The hot runner system is one of the most recent advancements in plastic injection molding, and has pretty much taken over from cold running systems. Let’s look at exactly what these systems are, how they work, and where and what they’re used for.
What is Hot Runner Injection Molding?
The hot runner system works by injecting the plastic into the mold through a heated system called a manifold, which keeps the plastic melted. It’s different from the old cold runner system method where plastic flows through cold runners (a series of disposable plastic channels), and then has to be cooled and removed after each cycle. There’s no waste from hot runners, so the cycle time is much faster.
Hot runners offer better control, and the process eliminates many of the arduous steps necessary in other plastic injection molding methods that require cold runner systems to work. They allow the molten plastic to flow better in the mold and basically make the whole process quicker, smoother, and more efficient.
What Are Examples of Hot Runner Injection Molding Project?
Hot runner injection molding projects encompass a diverse range of applications, demonstrating the versatility and effectiveness of this technology. In the automotive industry, hot runner systems are utilized to produce interior components, exterior parts, and engine components. These systems ensure the production of high-quality, dimensionally accurate parts essential for the automotive sector.
The packaging industry extensively relies on hot runner systems for manufacturing plastic packaging products. Bottle caps, closures, containers, and lids are efficiently produced with consistent quality and minimal waste using hot runner technology.
Hot runner systems find significant applications in the medical field for the production of intricate and precise parts used in medical devices. Syringes, inhalers, IV components, and surgical instruments benefit from the reduced cycle times and high precision enabled by hot runner injection molding.
Consumer goods manufacturing also benefits from hot runner technology. Electronic components, household appliances, toys, and consumer electronics can be efficiently produced, eliminating cold runners and minimizing waste during mass production.
In the industrial sector, hot runner systems are utilized for the manufacturing of critical components such as connectors, valves, gears, and enclosures. The precise control over molten plastic flow ensures consistent quality and dimensional accuracy for these essential industrial parts.
How Do Hot Running Injection Molding Systems Work?
The big selling point of hot runners is that they heat the entire runner system with an adjustable temperature controller so that the plastic stays in liquid form as it moves through the mold. It’s made of three main parts: a heated barrel that keeps the plastic hot, a manifold that shares out the molten plastic, and nozzles that show the plastic the way to the mold cavities. These all work together to keep the plastic hot until the cavities are all filled up. It’s then allowed to cool and set in the shape of the mold.
Also called hot runners or hot drops not only conserve plastic per molded shot cycle, but also increase the output and reduce variability on the gate vestige of a part.Greg PaulsenDirector, Applications Engineering
Hot running injection molding systems are known for producing better quality parts thanks to their ability to keep a consistent temperature.
What Is the Hot Runner System in Plastic Industry?
A hot runner system is a specialized component used in the plastic injection molding process. It is designed to maintain a consistent temperature in the channels or "runners" through which molten plastic flows into the mold cavity. When plastic parts are manufactured through injection molding, the molten plastic material is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic material solidifies and takes the shape of the mold, forming the desired plastic product. In a conventional injection molding system, the plastic is injected into the mold through a sprue, which leads to a cold runner system. The cold runner is a set of channels that distribute the molten plastic from the injection molding machine nozzle to the individual mold cavities
In contrast, a hot runner system eliminates the need for a cold runner by using heated channels. The hot runner system consists of a manifold, which is a heated block with multiple channels, and a series of nozzles that deliver the molten plastic directly into the mold cavities. The channels and nozzles in the hot runner system are heated to maintain the plastic in a molten state throughout the injection molding process.
What Are the Advantages of Using Hot Runner Molding System?
- Cost savings: In the long run, it’s a more cost-efficient option as it offers reduced waste and better productivity.
- Reduced waste: There are no runners to remove after each cycle so waste is cut right down.
- Less chance of damage: It’s easy to reduce heat to the hot runner nozzle to prevent faulty parts.
- Faster production: Once the system heats up, it’s ready to go and doesn’t need any prep time for the next injection, so cycle times are brought down quite a bit.
- Cleaner parts: No extra plastic waste means the parts come out clean and don’t get in the way of other machines like robots or conveyors. There’s less chance of flash (excess plastic around the edges), too.
- Compatible with delicate materials: It’s efficient use of heat makes it easier to work with materials that have very specific temperature requirements.
- Less mold stress: They need less force to inject the plastic into the mold, meaning less stress on the mold and the machine holding it.
What Are the Disadvantages of Using Hot Runner Molding System?
- Higher cost: They’re more expensive to buy than cold runners so be prepared to invest.
- High maintenance: Looking after these systems takes a lot of time and effort.
- Extra heating: To work, they need extra heating elements/sources, something that can also increase operating costs.
Why Use Hot Runner Injection Molding Instead of a Cold Runner Injection Molding System?
The main difference between hot and cold running systems is that hot runners keep the plastic molten inside the system, so there’s no need for extra material like runners, but cold runners let the plastic cool and harden, which means they need to be removed later (read: more waste). These differences can be seen in the image below.
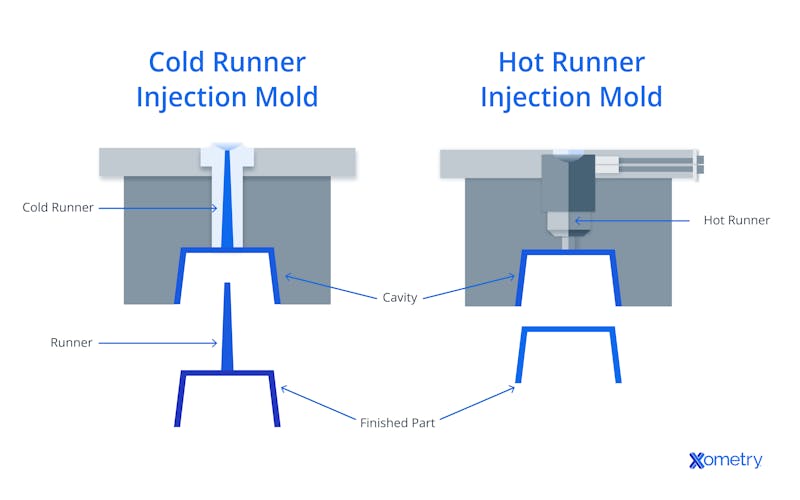
What Are the Factors To Consider When Using a Hot Runner Injection Molding System?
Not all hot running injection molding systems are the same, although, admittedly, they do look similar. Each one has its own unique needs, so to choose the right one, you’ll need to involve the hot runner manufacturer in the design process from the start. Also, different projects will likely need different hot runner configurations so the system you choose will need to match your needs, i.e., the type of material you’re molding and the color you want. The main things to watch for are the nozzle hot tip’s material and shape, and the size of the gate which will depend on things like the part’s weight, wall thickness, and the material’s quality.
- Consider the Design: Each hot runner system has unique requirements, even within standardized systems. It is crucial to involve the hot runner manufacturer in the system design process to ensure proper operation.
- Consider the Application: Hot runner system configurations vary significantly depending on the application. For example, the design will differ based on whether the system needs to gate directly to the part or use a sub-runner attached to the part. Configurations will also change for high-temperature requirements, high-volume projects, or other application-specific needs.
- Other Considerations: The type of material being molded and the color requirements have an impact on the type of hot runner system that is suitable. While cost is typically a primary consideration due to the expense of hot runner systems, the benefits provided by these systems often outweigh the initial costs.
What Is the Significance of Precise Temperature Control for Runner Injection Molding Systems?
Precise temperature control is of utmost importance in runner injection molding systems due to several key reasons:
- Material Quality: Different types of plastics used in injection molding have specific temperature requirements for optimal processing. Precise temperature control ensures that the molten plastic remains within the correct temperature range, allowing for proper material flow, viscosity, and homogeneity. Maintaining the ideal temperature throughout the molding process helps prevent issues like material degradation, inconsistent part quality, or defects caused by improper material behavior.
- Part Quality and Consistency: Temperature control directly affects the quality and consistency of the molded parts. Deviations in temperature can lead to variations in part dimensions, warping, sink marks, or other cosmetic defects. By tightly controlling the temperature, the molder can produce parts that meet the desired specifications consistently, minimizing rejects and ensuring consistent product quality.
- Cycle Time Optimization: Efficient temperature control allows for precise timing and control of the cooling and solidification process. Proper cooling is crucial to achieving shorter cycle times in injection molding. By accurately controlling the temperature of the mold and the molten plastic, the cooling time can be optimized, reducing overall production cycle times and increasing productivity.
- Energy Efficiency: Precise temperature control helps minimize energy consumption in runner injection molding systems. By maintaining the required temperature within a narrow range, energy wastage due to excessive heating or cooling can be avoided. Energy-efficient systems not only reduce operational costs but also contribute to environmental sustainability.
- Process Stability and Control: Temperature fluctuations can have a significant impact on the stability and repeatability of the injection molding process. Precise temperature control enables greater process stability, reducing the likelihood of process variations and deviations. This stability allows for better process control, making it easier to fine-tune the parameters and optimize the molding process for consistent and reliable production.
What Are the Different Types of Hot Runner Systems?
There are three different types of hot runner systems:
- Hot Tip Hot Runner System: This system uses a hot tip at the end of the front of the nozzle, and a cooling mechanism to precisely control and adjust the temperature at the gate (the point where the plastic enters the mold). It’s ideal for small to medium-sized parts with gate diameters around 0.5–2.0mm and can be used with many different plastic materials.
- Sprue Hot Runner System: This system is better for medium to large parts. It has a larger passage — a sprue — for the plastic to flow through and get to the mold gate at a lower pressure. It has a low shear rate (how quickly the layers of plastic move past each other as they flow) which leads to much less stress and reduces the chances of the part warping or deforming. With sprues, the gate is bigger than the one used in hot tips, so the parts might be left with more prominent gate marks, meaning it’s best for parts that don’t have to have a certain neat appearance, like structural components.
- Valve Gate Systems: This uses a needle with movement—from either mechanical, pneumatic, or hydraulic pressure—to control the nozzle’s opening and closing so that you can precisely control the flow of plastic. The result is a smooth cavity, so there are no defects or weld marks. This type is used for larger parts that need loads of gates that can be controlled one at a time.
Applications of Hot Runner Injection Molding
Hot running injection molding systems are used in many industries, just some of which you’ll find in the table below, along with what it’s used to make.
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
Industry Automotive | Applications Interior and exterior parts, engine components |
Industry Packaging | Applications Bottle caps, lids, closures, containers with minimal waste |
Industry Medical | Applications Medical device parts, syringes, inhalers, surgical instruments, IV components |
Industry Consumer goods | Applications Mass production of electronics, toys, household appliances |
Industry Industrial | Applications Connectors, valves, gears, enclosures |
Hot Runner Injection Molding Applications
Hot Runner vs. Cold Runner Injection Molding
As we covered above, the main difference between hot and cold running systems is that hot runners keep the plastic molten inside the system, so there’s no need for extra material like runners, but cold runners let the plastic cool and harden, which means they need to be removed later (read: more waste). These differences can be seen in the image below.
Hot running injection molding systems are able to keep the temperature consistent and allow you to control it, too. This makes them ideal for delicate materials that can’t survive really high heat. They can also make more detailed parts that are smooth and aesthetically pleasing (so they don’t have to be relegated to structural, i.e., hidden, uses). They might be more expensive to purchase, but they can churn out large amounts quickly with hardly any waste — they practically end up paying for themselves.
Are There Too Many Wastes During the Hot Runner Injection Molding Process?
No. Hot runner injection molding processes are generally known for producing less waste compared to cold runner systems. This is primarily because hot runner systems eliminate the need for a sprue and runner system, which typically generates waste material in the form of runners and gates.
Is a Hot Runner Injection Molding System More Expensive Than a Cold Runner Injection Molding System?
Yes, hot runner injection molding systems are generally more expensive than cold runner injection molding systems. In a cold runner system, the mold is designed with channels or passages called runners, which distribute the molten plastic to the various cavities in the mold. Cold runner systems are relatively simple and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for certain applications. On the other hand, hot runner systems are more complex and require additional components such as heated nozzles, manifold systems, and temperature controllers. The additional components and complexity of hot runner systems make them more expensive upfront.
What Is the Difference Between 3D Printing and Injection Molding?
3D printing and injection molding are two different manufacturing processes with distinct characteristics and differences. 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a process that produces three-dimensional objects by building them layer by layer from a digital model. Injection molding, on the other hand, involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity to produce a part. Listed below are some key differences between the two:
- Process: In 3D printing, objects are built layer by layer from the bottom up using a digital model. On the other hand, injection molding is a manufacturing process in which molten material is injected into a mold cavity and cooled to form the desired shape.
- Complexity: 3D printing allows for the creation of highly complex geometric shapes with intricate details, including internal features and undercuts. Injection molding, while capable of producing complex parts, may have limitations due to the need for mold design and ejection considerations.
- Materials: 3D printing supports a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites. Injection molding primarily uses thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers that can be melted and injected into the mold.
- Production Volume: 3D printing is often used for low-volume production or prototyping due to its flexibility and ability to create customized products. Injection molding is more suitable for high-volume production runs, as the cost per part decreases with larger quantities.
- Surface Finish: 3D printed parts typically have visible layer lines, which may require additional post-processing to achieve a smooth surface finish. Injection molding produces parts with a consistently smooth surface, requiring little to no post-processing.
- Cost: The cost structure of the two processes differs. 3D printing can be cost-effective for small production runs or highly customized parts, but it may become expensive for large-scale production. Injection molding generally has higher upfront costs due to mold design and manufacturing but becomes more cost-effective for large quantities.
How Xometry Can Help
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities including CNC machining, 3D printing, injection molding, laser cutting, and sheet metal fabrication. Get your instant quote today.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


