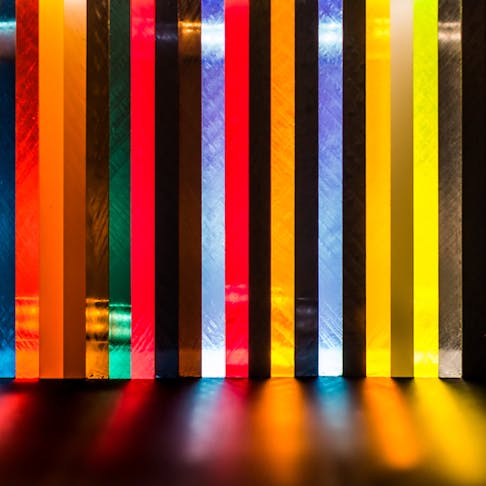
Laser cutting and engraving acrylic refers to a process where a CAD file is used as a guide to accurately cut a design from acrylic material. There are two types of acrylic material that are compatible with laser machines: cast acrylic (GS) and extruded acrylic (XT). Examples of the different types of acrylic sheets that can be cut with laser machines include Plexiglas®, Plaskolite, Perspex®, and Acrylite®.
Cast acrylic refers to acrylic sheets created by pouring liquid acrylic into molds that can be configured into a variety of shapes and sizes. Cast acrylic produces cleaner engraving results, while extruded acrylic yields smoother, flame-polished edges when laser cut.
CO₂ lasers are the best machines for cutting and engraving acrylics. This is because the CO₂ laser's wavelength (9.6 to 10.6 µm) is readily absorbed by acrylics, causing the plastic material to vaporize where the laser hits it. It can even cut through clear acrylics. The optimal power, speed, airflow, and focal length of the laser machine will differ on a case-by-case basis. Settings will depend on the type of acrylic and the material thickness.
This article will discuss the steps in laser cutting and engraving extruded and cast acrylic. It will also present recommended machine settings, tips for successful cutting and engraving, and alternatives to cast or extruded acrylic for CO₂ laser processing.
How to Laser Cut and Engrave Extruded Acrylic
Extruded acrylics are less suitable for engraving than cast acrylics because they tend to melt and produce less-defined engravings, but they can still be engraved at lower power settings if necessary. Extruded acrylic materials are better suited for the fabrication of parts and shapes by CO₂ laser cutting.
The steps in laser cutting extruded acrylic are:
- Create the vector design. Vector files specify the points, curves, lines, and shapes that must be followed by the laser beam making the cut. A good vector design is a prerequisite for all laser-cutting procedures and has a direct impact on the quality of the finished item.
- Carefully plan the cutting sequence when cutting many components from a single sheet of acrylic. To prevent overheating, ample cooling time between each cut made in a segmented area is needed.
- Properly fix the material on the worktable by elevating the material so that it is not in contact with the cutting table for optimal results. Lift the acrylic panel by using Epilog’s pin table or another type of support. This reduces backside reflection and grid markings on the material after cutting.
- Set the recommended initial values for critical laser cutter parameters such as power, speed, cutting frequency, and airflow. It’s also important to select the right lens, air nozzle, and set the focal point correctly before adjusting the laser settings. Cutting acrylic is best accomplished with high power and a relatively slow speed. For cutting acrylics, recommended pulse frequencies typically range from 5,000 to 20,000 Hz, regardless of whether the material is cast (GS) or extruded (XT); however, extruded acrylic often benefits from lower frequencies to reduce melting.
- Some refinement of the laser cutting parameters for your specific application may be necessary. It may be necessary to alter the cutting speed, laser frequency, and focal point to improve edge quality.
- Once your setup and calibration runs are complete, you can start using your production material to make perfect customer parts with optically clear edges.
How to Laser Cut and Engrave Cast Acrylic
Cast acrylics are best suited for laser engraving. The basic steps required to laser engrave cast acrylic are listed below:
- The laser engraver requires a vector design file to guide the engraving of the desired shape onto the work material. However, the design should still have minimal anchor points to ensure that the cutting process is uniform.
- The cutting sequence should be planned precisely to ensure that the laser engraving process is efficient and runs smoothly.
- Acrylics engrave nicely with low power and high speed. The desired designs can be produced with a relatively low-power laser. If the power is too high, some deformation in the material may occur.
- Do a test run of the engraving settings before doing the final piece. This ensures that all parameters are accurately set up to meet customer requirements for dimensions and aesthetics.
- Complete the final etching step.
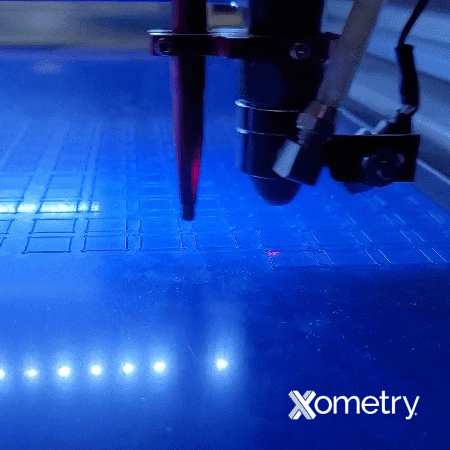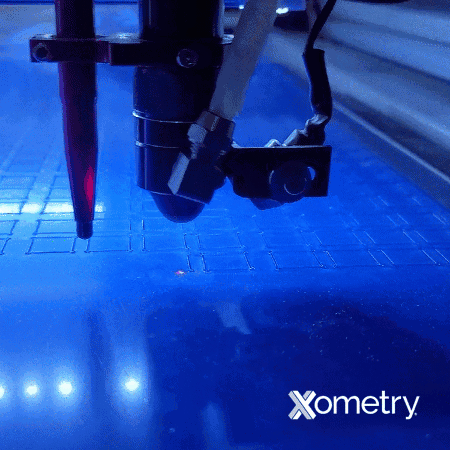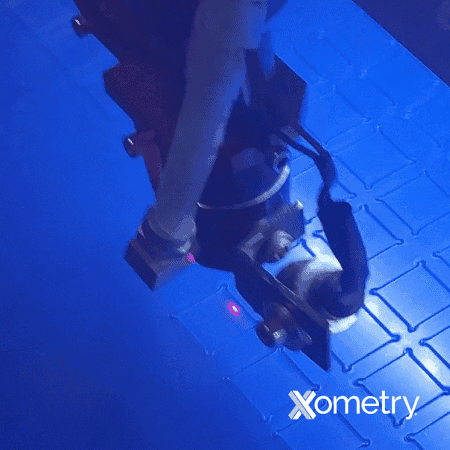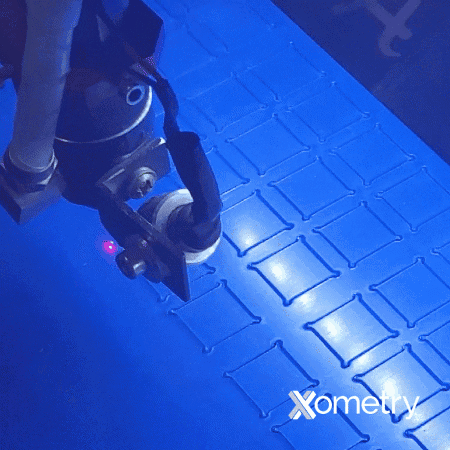
What Are the Differences Between General Cutting Parts and Presentation Part Cutting for Acrylic?
“General cutting” parts are parts that don’t require a cosmetic finish. The aesthetic details of these parts are not the top priority. The type of cut used to produce general cutting parts is sometimes informally called a separation cut. In this case, you want to operate at the highest speed and power possible when cutting the acrylics with the laser.
Presentation parts, on the other hand, refer to parts that should have polished edges for presentation purposes. Here, cast acrylic will yield better cutting results than extruded acrylic; however, both materials operate on the same principle. This type of cut is termed a quality cut, and as the name suggests, the cut quality is very important for superior aesthetics.
What Is the Fastest Acrylic Laser Cutting Speed for Presentation Parts?
The cutting speed for presentation parts is dependent on the desired cut quality, the power of the cutting machine, and the thickness of the material. For quality cuts, a lower cutting speed is required to ensure that the cut has no burrs, is flat, and is perpendicular.
There is a direct relationship between cutting speed and laser power: a higher-power laser can cut the same material thickness at a faster speed. As a general rule, presentation cuts require high power and low speed to produce smooth, polished edges. However, if too low a speed is used, the cut part might not be dimensionally accurate due to too much material being cut away by the heat.
One of the advantages of extruded acrylic for laser cutting is that it softens more readily under heat than cast acrylic, so it can often be cut at slightly lower power settings.
What Is the Best Laser Power for Acrylic Laser Cutting With General Parts?
The best laser cutting power level to use for general part cutting of acrylics (separation cutting) varies depending on the thickness of the material and the type of acrylic, whether extruded or cast. For general-purpose cuts, the user can, within the range of the manufacturer's recommended settings, choose to either maximize speed (using the minimum power that will cut through the full material thickness) or to minimize power level, slowing the speed to a rate that makes the cut possible.
What Is the Best Laser Power For Acrylic Laser Cutting With Presentation Parts?
The best laser power for presentation parts is dependent on the thickness of the part being cut. For quality cuts, use higher power and lower speed to produce smooth, polished edges.
Does the Type of Acrylic Affect the Speed and Power Required for Laser Cutting?
Yes, the type of acrylic being cut affects the required laser speed and power settings. Cast acrylic requires more power to cut a given material thickness because it has a higher melting point than extruded acrylic. The cutting speed, on the other hand, must be selected based upon the laser power level, the quality requirements for the cut, and the thickness of the work material.
How Does Acrylic Sheet Thickness Affect Laser Cutter Power Requirements?
The thicker the acrylic sheet, the higher the power requirement. The thickness of the sheet that needs to be cut has a significant impact on the amount of laser power needed to cut acrylic. As a general guideline, CO₂ laser systems typically require 8-15 W of power per millimeter of acrylic thickness, depending on cut quality expectations, beam focus, and airflow. Lower power levels can be used, as long as the cut speed is slowed down to allow enough energy input to melt and cut the material. However, if the power is just too low for even a slower speed to compensate for the low power, then the cut quality may be insufficient for the application.
What Is the Best Setting for Laser Cutting Acrylic?
Laser cutter settings should use the machine manufacturer's recommendations as a starting point. The final settings will depend on material thickness, the type of acrylic being cut, and part appearance requirements. Meeting the customer's requirements efficiently and economically may drive adjustments to laser power level, cutting speed, frequency, and focal point size.
Listed below are some recommended starting point settings:
- Power: Approximately 10 W of laser power is required to cut each millimeter of acrylic material. Higher continuous power and stable beam quality, rather than peak power alone, determine cutting efficiency and edge quality in CO₂ laser acrylic cutting.
- Frequency: The most appropriate laser frequency value will vary based on the material and the type of cut you're trying to produce. For flame-polished edges, higher pulse frequencies (typically 10-20 kHz) can improve smoothness, whereas lower frequencies help reduce heat buildup on extruded acrylic. Exact values vary by machine.
- Speed: The laser cutting thickness and speed settings in Tables 1 and 2 below show the maximum speed and optimal speed for different laser power and material thickness:
| Power (W) | 3mm | 5mm | 8amm | 10mm | 15mm | 20mm | 25mm | 30mm | 35mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Power (W) 25 | 3mm 8 | 5mm 4 | 8amm 1 | 10mm — | 15mm — | 20mm — | 25mm — | 30mm — | 35mm — |
Power (W) 40 | 3mm 15 | 5mm 8 | 8amm 4 | 10mm 3 | 15mm — | 20mm — | 25mm — | 30mm — | 35mm — |
Power (W) 60 | 3mm 20 | 5mm 10 | 8amm 5 | 10mm 4 | 15mm 2 | 20mm — | 25mm — | 30mm — | 35mm — |
Power (W) 80 | 3mm 25 | 5mm 12 | 8amm 9 | 10mm 6 | 15mm 3 | 20mm 1.5 | 25mm 0.5 | 30mm — | 35mm — |
Power (W) 100 | 3mm 30 | 5mm 15 | 8amm 10 | 10mm 7 | 15mm 4 | 20mm 2 | 25mm 0.8 | 30mm 0.3 | 35mm — |
Power (W) 130 | 3mm 35 | 5mm 17 | 8amm 12 | 10mm 8 | 15mm 5 | 20mm 3 | 25mm 1 | 30mm 0.5 | 35mm 0.2 |
Power (W) 150 | 3mm 40 | 5mm 21 | 8amm 15 | 10mm 11 | 15mm 7 | 20mm 4 | 25mm 1.8 | 30mm 0.8 | 35mm 0.4 |
Power (W) 180 | 3mm 45 | 5mm 25 | 8amm 18 | 10mm 16 | 15mm 9 | 20mm 5 | 25mm 2.5 | 30mm 1.3 | 35mm 0.6 |
Power (W) 200 | 3mm 55 | 5mm 30 | 8amm 25 | 10mm 20 | 15mm 11 | 20mm 7 | 25mm 5 | 30mm 3 | 35mm 1 |
Table Credit: https://artizono.com/
| Power (W) | 3mm | 5mm | 8mm | 10mm | 15mm | 20mm | 25mm | 30mm | 35mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Power (W) 25 | 3mm 5 | 5mm 2 | 8mm — | 10mm — | 15mm — | 20mm — | 25mm — | 30mm — | 35mm — |
Power (W) 40 | 3mm 10 | 5mm 5 | 8mm 2 | 10mm — | 15mm — | 20mm — | 25mm — | 30mm — | 35mm — |
Power (W) 60 | 3mm 15 | 5mm 7 | 8mm 3 | 10mm 2 | 15mm 0.8 | 20mm 0.3 | 25mm — | 30mm — | 35mm — |
Power (W) 80 | 3mm 20 | 5mm 8 | 8mm 5 | 10mm 3 | 15mm 1.5 | 20mm 0.5 | 25mm 0.2 | 30mm — | 35mm — |
Power (W) 100 | 3mm 25 | 5mm 10 | 8mm 6 | 10mm 4 | 15mm 2 | 20mm 0.7 | 25mm 0.3 | 30mm — | 35mm — |
Power (W) 130 | 3mm 30 | 5mm 12 | 8mm 8 | 10mm 5 | 15mm 3 | 20mm 1 | 25mm 0.4 | 30mm 0.3 | 35mm — |
Power (W) 150 | 3mm 35 | 5mm 15 | 8mm 10 | 10mm 7 | 15mm 4 | 20mm 1.5 | 25mm 0.8 | 30mm 0.5 | 35mm 0.1 |
Power (W) 180 | 3mm 40 | 5mm 18 | 8mm 12 | 10mm 10 | 15mm 6 | 20mm 2 | 25mm 1.2 | 30mm 0.8 | 35mm 0.3 |
Power (W) 200 | 3mm 45 | 5mm 25 | 8mm 15 | 10mm 13 | 15mm 8 | 20mm 4 | 25mm 3 | 30mm 1.5 | 35mm 0.7 |
Table Credit: https://artizono.com/
- Nozzle Size and Airflow: Manage airflow onto the material surface to ensure that acrylic is cut smoothly. Use moderate air assist to remove debris and prevent flare-ups, but avoid excessive pressure that can cause frosting or edge haze. Recommended air-assist pressure for acrylic is typically 0.2-1.0 bar, depending on laser power and setup.
- Focal Point: For thicker acrylics (typically above 6 mm), offset the focus slightly below the top surface, often around one-third to halfway through the material thickness, to maintain vertical edges and full-depth penetration. This will improve the perpendicularity of the cut edge.
What Are the Acrylic Projects for Laser Cutting?
Laser-cut and laser-engraved acrylic materials can be used for a wide range of projects. Here are a few examples of industrial laser-cut/engraved applications:
- Advertising: LED wall-mount logos, indoor and outdoor signs
- Building Materials: Transparent panels, balustrades, signage, and decorative glazing, but not structural stairways or load-bearing balconies
- Automotive: Interior panels, light diffusers, and decorative trim elements, but not windshields or headlamp covers, which are typically made from laminated glass or polycarbonate, not acrylic
- Household Merchandise: Fish tanks, chandeliers, drawer separators, cutlery, baking and cooking tools, food containers, coasters, storage bins, and organizers are some examples of household items made from acrylics
- Awards: Trophies and plaques
- Architecture: Models of buildings
- Jewelry: Earrings/buttons/pendants
- Packaging: Containers/boxes
- Toys: Puzzles and mazes
- Personalized Items: Flashy business cards, bookmarks, table numbers, wall art, and stationery
What Are the Alternatives to Acrylic for Laser Cutting?
There are several alternatives to acrylic for laser cutting. Other plastics that can be laser cut include:
- Delrin®
- Polycarbonate
- Mylar
- Polyimide
- Fluoropolymers*
*Effective fume extraction and filtration systems are required to safely remove the gases produced during laser cutting of fluoropolymers.
Frequently Asked Questions About Extruded and Cast Acrylic
What Are the Common Mistakes Made When Laser Cutting Acrylic?
The following is a list of some of the common mistakes made when laser cutting acrylic:
- Using the incorrect settings for acrylic type. The settings of the laser need to be adjusted depending on the type of acrylic and the desired edge finish.
- The lens of the laser cutter plays a big role in determining the accuracy of the cuts, and should be selected accordingly.
- Incorrect spacing of cuts. It’s very easy not to leave enough space between cut paths. This can lead to the design not being cut accurately.
What Are the Beginner Tips for Laser Engraving Acrylic Sheet (Plexiglass®)?
The following list shares some beginner tips for laser engraving of Plexiglass® sheets:
- Remove the protective paper covering on the side you want to engrave, but leave the other side in place to protect against bumps and scratches.
- Make sure you understand the best settings for the type of acrylic you are using.
- Engrave the back side of the acrylic sheet for a see-through effect, but remember to mirror your desired image.
- Change your settings to engrave from the bottom upwards. This avoids some of the debris being blown over sections that have already been engraved.
Which Laser Cutter Is Best for Acrylic Laser Cutting?
The best laser cutter for acrylic processing is a CO₂ laser (typically 10.6 µm wavelength), but medium-power systems (40–150 W) are generally sufficient for sheet cutting, while higher powers are used for thicker stock or production speed. Laser light wavelengths between 9 and 11 µm are readily absorbed by acrylics, causing the plastic material to melt or vaporize. As a result, CO₂ lasers can even cut through clear acrylic sheets.
The light from a diode laser, on the other hand, will travel through clear acrylic without significantly altering the acrylic workpiece. A low-power diode laser machine can, however, be used to engrave acrylic, and it can even provide good cutting results after several passes. Fiber lasers are not suitable for cutting or engraving standard acrylic (PMMA) because their short wavelength (~1.06 µm) passes through the material with minimal absorption.
The following is a list of currently available laser cutters that can produce high-quality results with acrylic, depending on the laser strength, performance, and material capacity:
- OMTech AF2028-60
- Glowforge Pro
- Full Spectrum Laser Muse Core
Why Is Plexiglass® Better for Acrylic Laser Cutting?
Some plastics, like Plexiglas®, lend themselves more easily to laser cutting than others. The best results are obtained with acrylic (PMMA) materials such as Plexiglas®, not polypropylene, since polypropylene tends to melt and produce rough or burnt edges when laser cut. This is because it can generate cuts with smooth edges without any scorch marks.
Summary
This article presented extruded and cast acrylic, explained what they are, and discussed how to laser cut each of them. To learn more about extruded and cast acrylic, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including sheet cutting and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Copyright and Trademark Notices
- PLEXIGLAS® and ACRYLITE® are registered trademarks of Röhm, the company owned by the German inventor of PLEXIGLAS®, Otto Röhm.
- OPTIX®, FABBACK®, DURAPLEX®, and VIVAK® are registered trademarks of Plaskolite, LLC.
- PERSPEX® is a trademark of PERSPEX INTERNATIONAL LIMITED.
- OMETCH® is a registered trademark of Yabin ZHAO.
- Glowforge® is a registered trademark of Glowforge Inc.
- FULL SPECTRUM LASER® is a registered trademark owned by FULL SPECTRUM, LLC.
- DELRIN® is a registered trademark owned by DuPont Polymers, Inc.
- Mylar® is a registered trademark of the DuPont - Teijin Corporation.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


