Laser cutting is a highly efficient and versatile technology that has revolutionized the automotive industry. It offers a range of benefits that have led to its widespread use. Laser cutters are used in a variety of applications in the automotive industry, including cutting plastic parts, fabricating metal components, and marking and engraving parts for identification and branding. This makes the automotive industry more efficient and cost-effective.
This article highlights the five benefits of using laser cutting in the automotive industry. These benefits include: precision and clean cuts, versatility in cutting a wide range of materials, compactness, fast processing, high-quality results, and the ability to engrave materials in a single operation.
1. Laser Cutting Produces Clean, Precise Cuts
Laser cutters use a high-density heat source for cutting, which results in precise and clean cuts. CO₂ lasers typically operate at a wavelength of 10.6 microns (10,600 nm), not 10,000 nm. Precision cutting occurs when the metal absorbs laser energy, causing rapid localized melting that enables clean and accurate cuts. The beam parameter product (BPP) is also used to assess the laser beam quality. The Beam Parameter Product (BPP) for CO₂ lasers is typically measured in mm·mrad, not mm. Values usually range from 2.5 to 4 mm·mrad for industrial CO₂ lasers. This, along with the intensely concentrated heat, accounts for the cut’s near-perfect quality and the method's widespread use in the automotive industry.
Laser cutters are particularly ideal for cutting and sealing airbags. They are frequently used for cutting and sealing airbag materials due to their non-contact operation and precision. The laser cutter’s powerful and precisely focused heat is the primary advantage in sealing airbags.
2. Laser Cutting Is Incredibly Versatile and Can Cut a Wide Range of Materials
Laser cutters move precisely to cut the outlines that have been programmed into the laser cutting machine since their cutting heads are CNC-controlled. This is an extremely useful technology for the automobile sector because it enables the consistent production of complex components with minimal manual intervention. This also gives this technology the advantage of being versatile in design flexibility and complexity.
Lasers can process a broad range of automotive materials, supporting complex geometries and multi-material assemblies. Laser-processed components can be found throughout both the exterior and interior of modern vehicles, particularly in body panels, fabrics, and trim elements. Today, lasers are widely used throughout many stages of automotive production, from prototyping and component fabrication to marking and quality assurance.
3. Laser Cutting Machines Are Extremely Compact When Compared to Other Tools
The compactness of laser cutters is a key factor in their widespread use and popularity in the automotive industry. The use of the laser cutting machine becomes a crucial output-to-space efficiency for vehicle manufacturers because it is relatively small in comparison to its throughput.
The compact nature of laser cutters allows for easy integration into a manufacturing line. The machines take up minimal space and free up valuable floor space for other equipment. Smaller laser systems are available for prototyping or trimming non-metal components, while industrial laser cutters used in automotive production typically require dedicated floor space and support systems.
4. Laser Cutting Machines Process Quickly and Produce High-Quality Results
Laser cutters are known for their rapid processing speed, making them well-suited for high-throughput automotive production. They are known for their fast operation and ability to maintain tight tolerances across repeated parts. These advantages make laser cutters ideal for streamlining automotive part fabrication—from prototyping and development to full-scale production.
In automotive production, lasers are often combined with robotic arms or multi-axis systems to cut or trim complex 3D-formed components, especially in body-in-white and trim applications. In certain circumstances, a robot will pick up a part, present it to a stationary processing head, and manipulate it as necessary to finish the cut. Alternatively, the laser might be installed on a robot arm to guide the beam around the part's 3-dimensional contours.
Combining these two techniques allows for a wide range of processes. It manages the workpiece and the laser head to carry out numerous cutting operations as effectively as possible. Multiple laser processes can often be carried out within a single robot cell, speeding up production and reducing cycle times.
Lasers aren't just used in mass production, however. They are also being used in high-end, custom car manufacture, where throughput is low and some tasks are still done by hand. Here, the goal is to increase processing quality, repeatability, and dependability rather than to scale up or speed up production. This will lower rejection rates and reduce the waste of expensive materials. This capability makes laser cutters ideal for both small-scale and large-batch productions.
5. Laser Cutting Machines Can Engrave Materials in a Single Operation
While laser marking systems have higher upfront costs, they are often more cost-effective over time due to minimal maintenance and the absence of consumables like inks. In most situations, laser marking creates a durable and indelible mark on the material surface. Hot stamping provides durability and high-quality marks, but at the sacrifice of flexibility because each mark needs a different die. Contrarily, laser marking is quick, flexible, and adaptable. The information and visuals to be marked can be quickly modified without the need for tool modifications or downtime. For more information, see our guide on Laser Engraving.
Laser cutting stands out for its precision and adaptability. I often rely on it when tight tolerances and clean results are essential.
What Are the Uses of Laser Cutting in the Automotive Industry?
Laser cutters have a wide range of applications in the automotive industry. These include:
- Plastic Parts: While most plastic components like bumpers and dashboards are molded, lasers are used to trim excess material, create mounting features, and process decorative inserts or layered structures. A wide range of plastics, including ABS, acrylic, HDPE, polypropylene, polycarbonate, and TPO, can be used to make automotive components. Plastics can be plain or painted. They can also be integrated with other materials, such as interior pillars covered in fabric and support systems reinforced with carbon or glass fibers. Lasers can be used to trim extra plastic residue from the injection molding process and to cut or drill holes for fixing points, switches, parking sensors, lights, and other components.
- Cutting and Sealing Airbags and Seat Belts: Laser cutters are ideal for shaping airbag materials and simultaneously sealing the cut edges, reducing wear and fraying compared to mechanical methods. Flat-woven airbag materials must be shaped by laser cutting before being stitched together. They are often silicone-coated to achieve the appropriate air permeability. One-piece-woven (OPW) airbags also need to be trimmed, and a laser is the best instrument for the job. Since there is no contact in both situations, handling of the fabric is limited, and the silicone coating is less likely to sustain damage, which could jeopardize the airbag's structural integrity.
- Cutting Synthetic and/or Real Leather: Laser cutters are ideal for cutting leather for car seats.
- Fabric: A car's interior normally consists of a variety of textiles, including upholstery fabric. The kind of fabric and thickness of the cloth will affect the processing speed. However, a more powerful laser will cut at a proportionately faster rate. The majority of synthetic textiles are precisely cut. The edges are sealed to prevent fraying during later stitching and seat assembly.
- Metal Parts: Laser cutters are commonly used to cut sheet metal components such as doors, hoods, body panels, and brackets. They are less commonly used for dense engine components, which are typically machined or forged.
For more information, see our guide on Uses of Laser Cutting.
What Is the Type of Laser Cutting Used in the Automotive Industry?
For laser cutting applications in the automotive industry, the two primary types of lasers are CO₂ and fiber lasers. These lasers offer the right balance of speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness for automotive production processes. CO₂ laser cutters are used for cutting non-metallic materials such as plastic, rubber, and fabrics. These machines are also very versatile and can be used to cut intricate shapes and patterns. On the other hand, fiber lasers are especially well-suited for cutting metals and select engineered plastics used in automotive assemblies. They are perfect for high-volume production runs due to their speed, accuracy, and efficiency. Compared to other kinds of laser cutters, they are also low maintenance and energy efficient.
Factors that influence the choice of the laser cutter in the automotive industry include the type of material being cut, the production volume, and the required level of accuracy and precision. To satisfy the needs of the sector, the laser cutter must also be capable of cutting the material quickly, precisely, and consistently.
For more information, see our guide on Types of Laser Cutters.
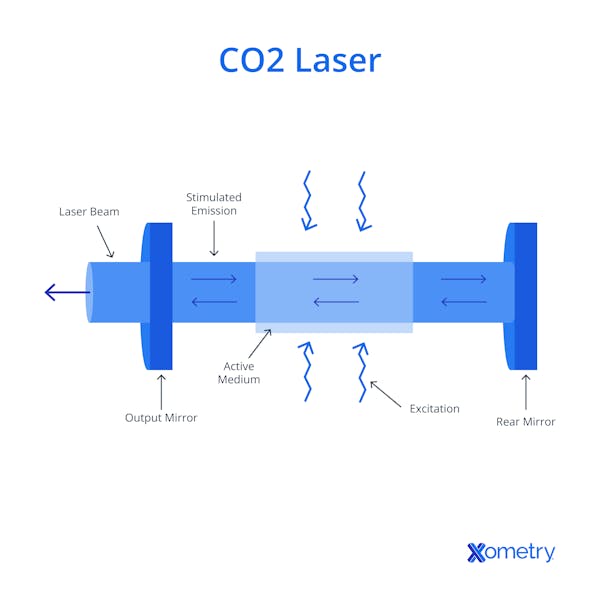
An illustration of a CO2 laser
Frequently Asked Questions About Laser Cutting in Automotive
How Effective Is Laser Cutting in the Automotive Industry?
Laser cutters have proven highly effective in improving quality and reducing rework in sheet metal and non-metal trimming applications. Laser cutters support rapid turnaround across many material types, helping to meet tight automotive production schedules. This leads to improved production times and lower costs. They also offer greater accuracy and consistency than traditional cutting methods, which can reduce the number of errors and defects in the final product. The use of laser cutters can also help to minimize material waste, as precise cuts allow for the efficient use of raw materials.
Is Laser Cutting the Best Choice for Cutting Materials in the Automotive Industry?
Laser cutting is one of the most effective cutting technologies for many automotive applications, particularly for sheet metal and non-metallic components that require precision and flexibility. Laser cutting offers excellent accuracy and production speed, particularly for mid-volume or variable production where flexibility is critical. They are also safer than mechanical cutting methods, provided proper enclosure and fume extraction systems are used. Laser cutters are also compact, resulting in high output-to-space efficiency.
Summary
This article the benefits of laser cutting in the automotive industry, explained what they are, and discussed each of them in detail. To learn more about laser cutting benefits in various industries, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including sheet cutting and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


