc. They include:
- It’s resistant to oxidation and corrosion.
- Its useful for environments involving moisture or corrosive elements.
- It is nontoxic so it’s safe for human contact.
- It can be applied as a plating to other metals to improve their properties.
- Zinc is recyclable, which contributes to sustainability.
Zinc Metal Disadvantages
Limitations of zinc include:
- Zinc is quite brittle, which can limit its usefulness in some situations.
- The relatively low melting point restricts use in high-temperature environments.
- While corrosion-resistant in most situations, zinc can corrode in heavily acidic or alkaline conditions.
- Zinc’s properties can change when mixed with other metals, also changing its behavior.
Physical Properties of Zinc Metal
The table below highlights the physical properties of zinc metal.
| Property | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
Property Melting Point | Description The temperature at which zinc changes from solid to liquid | Value 420 °C |
Property Boiling Point | Description The temperature at which zinc changes from liquid to gas | Value 907 °C |
Property Density | Description Mass per unit volume | Value 7.14 g/cm³ |
Property Atomic Number | Description Number of protons in a zinc atom | Value 30 |
Property Atomic Mass | Description The mass of a single zinc atom | Value 65.38 u |
Property Crystal Structure | Description Arrangement of atoms in a solid lattice | Value Hexagonal Close-Packed |
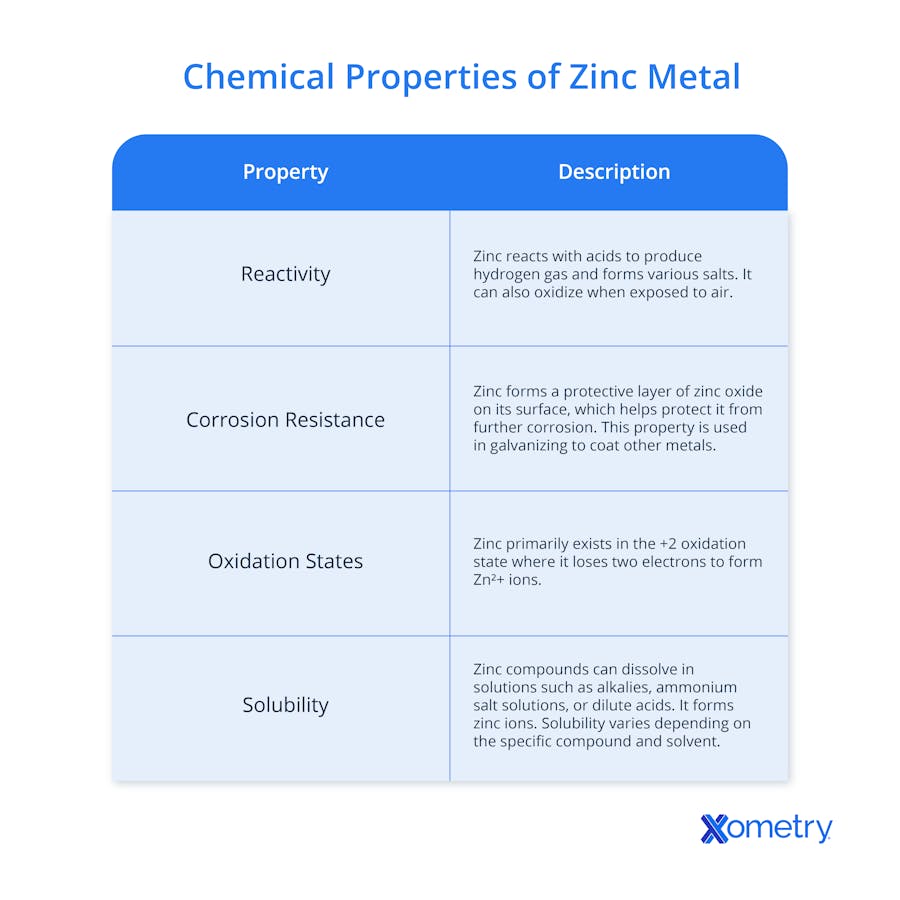
Different Types of Zinc Metal
Zinc comes in several varieties, and we list the main ones below.
Pure Zinc Metal
Pure zinc is made entirely of zinc atoms. It has exceptional corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity. Since it’s non-reactive, zinc is perfect for electrical parts, circuits, and medical equipment.
Zinc Metal Alloy
Zinc alloys are more common and the type of zinc that Xometry most often uses for die-cast components. Specifically, we offer Zamak alloys such as Zamak 2 and Zamak 3. Zinc alloys are often made by combining pure zinc with metals like aluminum or copper. Since they’re strong and corrosion-resistant, they’re commonly used for automotive parts and in marine environments.
Galvanized Zinc Metal
Galvanized zinc uses chromium or nickel to create a protective layer. This layer helps stop corrosion and rust, protecting against moisture and other issues. Because it’s resilient against harsh weather, it’s a top choice for important structures like bridges and roofs.
Zinc Metal Applications
Xometry serves a wide variety of customers and industries. As a result, we’ve seen zinc used for lots of different applications. Here are the ones where we’ve seen it used the most:
Galvanization
Iron and steel are both notorious for being susceptible to corrosion. Galvanization adds a layer of zinc to these types of materials, which protects them from corrosion. Zinc’s natural reactivity helps preserve structures in most environments. The galvanization process is common in construction and transportation.
Marine Industry
Marine vessels use sacrificial zinc anodes to stop corrosion. The anodes take on the rust instead of the structure itself. This prolongs the lifespan of ships, oil rigs, and underwater pipelines.
Automotive
As mentioned previosuly in this article, zinc alloys are very common in the auto industry. It makes car parts lightweight and corrosion-resistant. This creates more durable and fuel-efficient vehicles.
Energy Storage
Zinc can be used in energy storage solutions. The two types of zinc energy storage are zinc-carbon batteries and zinc-air batteries. Through these type of solutions zinc helps provide an affordable and eco-friendly source of portable power, and is used in items from remote devices to emergency backup systems.
Medical Devices
Zinc has antimicrobial properties and is biologically compatible with the human body. That makes it a vital part of the medical industry. Zinc improves safety and minimizes risk of infection in these type of devices.
Zinc Metal Compounds
Zinc compounds are in a wide variety of products. Zinc gluconate is a dietary supplement for immune-system health. Meanwhile, zinc oxide is used in rubber production, due to its heat resistance and UV protection properties. These compounds show zinc’s versatility.
Zinc Plated vs. Stainless Steel
Zinc plating is a thin coating that doesn’t provide much corrosion protection. Stainless steel inherently resists corrosion in the material itself because of chromium in its molecular structure. Ultimately, it’s more durable than zinc plating. To learn more, see our guide on Stainless Steel Material Properties.
How Xometry Can Help
We hope you’ve learned something new about zinc by reading this article! Xometry offers zinc metal plating as a standard finish option for machined metal components, bent sheet metal parts, and more. Just select it from our finishing drop down and you’re pricing will update instantly!
For those looking for high-volume zinc part production, our die casting service has multiple materials to choose from, including zinc alloys like ZA-2 and ZA-3. You can find these services by visiting the Xometry Instant Quoting Engine® today!
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


