Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) and selective laser melting (SLM) 3D printing methods both fall under the category of powder bed fusion (PBF). They also both use laser beams—sometimes more than one at a time, and are compatible with different metal powders. Given these similarities, it’s easy to confuse the two… but considering one of the printers can cost a million bucks—double the price of the other—it’s safe to say that they are different in many ways. Read on to find out how.
What is DMLS?
DMLS, a trademark owned by additive manufacturing company EOS GmbH, is used to make metal parts. It’s still often referred to as a sintering method, simply because when it was first invented in the mid-90s, it only sintered metal. EOS says that “DMLS” is actually a German acronym for Direkt Metall Laser Schmelzen, which more accurately translates to the melting of metal, instead of sintering. The company made the technology commercially available in 1995, and modern machines fully melt the metal powder in the printing process, something that creates much stronger parts.
It usually uses a high-powered fiber laser beam that traces each layer’s cross-section and melts the particles of metal together. When each layer is printed, the bed moves down so power can be applied to a new layer on top, and then it starts again. During the process, the build chamber is filled with inert gas to stop any oxidation. The following image breaks down what a DMLS printer typically looks like:
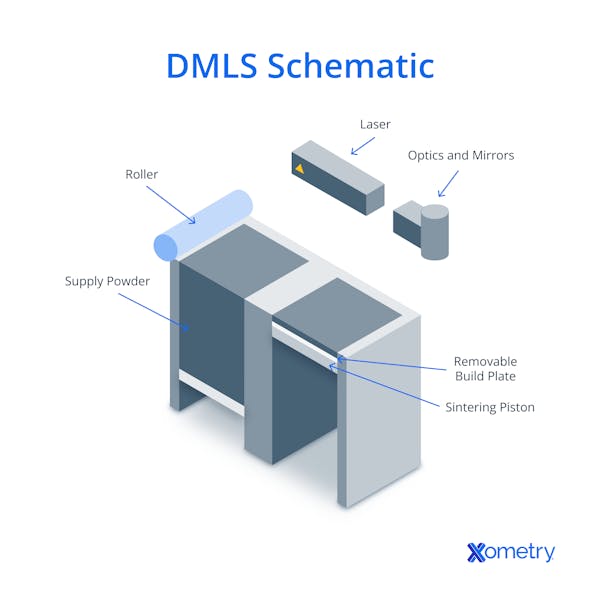
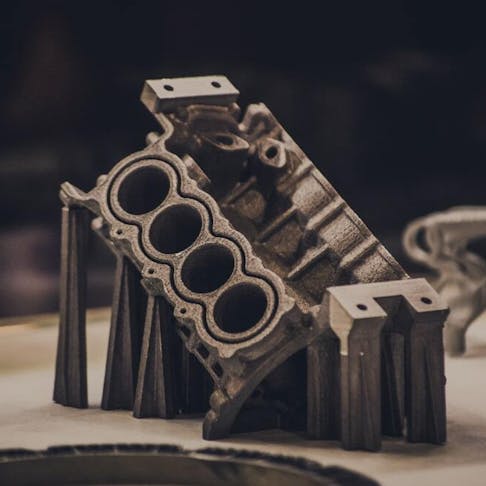
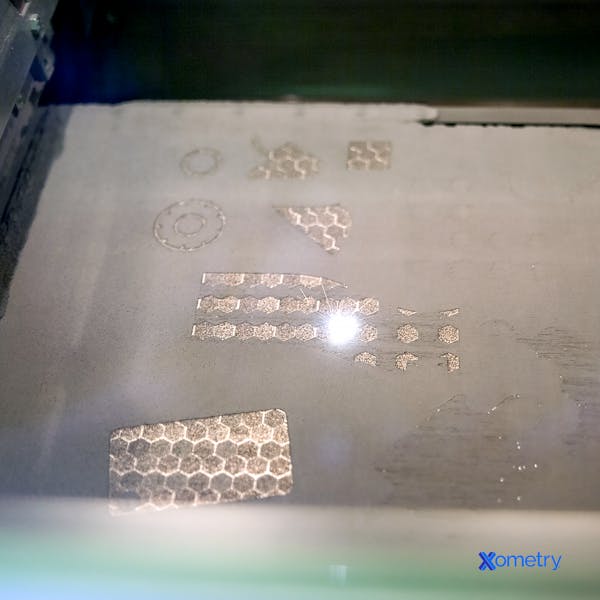
This 3D printing method has some awesome benefits, including the fact it makes very accurate and detailed parts and is compatible with a huge range of materials, even more than SLM, the method we’ll consider later on. The downsides to using DMLS, though, are that it can be rather slow because it uses less power and fewer lasers than SLM, and it can only create small melt pools, so it can’t print very thick layers. The following image shows you what parts being made in a DMLS machine look like:

What is SLM?
Quite similar to DMLS, SLM is yet another PBF 3D printing method that also made its debut in 1995 and was commercialized by the company SLM Solutions. It works very similarly to DMLS machines, using a laser to very quickly melt metal powder layer by layer. It also has to be filled with inert gas while it’s in operation. One of the main differences is that SLM machines usually use a laser with much more power. This is what a typical SLM machine looks like:
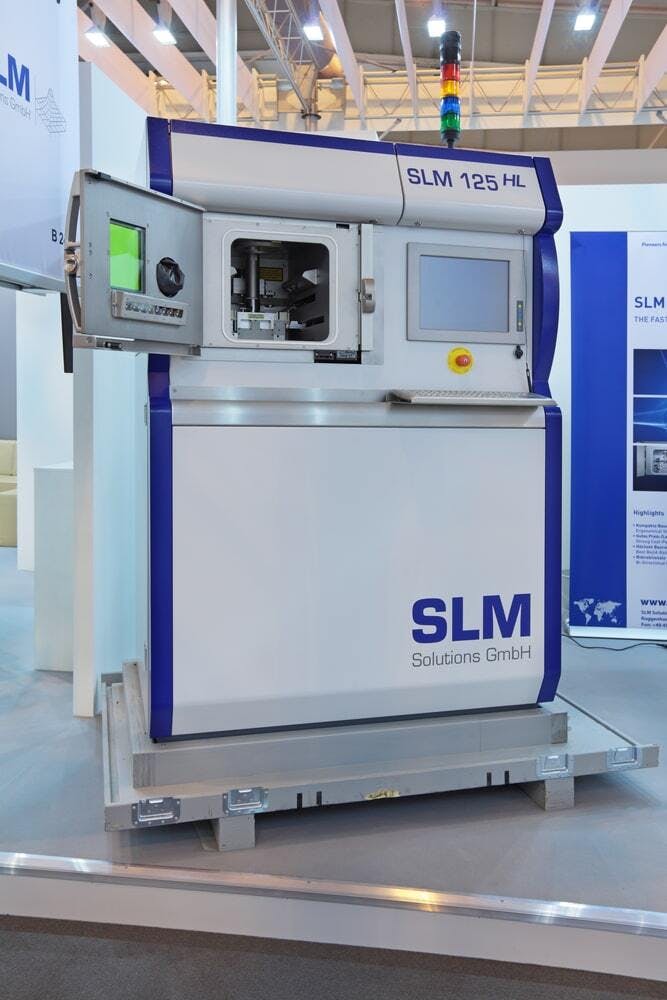

A typical SLM machine.
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com/ID1974
Another difference is the cost; SLMs are often double the price of DMLSs. Even still, there are many reasons you might want to invest in an SLM machine. The size of the laser can be adjusted depending on whether resolution or print speed is more important—if it’s speed, the printer’s 12 lasers will help get them made in no time. The high number of lasers does mean that the chamber can get extremely hot inside, which could potentially cause some part damage.
| Attribute | DMLS | SLM |
|---|---|---|
Attribute Laser point diameter | DMLS 40 microns (for smaller machines) | SLM 80 to 160 microns |
Attribute Laser quantity | DMLS 4 | SLM 12 |
Attribute Variable layer thickness and laser point diameter | DMLS No | SLM Yes |
Attribute Minimum feature size | DMLS 100 microns | SLM 140 microns |
Attribute Has isotropic material properties | DMLS Yes | SLM Yes |
Attribute Parts need to be cooled down after printing | DMLS Yes | SLM Yes |
Attribute Parts require support structures | DMLS Yes | SLM Yes |
Attribute Largest print volume | DMLS 400 x 400 x 400 mm | SLM 600 x 600 x 600 mm |
Attribute Typical power output | DMLS 400 watts | SLM 1000 watts |
Attribute Main applications | DMLS Famous for being used in the medical industry for things like implants and dental bridges | SLM Well-used in the automotive and aerospace sectors |
Attribute Surface roughness (average roughness) | DMLS Around 8 to 20 microns Ra | SLM Typically between 5 and 15 microns Ra |
Attribute Cost | DMLS Between $250,000 and $800,000 | SLM From $400,000 to over $1 million |
DMLS vs. SLS attributes
Frequently Asked Questions on DMLS vs. SLM
What examples of materials can I use with these 3D printers?
Both of them work with metal powders, but they have slightly different preferences of what they like to work with. SLM printers are better for pure, high-strength metals (titanium, aluminum, stainless steel, cobalt-chromium), while DMLS printers are designed more for metal alloys (nickel-based superalloys, tool steels, and aluminum alloys).
What’s the difference between DMLS and binder metal jetting?
Binder metal jetting bonds metal together with a polymer binder instead of a laser-like DMLS does. This binder is applied in the shape of the part’s cross-section. When each layer is finished, another layer of powder is added and the process repeats. The finished part will need to be post-processed to fuse the metal powder together, and burn the binder off.
What’s the difference between SLM and DED?
Instead of metal powder, DED (directed-energy deposition) feeds a metal wire through the printer’s nozzle to make parts. The wire is melted at the nozzle and dropped into the build plate, similar to how fused-deposition modeling printers do but with filament. DED can make parts that are consistent and uniform throughout their entire construction, while SLMs are better at complex and precise parts.
Are there any alternatives to these methods?
The main alternative is probably EBM (electron beam melting). It’s similar to both DMLS and SLM in that it uses an energy beam to melt powder, but instead of a laser, it uses an electron particle beam.
How Xometry Can Help
For help with anything additive manufacturing-related, get in touch! 3D printing is, after all, our forte. We also offer a wide range of manufacturing services, including CNC machining, laser cutting, and powder coating. You can get your project started as soon as today by requesting a free, no-obligation quote on our website.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


