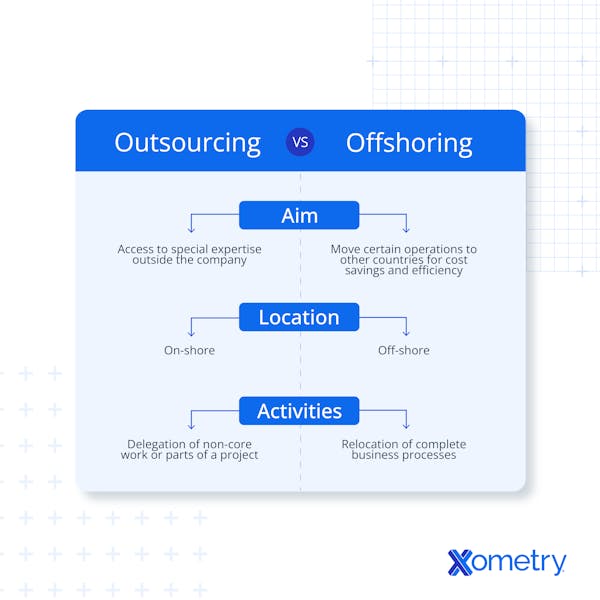
Outsourcing is a process in which a company contracts another entity to carry out work on its behalf. Offshoring means the company sets up (at least part of) its operation in a faraway foreign country. Both can be used to drive down costs. However, outsourcing is more often used to gain access to specialized skills, whereas offshoring is used to gain access to a wider labor market. Both strategies will have different risk profiles, limitations, and advantages.
This article will discuss the differences between outsourcing vs offshoring.
What Is Outsourcing?
Outsourcing is a business practice whereby business activities that could be performed in-house are contracted out to other companies. Outsourcing became a formal business strategy around 1989 and since then has become a common business practice used to cut costs.
To learn more, see our guide on Outsourcing.
How Does Outsourcing Work?
Outsourcing works by contracting a company for a service which could include: management, consultancy, production, testing, or any other business function. In the outsourcing process, the company contracting out the work will release a tender specifying the requirements of the contract, and then the potential contractors will bid for the work. The submission of a bid will detail how the contractor intends to complete the work in the tender. The company contracting out the work will then choose a contractor, and there will be an exchange of goods and services.
Why Do Companies Choose Outsourcing?
The main driver for companies to choose outsourcing is cost. Outsourcing work often drives down the costs of business operations. This could be because it's easier to contract out tasks to law and accountancy firms than to retain lawyers and accountants all year round. The same principle applies to production. It may be cheaper to outsource the production of specialized parts rather than attempt to buy the necessary equipment and employ and train staff. Other factors also play a role in outsourcing. For example, some tasks require a level of skill and knowledge that can’t be achieved by simply hiring more people. Contracting out work can also minimize some risk as companies can often cancel contracts easier than they can make staff redundant when the workload is low.
What Are Examples of Outsourcing?
Most companies outsource some business activity at some point. Here is a list of well-known brands that use outsourcing:
- American Express: Outsourced customer-support services to companies in India and the Philippines.
- Apple: Uses outsourcing for the production of its iPhones to companies in China.
- Starbucks: Uses outsourcing for its cybersecurity.
- WhatsApp: Outsources some of its software development to other companies.
- Microsoft: Uses outsourcing as a large part of its business strategy to reduce costs and outsources daily tasks including network management and PC procurement.
What Are the Advantages of Outsourcing?
There are many advantages to outsourcing, some of which are listed below:
- Cutting costs.
- More company bandwidth to focus on complex tasks.
- Better access to expertise.
- Minimized risk due to set pricing.
What Are the Disadvantages of Outsourcing?
Outsourcing does have some disadvantages which are listed below:
- Data protection risks.
- Possible increased logistics.
- Hard to retain talent.
- Limits intellectual property.
What Is Offshoring?
Offshoring is the practice of carrying out some of the company's business activities offshore in another country. This is usually done to drive down costs, particularly labor costs. While offshoring could be done in-house by a company in another country, it can also be outsourced to a company in another country.
How Does Offshoring Work?
Offshoring can work in two ways. The first way is the company can set up an outsourcing agreement with a company in another country for goods and/or services. The second way is for the company to create its own presence in another country to access that labor market. In either case, the activity that would have originally been done in the company’s country of origin is instead done in another country.
Why Do Companies Choose Offshoring?
There are several reasons why a company may choose offshoring. Often, the reason is to access cheaper labor than in the country of origin. Another reason is to access more skilled labor. Often, there is only so much labor available in one country, so companies need access to other labor markets to fulfill their business requirements. Many offshoring activities involve customer support services. Offshoring part of that function to a faraway country makes it easier to provide 24/7 customer support. Finally, different countries offer different incentives and tax breaks, which often makes offshoring more desirable.
What Are Examples of Offshoring?
Some examples of offshoring are listed below:
- WhatsApp: At the time at which Facebook (now Meta) bought WhatsApp for US $19 billion, WhatsApp only had 55 employees and 450 million users. WhatsApp achieved this by offshoring software development to companies in Eastern Europe.
- Google: In 2020, Google used offshoring in Ukraine when it bought CloudSimple for its cloud-based services.
- IBM: IBM is a company that heavily uses offshoring, with operations in 170 countries. IBM uses offshoring to access talent in software development, consulting, research and development, and cloud-based systems.
What Are the Advantages of Offshoring?
The advantages of offshoring are listed below:
- Often the cost of labor is cheaper in the offshoring country compared to the company’s country of origin.
- A company can usually gain access to more customers from other countries by offshoring.
- Often, establishing a business in an offshore country allows a company to better understand market trends, market risks, and cultural norms.
- Other countries often have favorable tax schemes to bring in companies from offshore.
What Are the Disadvantages of Offshoring?
The disadvantages of using offshoring as a business strategy are:
- Different regulations could result in a change in the standard of goods or services produced.
- Although the modern world is finding many solutions to working globally, there are still challenges in working together. For example, having a call with business partners in faraway time zones means working very early or very late.
- Exchange rates can be a challenge as having to do business in foreign currencies can lead to less predictable costs.
How To Choose Between Outsourcing and Offshoring?
To choose between outsourcing and offshoring, you will need to consider several factors. These factors will include: cost comparison, risk profile, logistics, legal restrictions, and access to skilled labor. Additionally, you should consider whether the objective is to access specialized skills or a larger labor force. While both outsourcing and offshoring can be used to achieve either, outsourcing is usually used for accessing specialized skills. Offshoring is more commonly used to access a larger labor market.
What Are the Similarities Between Outsourcing and Offshoring?
Outsourcing and offshoring are strategies used by businesses to achieve similar goals. They are both used to drive down costs and gain access to a wider talent pool. However, that is where the similarity ends as both strategies use very different methods to achieve their goals. Offshoring involves a company setting up its site in a faraway country to gain low-cost labor, whereas outsourcing relies on using other companies to provide a lower-cost product or service by either obtaining low-cost labor or using a lower-cost process. There is a strategy in which these two methods are combined, referred to as offshore outsourcing.
How Do Outsourcing and Offshoring Differ in Terms of Industry Suitability?
Although both outsourcing and offshoring can benefit a range of industries, offshoring is more often used for the manufacturing of goods, whereas outsourcing is more often used for services. While the outsourcing industry is used more for finance, healthcare, and insurance sectors, offshoring is used more by sectors that manufacture goods such as: retail, automotive, and engineering.
How Do Outsourcing and Offshoring Affect the Economy?
Outsourcing is regarded as a positive for the free market because it allows smaller companies to afford production that can compete with established companies. This is considered to drive growth and competition. Offshoring is often blamed for taking jobs. However, there is broad agreement that offshoring drives the costs of goods and services down. This allows consumers to buy more and delivers more money to stakeholders.
Is Outsourcing Riskier Than Offshoring?
No, outsourcing is not considered to be as risky as offshoring. While both come with their risk profile, risks with offshoring often include: poor communication due to cultural differences, political and or civil unrest affecting business activities, changes in economic policy can harm multinational operations, and the infrastructure is often not as stable. However, outsourcing does not come with these same risks.
Which Is More Costly, Outsourcing or Offshoring?
Generally, outsourcing is considered more costly than offshoring. While the purpose of both is to reduce costs, outsourcing is also centered around taking advantage of specialized skills and is therefore more costly. On the other hand, offshoring is focused on getting access to a larger labor market.
Summary
This article presented outsourcing and offshoring, explained each of them, and discussed their key differences. To learn more about outsourcing and offshoring, contact an Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.