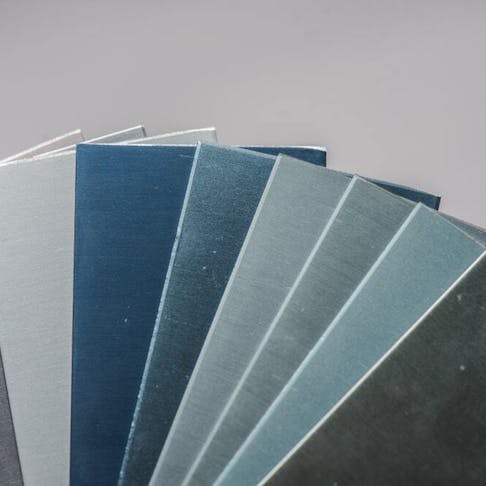
Thanks to its long-lasting effect, low maintenance, and ability to add durability to a material, manufacturers love to anodize any metal that can possibly be anodized. It’s a no-brainer really; it’s cost-effective and makes the metal look nicer, too. Let’s have a look at exactly what it is and how it works.
What is Anodizing?
Anodizing is an electrochemical technique that improves both the functionality and appearance of nonferrous metals, most commonly aluminum and its alloys, but also copper, titanium, manganese, magnesium, zinc, and stainless steel (each material reacts differently to it, but all get the benefits). The magic is in the thin and porous oxide layer created on the metal’s surface during the very controlled anodizing process that protects it from corrosion, oxidization, and wear and tear.
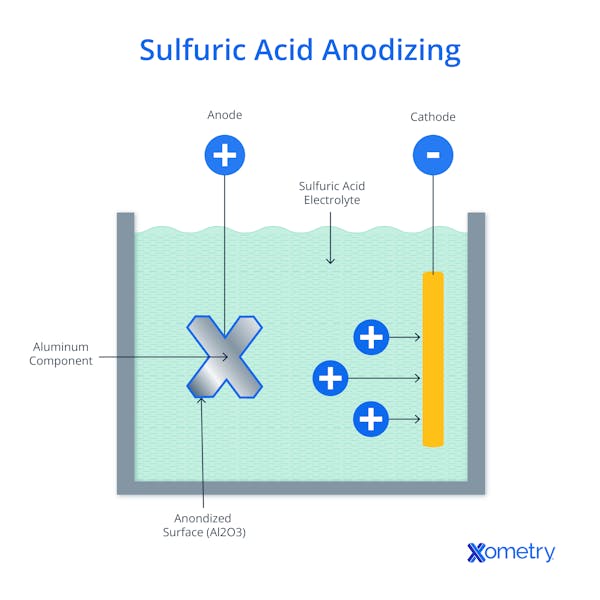
As you can see in the above image, the process involves submerging a metal in an acid bath solution and applying an electric current that drives a chemical reaction, and this is what forces the protective layer to build up. To get a little more technical, the metal to be treated acts as the anode in the electrochemical circuit. When an electric current passes through the system, negatively charged oxygen ions (anions) from the acidic electrolyte are drawn to the anode—these oxygen ions bond to form the oxide layer with the aluminum surface.
At the same time, positively charged hydrogen ions (cations) in the electrolyte are reduced (gain electrons) at the cathode, which is typically made of T-6063 aluminum alloy or other inert, conductive materials. The cathode and anode are connected to an external power source that provides the necessary driving force to sustain reactions and complete the circuit. The thickness of the layer can be customized and tailored to specific needs by changing the type of acid used, voltage, temperature, and process duration.
The process makes the material harder, stronger and a lot more durable than the metal underneath, and also smoother so it can be dyed in various hues and painted more easily—all while keeping the material’s natural appearance. But there aren’t all that many color options due to the chemicals used, and these coatings are more prone to scratches that can’t be discreetly retouched (touch-ups are annoyingly visible).
A Brief History
The method dates back to 1923 when G.D. Bengough and J.M. Stuart, two British inventors, filed a patent application for the method. An early use was to make seaplane parts made from an early aluminum called Duralumin, which is resistant to saltwater corrosion. In 1927, a new sulfuric acid-based process was patented, and it’s still the most common method used to this day. From the 1930-40s onwards, anodizing started being used in military, aerospace, and marine applications, and in other industries with heavy-duty demands, and, a bit later on, in architecture and electronics, too.
Anodizing Types
Although there are some specialized anodizing types available used for more niche purposes (i.e., phosphoric acid or titanium), these are the three main ones that are chosen based on the application, material, and desired end result:
Type I
- Electrolyte: Chromic acid
- Layer thickness: 0.00002 to 0.0001 inches (0.5 to 2.5 microns)
- Properties: Excellent bonding, non-conductive, electrically insulating, minimal dimensional impact, compatible with complex shapes
- Applications: Adhesive applications, paint and coating primer, aerospace components, welded parts
This type produces the thinnest oxide layer of the three, but if it’s properly sealed, it can give your metal as much corrosion resistance as the thicker layers formed by the other two. These coatings absorb less dye, resulting in a grayish look that limits its use for decorative applications. But you can dye the coating black, which is great for things like optical component housings where protection and light absorption are needed.
Type II
- Electrolyte: Sulfuric acid
- Layer thickness: 0.0002 to 0.001 inches (5 to 25 microns)
- Properties: Highly porous, hard, abrasion and corrosion resistant, more affordable, compatible with a wider range of aluminum alloys
- Applications: Optical and electronic components, hydraulic valve bodies, electronic and computer enclosures
This is the most widely used type; it creates a more rigid coating than Type I and is more affordable than both the other methods because it doesn’t need as much energy and time or as many chemicals. Also, treating waste from sulfuric acid anodizing is simpler and less expensive than waste management for chromic acid types. It can absorb dyes (which are available in many different shades) before it’s sealed, thanks to its porous layer. Post-dye sealing will minimize color fading under regular use but it won’t be able to stop the color from wearing off in prolonged UV exposure. The final look is clear and natural, making it an excellent base for dyeing, but it can also be left uncolored.

Type III
- Electrolyte: Sulfuric acid-based
- Layer thickness: 0.0005 to 0.002 inches (12.5 to 50 microns)
- Properties: Superior wear and corrosion resistance, non-conductive, insulating
- Applications: Electrical system components, valves and pistons, sliding parts, gears, joint swivels, blast shields, electrical insulation, high-friction and high-load applications
Also called hard or hard coat anodizing, this is done under tightly controlled conditions as it creates a denser, sturdier oxide layer than standard sulfuric acid anodizing that can extend the service life of components. It can be combined with lubricants to improve the performance of sliding parts, reducing wear and friction, and the thickness and uniformity of the coatings make them great for refurbishing worn components or remanufacturing parts that fall out of specification.
How to Anodize Aluminum
The steps involved in anodizing aluminum are pretreatment, anodizing, coloring, and then sealing. We’ve already covered anodizing above, so here are how the other steps factor into the overall process:
1. Pretreatment
The surface of the metal has to be very clean and even before the process can start. To remove any dirt, oils, grease, and other contaminants, mechanical methods like polishing, shot peening, and sandblasting can be used, but this is done many times with chemical pre-treatments, such as:
- Degreasing, where the metal is plunged in a grime-busting solution to remove any impurities, then rinsed in hot water.
- Etching, which uses a bath of caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) to even out texture and remove minor imperfections. This breaks off into two further branches—light etching for a satin, matte finish, and bright dip anodizing that uses phosphoric/nitric acid for a more luminous look.
- Desmutting treats the material with an acid solution, often nitric acid, to remove any residual smut (a combination of impurities and alloying elements). This helps the oxide layer stick evenly across the metal and gives it a smooth surface.
2. Coloring
The porous oxide layer formed in the anodizing step (just before this one) allows for easy color dying, which appeals to custom manufacturers—it’s not a necessary step but is used a lot for branding and decorative purposes. While there are many color options, the final result will depend on factors like the type of dye used, the bath’s chemical composition, and how long it’s immersed. The coloring methods are:
- Electrolytic: Dipping the material in a tin, cobalt, nickel, or other inorganic metal salt solution and then zapping an electric current through it. These salts create the colors by oxidizing and settling into the layer’s pores.
- Dip: Immersing the material in a solution with inorganic or organic dyes. The porous layer will have absorbed the dye so rinsing the surface is a must to avoid any further reaction from happening—but this option could mean the color fades quickly, and it isn’t UV-resistant.
- Advanced technologies: These are on the up and allow for custom color matching. They’re not yet as common as the above two but include lasers, software, and nanotechnology.
3. Sealing
Sealing is really important to the overall anodizing process because it removes any remaining porosity on the surface so that the piece truly stays protected from harsh external environments and elements, scratches, and staining. There are three ways it’s done:
- Cold sealing with room-temperature solutions (typically nickel or cobalt salts)
- Hot sealing, which involves boiling water or steam to hydrate and seal the oxide layer
- Hybrid sealing, which is a combination of the hot and cold methods

FAQs on Anodizing
Why is aluminum the most commonly anodized metal?
Aluminum is the most widely used metal for industrial and commercial use—even more than steel and titanium—which explains why it’s the most commonly anodized. As well as all the benefits mentioned above, anodizing gives the metal a surface that’s three times tougher than if it were left untreated. It doesn’t flake, chip, or peel (unlike some other coatings), even when colored or dyed.
What colors can be achieved with anodizing?
The most common colors you can get are red, blue, green, black, yellow, purple, and orange—not because they’re the nicest colors available, but because these are generally the most cost-effective and are easy to produce shades. You can also get gold, bronze, nickel, and transparent finishes. It’s worth repeating that the final appearance will depend on several factors, like the alloy composition, the layer’s thickness, and dye quality.
How Xometry Can Help
Processing your metal parts is more than possible at Xometry and we have a long list of manufacturing services you can get instant quotes for depending on your needs, including for anodizing and other customized services. Take a look at our plastic 3D printing, plastic extrusion, and plastic laser cutting pages for more information. You could always reach out to one of our representatives, who will be more than happy to assist, or go straight to requesting your free, no-obligation quote on any service.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


