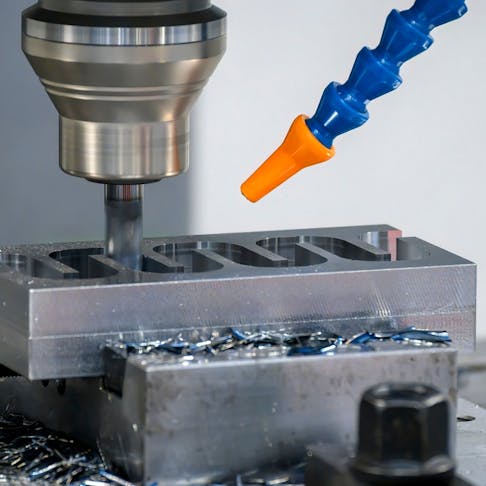
Slot milling is a fundamental machining technique used across industries such as manufacturing and woodworking. This technique uses specialized tools called slot milling cutters to make slots or grooves in a workpiece. Understanding the different slot milling methods, their functions, and their pros and cons is essential for selecting the right approach for each machining task.
This article explores how slot milling works, its main types, advantages, and disadvantages.
What Is Slot Milling?
Slot milling is a versatile and precise machining method used to create precision slots, keyways, or channels in components.
What Is Slot Milling Used For?
Slot milling is mainly used to create pockets, keyways, and slots in various workpieces. Products and machines produced by a variety of industries require slots for assembly or basic functionality. Slot milling allows for the precise fabrication of components such as gears, pulleys, and other mechanical parts. Slot milling enables the production of dimensionally accurate geometries that would be difficult to achieve by other means.
Are Slot Milling and Groove Milling the Same?
Yes, slot milling and groove milling are generally considered the same. Both terms describe a machining process in which a rotating cutting tool cuts a slot or groove into a workpiece.
How Does Slot Milling Work?
Slot milling is a machining process that uses a rotating tool with multiple cutting edges. Key factors affecting the outcome include the required geometry (width, depth, undercut) and the workpiece material. The correct choice of tools, feed rate, speed, and cooling fluids can have a dramatic effect on the ultimate quality of the machined feature.
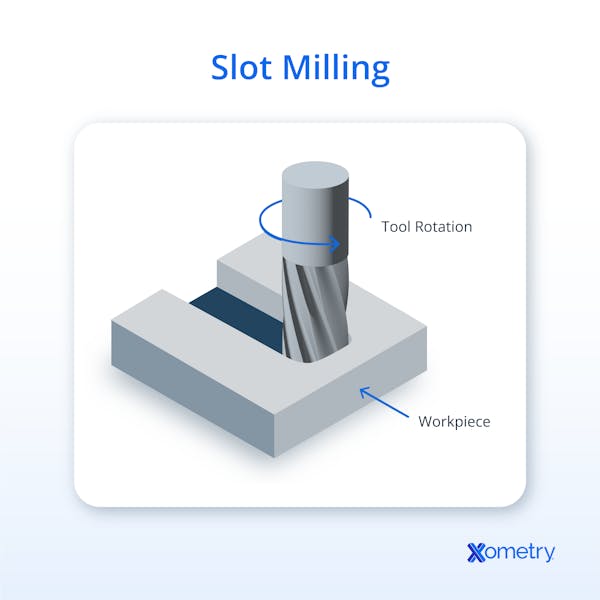
How Does Slot Milling Differ From Other Milling Types?
The primary distinguishing factor between slot milling and other milling types is the tool's axis orientation with respect to the workpiece. In slot milling, the cutter moves along its own axis, whereas in face milling, the cutter moves perpendicular to the workpiece surface, and in peripheral milling, it cuts along the edge of the workpiece. This axial movement allows the creation of slots or channels in the workpiece. The different axis orientations affect the kinds of operations that each milling technique performs well. While peripheral milling works well for contouring, face milling produces flat surfaces. Slot milling, with its axial movement, is ideal for producing precise grooves or slots. Understanding these differences helps machinists choose the most suitable technique for specific applications, taking into account factors like material properties, surface finish requirements, and machining efficiency.
What Are the Types of Slot Milling Cutters?
The types of slot milling cutters are listed and discussed below:
1. Face Milling Cutter
Often used in slotting operations, face milling cutters are best suited for jobs involving linear grooving. These cutters have a flat surface with several cutting teeth positioned around the edge. During slotting, the cutter engages the workpiece to produce a straight-sided groove. Their usefulness is limited, though, since they work best when creating linear slots. Face milling cutters are not as adaptable for non-linear or more complex slotting applications due to their design. Despite this limitation, they remain useful for applications where linear grooving is the primary requirement.
2. Side Milling Cutter
The side milling cutter is well-suited for various milling operations due to its effective metal removal from the sides of a workpiece. It has teeth on both or all of its sides, as well as along its periphery. Designed specifically for cutting slots and keyways, this cutter comes in various configurations: staggered-tooth, interlocking, plain, and half side milling cutters. These variants suit specific machining needs and enable different slot geometries, depths, and applications. Side cutters are particularly stable and productive when handling long, deep, open slots.
3. End Milling Cutter
End milling cutters feature a central ‘dead’ zone and a design suited for various milling applications. With limited cutting edges on the sides and outer edge, they are well-suited for precision machining, particularly for complex closed slots. End mills are used to cut angled, curved, or straight slots. They are a go-to tool for many machining tasks due to their ability to cut designated pockets and move through gaps wider than the tool’s diameter.
4. Gang Milling Cutter
Gang milling cutters create precise slots efficiently by using multiple groove cutters mounted on a single arbor. In slot machining, this simultaneous multi-cutter method greatly increases productivity and saves time. A key advantage is the ability to cut slots of different designs in a single pass. However, this efficiency comes with a drawback: the process generates significant cutting forces. The machine tool and arbor must be highly rigid to fully utilize gang milling cutters. This highlights a key point: a robust setup is essential to withstand the forces involved and ensure optimal slot milling performance.
5. Woodruff Key Slotting Cutter
Woodruff Key Slot Cutters are circular cutters, usually of HSS M2 grade, with a parallel shank for stability. They are essential for creating keyways in shafts. Woodruff-style narrow-width slotting cutters are ideal for producing accurate, narrow keyways in shafts. These cutters resemble side milling cutters but feature concave sides for cutting semicircular profiles.
They cut semicircular cross-sections, creating slots with rounded bottoms that may also be squared in follow-up passes. Milling a Woodruff key slot involves positioning the cutter over the workpiece and modifying the depth in accordance with standard Woodruff key sizes. Several workpiece securing techniques include using a vise, chuck, between centers, or clamping to the milling machine table.
6. T-Slot Cutter
A T-Slot cutter is designed to cut undercut slots that extend below the surface of a previously milled groove. Its design allows it to create a T-shaped profile with an undercut section beneath the surface. With flexibility in machining applications, this tool is useful for operations requiring slots to reach beneath the surface of the material. The cutter engages the workpiece perpendicularly to its axis of rotation, enabling accurate positioning of the undercut. This makes the T-slot cutter a crucial tool for various machining processes, offering efficiency and precision in creating slots that go beyond the surface of the material.
What Are the Advantages of Slot Milling?
Some advantages of slot milling include:
- Slot milling allows for efficient material removal in linear grooves and channels, especially when deeper cuts are required across long distances.
- Slot milling simplifies the machining of certain internal and external features by reducing the need for complex tool paths or frequent spindle repositioning.
- Slot milling cutters are well-suited for shaping components like guide bars and mandrels, enabling accurate slot creation with high repeatability.
What Are the Disadvantages of Slot Milling?
The following are a few drawbacks of slot milling:
- Slot milling can result in high vibrations, especially when cutting deep slots or machining hard-to-cut materials.
- Slot milling’s continuous cutting action generates high radial forces, which can cause tool deflection and reduce accuracy in deep cuts.
- The cutting operation can lead to rapid heat buildup in the tool and workpiece, affecting tool life and part quality.
How To Choose Slot Milling Cutters?
The choice of a slot milling cutter must take into account several important factors:
- Material: Different materials call for different kinds of cutters and cutter coatings.
- Geometry: The dimensions of the required slot will determine cutter size, as well as process variables such as cut depth, feed rate, and speed.
- Machine Capabilities: Ensure the machine can provide the necessary speed, feed, and control features for the chosen tool and material.
- Chip Removal: Choose a tool that has good chip evacuation characteristics.
- Surface Finish: Select a tool with cutters designed to produce the surface finish quality needed for your application.
Lastly, consider your budget and select a cutter that balances cost and performance for your specific machining needs.
What Is the Importance of Choosing the Right Slot Milling Cutter?
Selecting the right slot milling cutter directly impacts workpiece quality, tool life, and machining efficiency. The right cutter enables effective material removal, which cuts costs and machining time. Additionally, it prolongs the tool's life. Finally, choosing the right cutter for the material and slot dimensions produces an accurate slot geometry and a smoother surface finish, improving the machined part's overall quality.
How Does the Choice of Slot Milling Cutter Affect Its Performance?
Selecting the right tool significantly improves surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
How Can Xometry Help in Choosing the Right Slot Milling Cutter?
Using its online platform, Xometry, a top manufacturing marketplace, can help select the best slot milling cutter. Users can specify their slot milling needs and get fast quotes for custom CNC machining. Xometry's manufacturing supplier network offers tool selection expertise to ensure the appropriate cutter is used. Support staff may also advise customers so they can make the best decisions possible for the best machining outcomes.
How To Use a Slot Mill?
The first step in slot milling is to select the proper slot milling cutter based on the material and slot dimensions. Then, clamp the workpiece into the machine vise. After adjusting the feed rate and spindle speed, carefully position the cutter at the starting point of the intended slot on the workpiece. Once in position, initiate the milling process by turning on the cutter. Make successive passes along the slot path as needed, ensuring effective chip evacuation for a smooth and efficient operation.
What Are Some Tips for Successful Slot Milling?
The following is a list of tips that can result in successful slot milling operations:
- Opt for down milling to enhance stability and improve chip evacuation.
- Ensure that at least one cutting tooth is always engaged to improve surface finish and reduce vibration.
- Manage chips effectively with multiple passes, chip-breaker cutters, and coolant/lubricant flushing.
- Balance cutting feed rates to prevent thermal issues while maintaining productivity.
- Use larger diameter cutters for deep slots, and ensure both the tool and workpiece are rigid enough to minimize deflection.
- Use a ramp-down motion for smoother cutter entry, reducing vibrations.
Is Slot Milling Better Than Side Milling?
No. Slot milling and side milling are different machining operations, even though a side milling cutter can be used for cutting slots. The choice between these milling techniques depends on the specific machining requirements. Slot milling is used for creating slots and grooves, while side milling is the creation of a flat, vertical surface on the side of a workpiece. Ultimately, the decision should depend on whether or not you want to make a slot. Other factors should also be considered, including material, tool geometry, and desired surface finish.
What Is the Difference Between Slot Milling and End Milling?
The primary distinction between end milling and slot milling is the way they cut. A slot mill may plunge like a drill and then cut across like an end mill, combining drilling and lateral cutting capabilities. An end mill, on the other hand, primarily performs lateral and horizontal cutting.
Summary
This article presented slot milling, explained it, and discussed how it works and the various types of slot milling. To learn more about slot milling, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including machining and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


