Laser beam quality is a critical parameter in any laser device. The M2 factor is a dimensionless value assigned to different laser beams used to identify beam quality in a quantitative way. It is calculated using the waist width and divergence of a laser beam. The higher the M2 value, the worse the beam quality. The ideal M2 value is 1, which is the value for a Gaussian beam that has a bell-shaped peak along its central optical axis. However, the Gaussian beam is a theoretical idealized beam that is not achievable in reality.
What Is the M2 Factor of a Laser?
The M2 factor is defined by how tightly a laser beam’s waist can be focused. A laser with an M2 factor of 1 is considered a perfect Gaussian TEM00 beam. A Gaussian beam is an ideal conical-shaped beam. This isn't possible from actual devices, though, so the goal is to get as close to that value as possible. Power intensity per unit area of a beam is usually more widely distributed, so the beam can’t reach perfect performance.
What Is the Another Term for M2 Factor?
The M2 factor is also known as the beam propagation factor, beam propagation ratio, or beam quality factor. All terms refer to the same dimensionless number that gives a quantitative indication of the quality of a laser beam.
How Does M2 Factor Work?
The M2 factor works by measuring the waist width and divergence angle of a laser. These parameters are then used to determine the M2 factor using the equation detailed later in this article. By identifying the M2 factor of the laser, one can estimate how well its power output is applied to the target. The higher the M2 value the worse the beam quality.
What Is the Importance of the M2 Factor in Laser Cutting?
The M2 factor is important in every laser device as it determines the beam's quality in terms of focusability. Applications such as: welding, cutting, printing, and drilling require high-quality beams to produce deep welds, cut thicker metals, and reduce power consumption. Two beams with the same power output but different M2 factors will produce different results. This is because the M2 factor is a measurement of the spatial intensity of the beam. For more information, see our guide on What Are Laser Cutters?
Is the M2 Factor Important in Laser Welding?
Yes, the M2 factor is important in laser welding. Most manufacturers use a low M2 valve as a selling point. The lower the beam's M2 factor, the greater the effective output power density for a given input power. High M2 values will thus make laser welding more efficient. A low M2 will also reduce the heat-affected zone around the weld, preventing damage to the material. For more information, see our guide on How Laser Welding Works.
How Do You Determine the M2 Factor of a Laser?
The International Organisation for Standardization (ISO) made ISO 11146 to define how to properly measure an M2 factor. The main steps to calculating the M2 factor are:
- Create a collimated beam.
- Use an aberration-free lens to focus the laser.
- Measure the diameter of the beam at various focal points.
- Find the best line of fit for the data points using a regression for a hyperbola.
- Extract values for theta and w0.
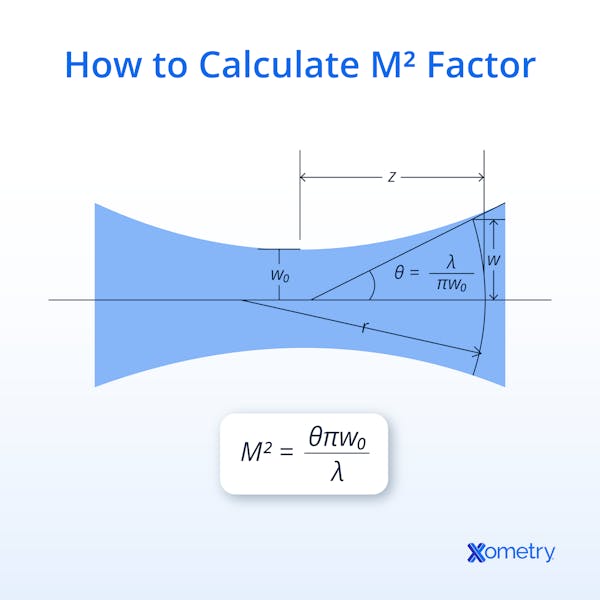
The M2 factor is calculated using the divergence (Theta) and waist width (w0). The divergence is the angle at which the laser diameter widens as it moves further away from the emission orifice. The waist width is the narrowest point of the laser’s beam. The formula used to calculate M2 is as follows:
M2 =(Θ*𝜋*w0)/𝜆
Where:
𝜋 = 3.14
Θ = Divergence angle
𝜆 = wavelength
W0 = Waist width
What Is the Perfect M2 Factor Measurement in a Laser?
The perfect M2 factor for a laser is 1. Any beam with an M2 of 1 would be considered a pure Gaussian TEM00 beam. Laser beams can be defined using four parameters: waist width, divergence, wavelength, and power. However, using all of these factors makes it hard to compare one laser beam to another. The formula for M2 includes both the waist width and divergence to compare how closely the beam approximates a pure TEM00 beam.
How Does M2 Factor Affect Laser Beam Quality?
The M2 factor of a laser identifies the laser beam quality by quantifying the relative similarity of the laser beam in question to a Gaussian beam. Higher M2 factors equate to more divergence and thus more power loss.
How Does a High M2 Factor Affect Laser Beam Divergence and Focusability?
The lower the M2 value, the better the laser beam’s focus. This results in more efficient use of power for that laser. A low value indicates that either the beam is minimally divergent or has a very narrow waist width (or, more likely, both). The M2 factor itself does not affect divergence or focusability — the laser’s divergence and focus determine the M2 factor.
Does M2 Factor Affect the Power and Speed of the Laser?
No, the M2 factor does not have an effect on the power and speed but it does indicate the power density. While the M2 factor has no bearing on the power produced, it describes how tightly the power is concentrated when the laser hits its target. A lower M2 factor is indicative of a low divergence angle which means all of the laser’s power output is focused where it is intended to be.
Does the M2 Factor Vary Depending on the Type of Laser Used?
Yes, the M2 factor will vary depending on the type of laser used. Some types can achieve an M2 factor of less than 1.1, others range between 1.1 and 2, and some have very poor beam quality at around 3 to 4.
What Are Some Examples of M2 Factor Values for Laser Beams?
The ideal M2 value of a laser beam is 1, but this is only achievable in theory. Some examples of real values are listed below:
- Helium-neon lasers have a value of less than 1.1.
- Ion lasers fall between 1.1 and 1.3.
- Collimated TEM00 diode lasers can have an M2 factor between 1.1 and 1.7.
- Higher-energy multimode lasers can have an M2 factor of 3 or even 4, which is not desirable.
Summary
This article presented M2 factor, explained it, and discussed how its calculated for laser cutting. To learn more about M2 factor, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including sheet cutting and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.

