The rigid structure of a shampoo bottle and the stretch of a grocery bag may seem like they’d be made from very different materials with contrasting traits, but both are thanks to one type of thermoplastic: low-density polyethylene. You might already be aware of polyethylene and its unique set of mechanical and physical traits, but there is more than one type — making it easy for manufacturers to find the right fit for the products they’re looking to produce.
Low-density polyethylene has its own list of handy characteristics. Here’s what separates it from other kinds of polyethylene and the types of applications you’ll find it’s commonly used.
What Is Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)?
Low-density polyethylene is a type of thermoplastic in the polyethylene family. It’s formed of long chains of ethylene molecules called monomers. Its chemical formula is (C2H4)n — the same as high-density polyethylene. Their differences lie in density, as their names suggest. Once LDPE is created, it’s typically flexible and transparent in color.
It’s a common choice for manufacturing plastic goods like cling wrap and juice containers because it’s corrosion-resistant, flexible, durable, and low-cost. On products, you’ll recognize it through the number four in a triangle (usually on the bottom or side of the item).
How LDPE Is Made
To make low-density polyethylene, you’ll need to call on the radical polymerization process. This involves extreme heat (up to 570 degrees Kelvin) and an immense amount of pressure (up to 3,000 atm). First, the raw petroleum-based materials are broken down into small molecules, then the ethylene gas is separated and funneled into a reactor.
In the reactor, it’ll come into contact with an initiator like oxygen or organic peroxide. Then, the polymerization will begin.
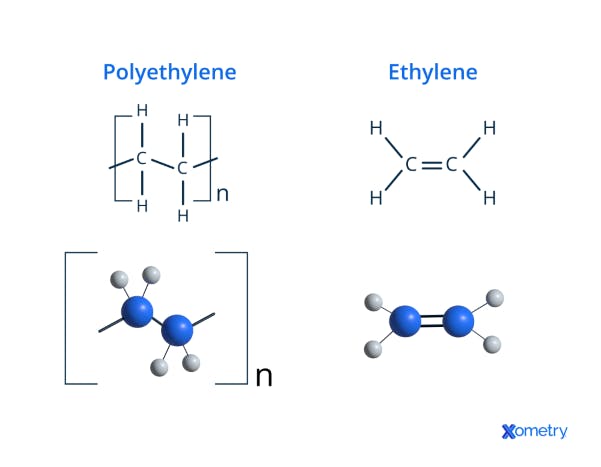
The image beneath shows how polyethylene and ethylene molecules and their chemical formulas look visually.
Low-density polyethylene can shapeshift a little, becoming pellets or granules. These formats make it easy to turn the material into other products. At Xometry LDPE is a common material we quote for in our injection molding and plastic extrusion processes. Other fabrication processes that can use this type of polyethylene include:
- Blow molding
- Thermoforming
- Vacuum casting
- Film making
Need Custom Parts Made From LDPE?
Properties of Low-Density Polyethylene
There are a few standout properties of low-density polyethylene that make it a good choice when you’re after strong but flexible materials. It has high corrosion and chemical resistance and offers strength and toughness other plastics might not. Because of the structure of its molecules—it has more branching than its high-density cousin—it’s less dense and more flexible. This flexibility remains even in very cold temperatures.
Below is a table that shares the different properties of low-density polyethylene:
| Property | English | Metric |
|---|---|---|
Property Density | English 0.0331-0.0347 (lb/in3) | Metric 0.915-0.960 (g/cm3) |
Property Tensile Strength, Yield | English 1100-2030 (psi) | Metric 7.60-14.0 (MPa) |
Property Tensile Strength, Ultimate | English 1300-7830 (psi) | Metric 8.96-54.0 (MPa) |
Property Modulus of Elasticity | English 22.0-42.1 (ksi) | Metric 0.152-0.290 (GPa) |
Property Elongation at Break | English 226-650 (%) | Metric 226-650 (%) |
Property Hardness, Shore D | English 42.0-56.0 | Metric 42.0-56.0 |
Property Melting Point | English 216-235 (oF) | Metric 102-113 (oC) |
Property Processing Temperature | English 293-644 (oF) | Metric 145-340 (oC) |
Property Moisture Vapor Transmission (@37.8oC/100oF) | English 1.04 (cc-mil/in2-24hr-atm) | Metric 0.410 (cc-mm/m2-24hr-atm) |
Property Water Vapor Transmission | English 0.0167-1.55 (g/100in2/day) | Metric 0.260-24.0 (g/m2/day) |
Applications of Low-Density Polyethylene
The stretchy but strong nature of low-density polyethylene makes it a great candidate for materials that need to hold heavier weights without snapping or disintegrating. That’s why LDPE is used for things like grocery bags or six-pack rings for soda. Here are a few other ways that you’ll find LDPE implemented:
- Juice containers
- Cling wrap and films
- Bags (like those used for groceries or food)
- Trays
- Six-pack rings
- Tubing
- Prosthetics
- Ice cream lids
- Laminates
Advantages and Disadvantages
There are good reasons to use low-density polyethylene, but depending on the type of product you’re manufacturing, there are also disadvantages to be wary of.
Advantages:
- Flexible: LDPE bends, stretches, and has low crystallinity.
- Moisture resistance: LDPE has no problem deflecting moisture and water.
- Impact and chemical resistance: LDPE won’t break down if it’s exposed to diluted or concentrated chemicals.
- Low price point: LDPE is fairly cheap to produce and can be recycled.
Disadvantages:
- Cracking and lower strength: LDPE might crack or break when it has to hold heavier objects.
- Has a Max Temperature: LDPE can handle pretty hot temperatures, but above 221 degrees Fahrenheit, it will start melting.
- High gas permeability: Gasses like carbon dioxide can easily slide through LDPE.
- Poor UV resistance: LDPE struggles to keep its shape, color, and integrity when it’s exposed to UV rays.
- Recycling can be tricky: LDPE is recyclable, but not every product made of it can go in standard home or business recycling containers. It will need to be sorted properly or specially processed at particular facilities, especially for softer, more flexible items like cling film.
Low-Density vs. High-Density Polyethylene
High-density Polyethylene is another material Xometry offers in its molding and machining processes. There are a few differences between low-density and high-density polyethylene, but let’s start with similarities. Both are types of polyethylene, and each has flexibility, chemical resistance, and decent strength. They’re also both relatively affordable to create and manufacture.
Differences arise in their polymer chains and resulting weights and properties. LDPE has a looser molecular structure, giving it its signature flexibility. HDPE’s monomers are tightly packed together, so it’s not as flexible as LDPE.
You probably won’t be surprised to learn that HDPE is stronger and more durable than LDPE. It’s a great choice for industrial applications that need a certain level of stiffness and chemical resistance. Still, LDPE has its perks. It can provide you with an elasticity that its high-density counterpart can’t provide.
To learn more, see our in-depth guide on High Density Polyethylene (HDPE).
Here are a few other commonly asked questions when it comes to the nature of low-density polyethylene:
Summary
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities including CNC machining, 3D printing, injection molding (using LDPE), laser cutting, and sheet metal fabrication. Get your instant quote today.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


