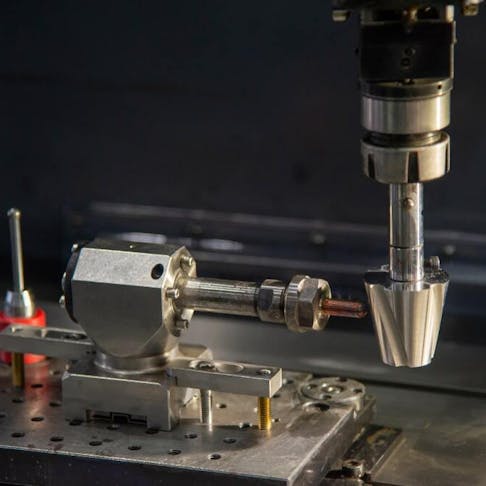
As a form of electrical discharge machining (EDM)—a process that shapes hard metals using electricity—sinker EDM is used to make detailed molds, dies, and complex parts that other tools struggle with. Whether you know it as sinker, plunge, ram, volume, or cavity EDM (yes, it goes by a lot of names), this is one method worth knowing about, especially if you need highly accurate parts.
What is Sinker EDM?
A process that’s been around since 1770, sinker EDM uses spark erosion to produce parts through an electrode that creates cavities in metal workpieces. It’s a subtractive process that gets its name from the fact that the electrode actually sinks into the material, though there are machines available that work at other angles too, including horizontally.
This machining method is especially useful for making cavities that can’t be made using other methods like computer numerical control (CNC) milling. And the hardness of a material won’t affect the electrode’s performance, so you can use this method even on hardened steels for making injection molds. Another benefit of using this method is that it can be very accurate, as long as the electrode is properly machined. Unlike CNC machining, this process doesn’t expose the tool to loads that could distort it, which is why it can be controlled better. It also has the ability to produce irregular shapes, which are pretty much impossible to make using other methods.
No special tools are required, even with very hard materials. As long as the material is conductive, sinker EDM can work on it. Compared to CNC milling, this method is rather slow, and it’s also expensive to operate. The fact it’s limited to conductive materials might also be a con for some.
How it Works
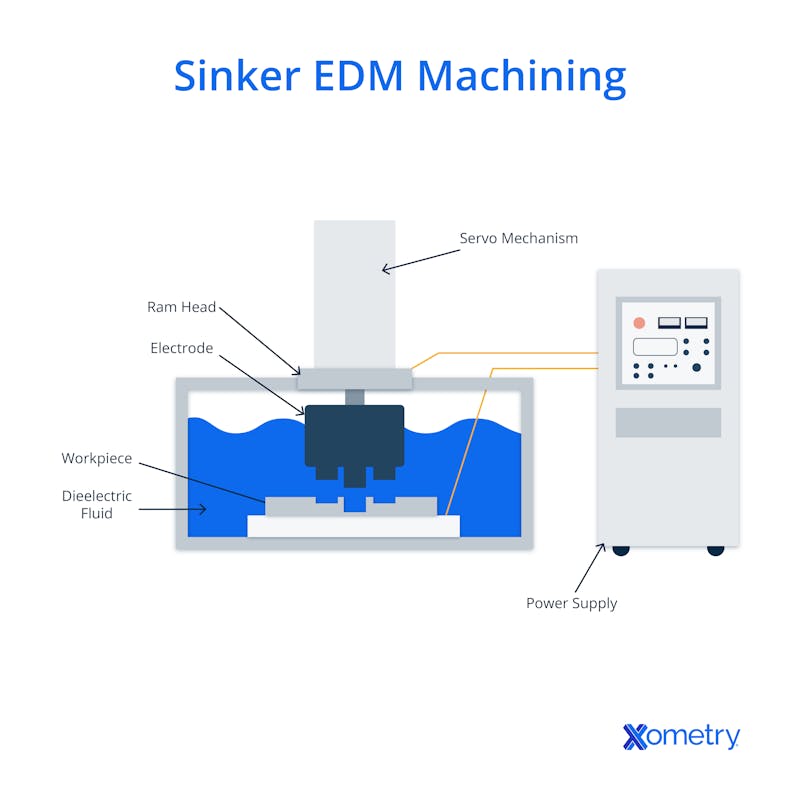
The electrode used in the process (usually made from graphite or copper) needs to have the same shape as the feature you’re trying to make. When the process starts, the electrode moves toward the material, which has been immersed in a dielectric fluid. Just as the electrode is about to touch the material's surface, a high-voltage spark—up to 12,000°C—jumps between them, melting away a bit of the workpiece (this is sometimes called “burning”).
The workpiece is immersed in dielectric fluid because the fluid serves as a coolant to manage high temperatures and acts as an insulator. This insulation prevents a continuous electrical current from passing between the part and electrode, ensuring sparks only form when the voltage is high enough. The dielectric fluid is constantly filtered to remove metal debris, and it’s cycled through a chiller to keep the temperature under control. Here’s a visual of the sinker machine and process.
Frequently Asked Questions on Sinker EDM Machining
Exactly how accurate is this method?
Its tolerances can be as low as +/- 0.004 mm as long as everything is up to par. As well as being controlled by a CNC machine, the electrode wears evenly, so it stays consistent in terms of dimensional accuracy. Some of these machines can even polish a part, bringing its surface roughness to around 0.18 microns.
How do sinker and wire EDM differ?
A wire EDM machine uses a thin, electrically charged wire to cut complex, two-dimensional shapes through thick material. It doesn’t sink electrodes into the material like sinker EDM and it’s better for cutting through materials instead of making internal shapes within solid blocks.
What are the best sinker EDM machines?
There are several sinker EDM models on the market, including:
- GF Form P350: Great tool life management, can polish with a surface roughness of 0.12 microns
- Makino EDAF3: Dielectric tank underneath, automatic tool changer
- Mitsubishi SV12P: AI capabilities for up to 30% reduced machining time
How Xometry Can Help
If you have any further questions about this topic or anything else related to manufacturing, one of our representatives would be happy to assist you. In addition to offering sinker EDM machining services, Xometry has you covered with a huge variety of capabilities, from 3D printing to laser cutting, to powder coating and everything in between. Get started today by requesting a free, no-obligation quote.
Summary
Copyright and Trademark Notices
- MITSUBISHI is a trademark of MITSUBISHI CORPORATION.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


