Injection Molding vs. Extrusion - Applications and Cost Comparison
This article will explore the similarities and differences between injection molding and extrusion, as well as the relative advantages, disadvantages, costs, and end-use applications for each manufacturing process.

Introduction: Similar at a glance, different in application
At an initial glance, extrusion and injection molding may appear to be very similar manufacturing processes. Both processes send molten material through machines to mass-produce low-cost parts of the desired shape. Both are a continuous production processes that amortizes costs as one orders higher quantities of parts. But, as we will see, these similarities quickly disappear when examining the differences between extrusion and injection molding.
The Injection Molding Process
Injection Molding is the most cost-effective way to make plastic products at scale. This plastic manufacturing process takes plastic resin, melts it into molten material, and injects it into a “mold tool.” After cooling, plastic manufacturers eject the formerly molten plastic material from the injection unit, creating complex three-dimensional shapes with a smooth surface finish. This process can rapidly repeat hundreds or thousands of times, amortizing the cost of the mold tool and driving down costs as one orders more plastic products. Since the same mold tool is used for each part, and the plastic pellets used for plastic molding are so cheap, this plastic manufacturing is well suited to produce affordable parts of consistent quality.
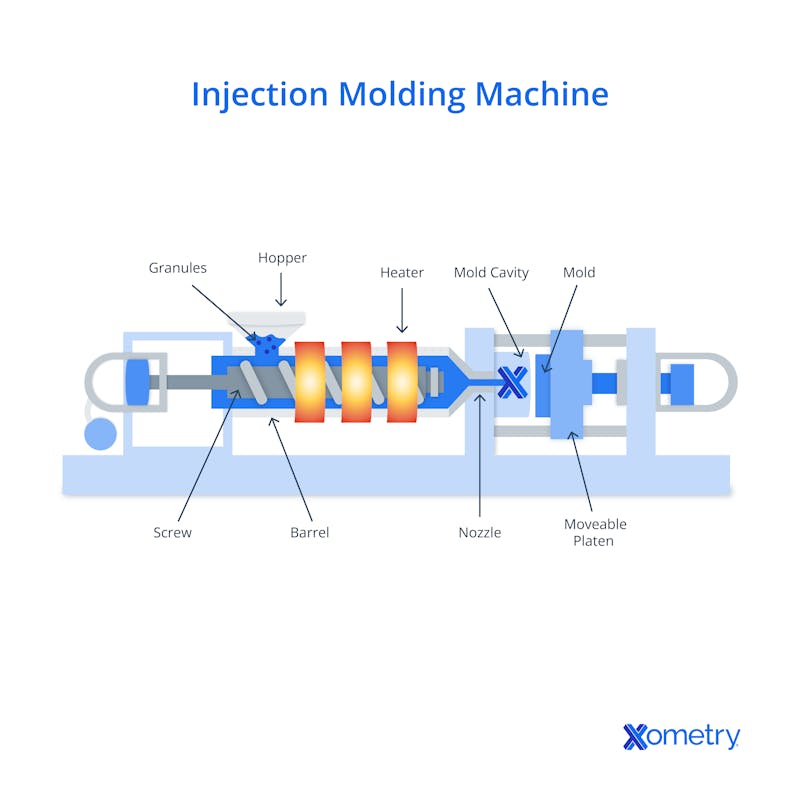
The Extrusion Process
The extrusion process is used to create continuous linear bars. After molten material is sent through an extrusion machine and comes out the other end of a two-dimensional die opening, creating rod-like shapes with complex cross-sections, outer shapes, and even inner voids. These complex shapes of long bar, often 100 or 1000 feet long, are typically cut with a band saw and can be shaped and post modified or placed in an assembly.
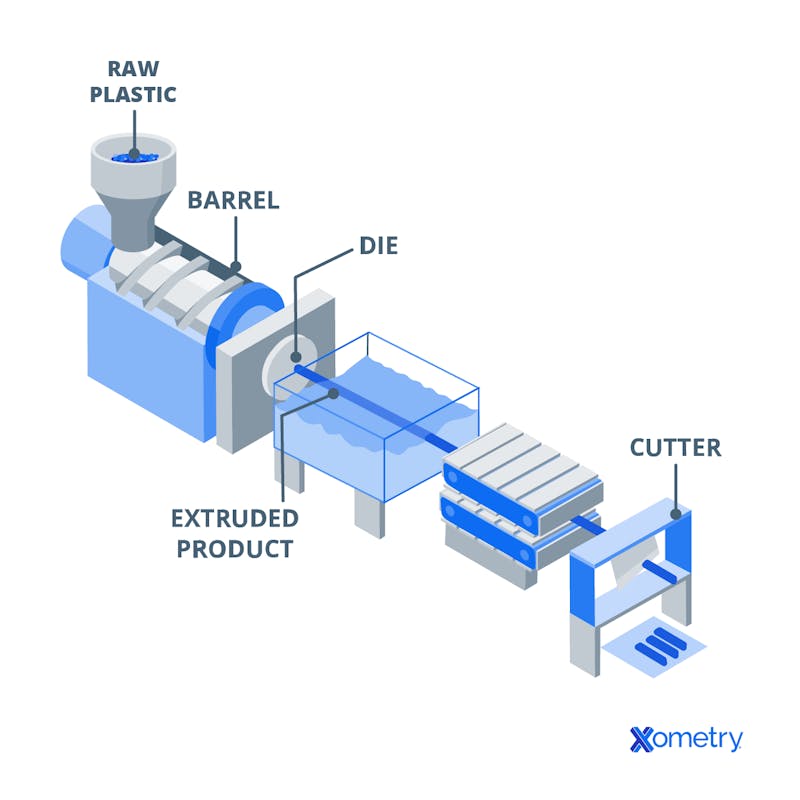
There are some similarities between the injection molding process and the extrusion process; Both injection molding and extrusion are affordable options if you want to create thousands of the same parts. But, before ordering, one should keep in mind the relative advantages and disadvantages of each method.
Benefits of Injection molding
Quality: Molded parts will typically perform better than a similar part that CNC machined or 3D printed from the same material.
Precision: Injection mold tooling can be CNC machined with a high level of precision and tolerances and produce a large number of identical parts with tiny, intricate details.
Plentiful Options: Injection molding has many materials, color, cosmetic, polish, and surface texture options compared to other manufacturing processes compared to 3D printing and CNC machining. Xometry also offers both overmolding and
insert molding services, which come with their own advantages.
Speed: along with a host of other advantages, thousands of parts can be produced incredibly quickly once you have a dedicated mold tool, with production cycles of 30 seconds or less.
Future Possibilities: Injection molding is a rapidly evolving technology, which means that its advantages will only grow over time. If you are interested in learning more, check out our article titled 4 emerging injection molding technologies.
FREE Injection Molding Design Guide
Benefits of Extrusion
Metal and Plastic: Extruded materials can be plastic and metal. Aluminum is the most common metal material, found in 80% of extruded metal parts; meanwhile, polypropylene is the most common plastic extrusion material.
Multiple Methods: There are different types of extrusion, including hot extrusion, cold extrusion, and friction extrusion, and each come with their unique options.
An Affordable Metal Option: Metal extrusion is significantly cheaper than other metal processes like CNC machining, which is much more cost-prohibitive to produce metal parts at scale.
Disadvantages of Injection Molding
Limited Metal Production: Although there is metal injection molding that can mass-produce metal parts, most injection molding is typically used to create plastic parts.
Processing Time: Plastic molding has disadvantages compared to other processes like 3D printing. IM can restock quickly but upfront tooling time drives lead time for first articles up, which means that eD printing may be better equipped to rapidly restock prototype parts far more quickly than molded parts that do not have an associated mold tool.
Environmental Cost: The environmental impact of injection molding uses quite a bit of power to produce plastic products.
High Upfront Cost: The initial design cost for injection molding can be relatively high if one doesn’t compensate for the cost of a mold tool by ordering a large number of plastic parts.
Disadvantages of Extrusion
Lack of complexity: The plastic extrusion method can’t make final shapes as complex as those produced by plastic injection molding; While a clamping unit can help create complex cross-sections, its capabilities pale in comparison to the complexity afforded by plastic molding. Naturally, this lack of complexity limits the number of use-cases for extrusion compared to plastic injection molding.
Environmental Cost: the environmental cost of metal and plastic extrusion can be pretty high, but thankfully the industry is finding ways to reduce the cost.
Less material options: When compared to other manufacturing methods, particularly injection molding, extrusion has far less material options than its counterparts.
Both processes can produce pieces at a lower cost, but one should note there are different cost drivers between the two methods. Injection molding has a high upfront cost for the mold tool, but this tool quickly amortizes, making parts very cost-effective in a short time. Meanwhile, The extrusion process is less costly upfront, with tooling costs 80% to 90% less than injection molding, but slightly more expensive over time as it produces parts at a more medium cost per part. The length of the extruded bar quickly amortizes this cost.
End-Use Applications
Both processes have their own advantages in certain industries and applications. Injection molding is ideal for aerospace, medical devices, consumer good, energy, electronic, automotive, robotic, and even toy industries. Many molded parts require a high level of certification to be used across these vast industries; thankfullyXomerty offers a wide range of certificates on molded parts, including the ISO 9001, AS9100, ISO 13485, UL, ITAR, and ISO 7 and 8 Medical Clean Room molding certifications. On the other hand, Extrusion is more suited for certain applications in the aerospace and automotive industries, as well as ladders, scaffolds, linear motion, conveyors, process control, agriculture, building construction, framing, and mining applications. The plastic extrusion molding process is useful to create products including “pipes, sheets, films, and wire covering.”(Source)
In Summary
Xometry’s injection molding and metal extrusion services are powered by thousands of suppliers in our global supplier network. We encourage you to head over to Xometry Instant Quoting Engine to get a quote on your next plastic molding order. Xometry offers expert engineering reviews and $500 off your first mold to help sweeten the deal. If you want to learn more, we encourage you to download our injection molding design guide and consider watching our webinar: top 10 considerations when injection molding. And, if you would like to place a high-volume metal extrusion order, let us know by submitting a request today. Our technical sales engineering team would love to help you save on your next low-cost plastic or metal order.
