Selecting the correct manufacturing method for a new product can be challenging. CNC machining and plastic injection molding are both widely used and cost-effective, but they differ completely in how parts are made. CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece to create the final part shape. Plastic injection molding injects molten plastic into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the final part shape. The key differences between the two methods lie in the range of materials they can process, the achievable production volumes, and the attainable tolerances and precision.
These differences also affect the overall manufacturing cost of each process. In this article, we discuss everything there is to know about CNC machining vs. plastic injection molding, including the advantages and disadvantages of each, and process alternatives to both.
CNC Machining Definition and Comparison to Plastic Injection Molding
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses equipment such as mills, lathes, drill presses, and saws to create highly precise parts. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) data is developed during the product design phase. This CAD data is then used as the basis for programming and optimizing the machine tool sequences and paths. The material is then cut using tools such as end mills and drill bits to form the desired part geometry. Auxiliary machinery, such as honing, hobbing, or grinding machines, may also be required to produce parts to customer specifications.
Manual machining dates back several centuries, but the concept of numerical control emerged in the late 1940s with early servo-controlled machines. Early numerical-control machines used punched tape or cards to encode coordinate commands for tool motion. In 1949, MIT developed the first experimental three-axis numerically controlled milling machine for the U.S. Air Force, intended for the precise machining of aircraft components such as rotor blades and structural skins. In the 1970s, CAD and CAM software began to be integrated into CNC systems. Now, CNC machining is one of the most widely used manufacturing methods in the world. It is used to make products for several industries, from automotive to agriculture. CNC machining is often preferred over injection molding because it easily accommodates design changes, achieves tight tolerances, and supports a wide variety of materials.
To learn more, see our guide on What is CNC Machining.

What are the Advantages of CNC Machining Compared to Plastic Injection Molding?
Listed below are some advantages of CNC machining over injection molding:
- Excellent surface finishes and tight tolerances are achievable with CNC machining because cutting parameters and tool geometries can be precisely controlled.
- CNC machining can process metals, plastics, and composites, offering access to a wide range of materials.
- Design modifications are simple, as programs and fixtures can be quickly updated to match new iterations.
- Tooling lead times are shorter since there is no need to manufacture complex molds.
What are the Disadvantages of CNC Machining Compared to Plastic Injection Molding?
Listed below are the disadvantages of CNC machining vs. injection molding:
- Producing large volumes by CNC machining results in a higher cost per part because each piece requires a longer cycle time.
- The process can be labor-intensive, particularly for low-volume or prototype runs where automated loading systems are not used.
Plastic Injection Molding Definition and Comparison to CNC Machining
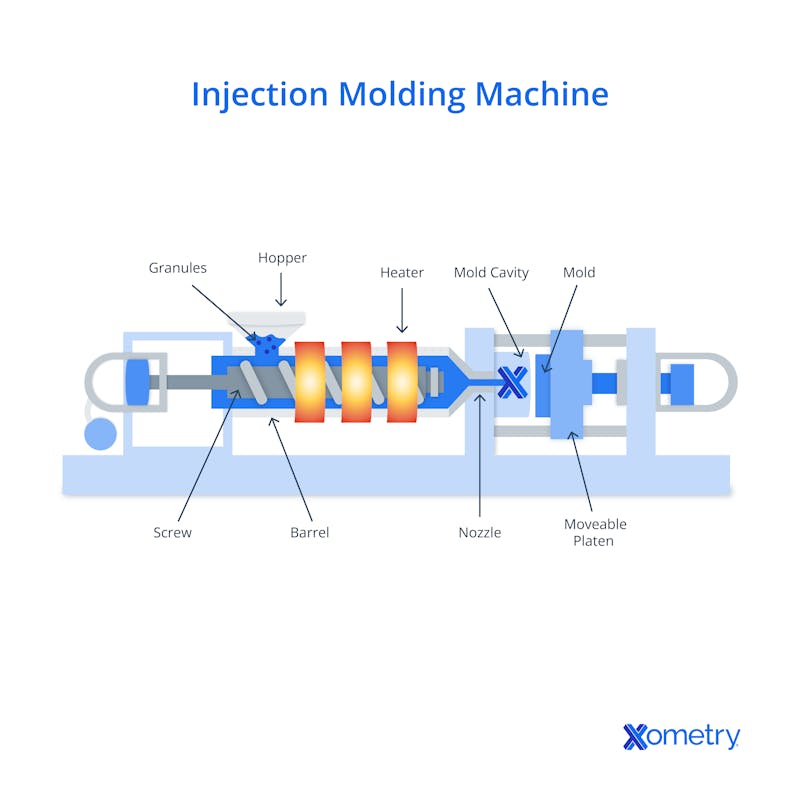
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing method that uses an injection molding machine (IMM) consisting of major components such as an injection unit (screw and barrel), a clamping unit, and a mold. Plastic pellets are fed into the barrel and are melted through the rotation of the screw and heater bands. The molten plastic is injected into the mold and formed into the geometry of the part. The IMM maintains holding pressure after injection to compensate for material shrinkage until the parts have solidified sufficiently to be ejected. The completed parts are ejected, and the cycle restarts.
Brothers Isaiah and John Hyatt developed injection molding in 1872 and used it to mold hair combs, buttons, and other small items. In the 150 years since that first machine, injection molding has blossomed into a multibillion-dollar global industry. Injection molding becomes more cost-effective than CNC machining for high-volume production, whereas CNC machining may be more economical for low-volume or prototype runs.
For more information, see our guide on what is plastic injection molding.
What are the Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding Compared to CNC Machining?
Listed below are the advantages of injection molding vs. CNC machining:
- It can easily produce large volumes of parts in a rapid and repeatable fashion since multiple-cavity molds can create many parts in one injection cycle.
- Injection molding offers one of the lowest per-part costs among manufacturing methods for large production volumes because molds have long service lives, and multi-cavity tools can greatly increase output.
- Minimal post-processing is needed because many parts can be shipped immediately after ejection, depending on the gate type used.
What are the Disadvantages of Plastic Injection Molding Compared to CNC Machining?
Listed below are the disadvantages of injection molding vs. CNC machining:
- It is difficult to accommodate product design changes since rework on complex molds with several plates, cams, and complex geometries can be troublesome.
- Imperfections on the mold surface or issues like venting, temperature imbalance, or contamination can result in surface defects on molded parts.
- A high upfront investment is required for mold fabrication, as multi-cavity molds can cost anywhere from a few thousand to hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Comparison Table Between CNC Machining and Injection Molding
Table 1 compares key attributes and properties of CNC machining and plastic injection molding.
| Attribute | CNC Machining | Plastic Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
Attribute Typical tolerances | CNC Machining +/- 0.001” | Plastic Injection Molding +/- 0.005” |
Attribute Fast per part cycle times | CNC Machining No | Plastic Injection Molding Yes |
Attribute Fast Lead Times for Tooling | CNC Machining Yes | Plastic Injection Molding No |
Attribute Easily make design modifications | CNC Machining Yes | Plastic Injection Molding No |
Attribute Wide range of available materials | CNC Machining Yes | Plastic Injection Molding No |
Attribute High-volume production (>1000 pcs) | CNC Machining No | Plastic Injection Molding Yes |
Attribute Large upfront investment | CNC Machining No | Plastic Injection Molding Yes |
With CNC machining, tighter-tolerance parts can be made from a broader range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, compared to injection molding, which is mainly limited to plastics. Injection molding can produce parts at a much faster rate, often requiring little or no post-processing, which makes it ideal for high-volume production. Injection molding requires a high upfront investment for mold fabrication; however, the cost per part decreases significantly as production volume increases, making the process cost-effective for large-scale runs.
In early-stage product development, I often balance between CNC machining for flexibility and injection molding for scale. Understanding where one process overtakes the other is key to cost-efficient design.
CNC Machining vs. Injection Molding: Lead Cost Comparison
Tooling costs for CNC machining are significantly less than for injection molding. CNC machining costs are associated with the fabrication of fixtures and jigs and the procurement of raw materials and tools. Molds for injection molding can cost from a few thousand dollars for simple single-cavity molds to several hundred thousand dollars for complex, multi-cavity production molds. An injection mold becomes cost-effective when its cost is distributed over a sufficiently large production volume. Assuming the necessary machinery is available and only tooling, such as molds, fixtures, and jigs, must be arranged, upfront costs for CNC machining are lower.
CNC Machining vs. Injection Molding: Speed Comparison
Both CNC machining and injection molding can produce parts relatively quickly, but injection molding achieves much shorter cycle times once tooling is complete. For small-volume runs, CNC machining is often preferred. Injection molding is preferred for larger runs because multiple-cavity molds can rapidly produce parts and reduce per-piece cost. Considering the mold-fabrication lead time, series production typically starts later with injection molding than with CNC machining. Consider using CNC machining for small production runs and injection molding for large runs.
CNC Machining vs. Injection Molding: Volume Comparison
Injection molding can produce far more parts per machine-hour and per dollar invested than CNC machining once production tooling is available. Molds used in injection molding can have multiple cavities, ranging from one to several hundred. Hence, injection molding can quickly produce large numbers of parts. In CNC machining, parts are typically produced sequentially; however, multi-part fixtures or pallet systems can enable limited batch production. While CNC machining is fast at producing parts, injection molding is even faster.
CNC Machining vs. Injection Molding: Materials Comparison
A broader range of materials can be used in CNC machining processes than in injection molding. CNC machining is capable of producing parts from various plastics, as well as metals such as aluminum and steel. Many elastomers and some thermoplastics are too soft or flexible for conventional CNC machining but can be readily molded into parts through injection molding.

Frequently Asked Questions on CNC Machining vs. Plastic Injection Molding
What are the Mutual Alternatives to CNC Machining and Plastic Injection Molding?
Mutual alternatives to CNC machining and plastic injection molding are:
- 3D Printing: With additive manufacturing (3D printing), highly complex geometries can be produced that are often impossible with CNC machining or injection molding. However, not all materials used in machining or molding are available for 3D printing, and mechanical properties may differ.
- Casting: Casting generally offers lower precision than CNC machining or injection molding. In plastic applications, resin casting involves pouring liquid polymer into an unpressurized mold and allowing it to cure chemically or thermally. It is a much more straightforward process than CNC machining or injection molding, but it can take much longer to produce parts. Casting is also not practical for large-scale production.
What are the Similarities between CNC Machining and Plastic Injection Molding?
A notable similarity between CNC machining and plastic injection molding is that both can process some of the same thermoplastics, such as polycarbonate (PC), HDPE, and ABS. However, the material grades and processing behavior differ. Aside from that, there are not many similarities between the two processes.
What are the Other Comparisons for CNC Machining Besides Plastic Injection Molding?
Another alternative to CNC machining is CNC laser cutting:
- CNC Machining vs. CNC Laser Cutting: With CNC laser cutting, a computer-controlled laser moves about a programmed path to cut, engrave, etch, and mark parts. CNC laser cutting can achieve high precision comparable to CNC machining for flat parts; however, it is limited to sheet materials and can only process certain plastics safely due to the risk of toxic fume emissions.
What are the other Comparisons for Plastic Injection Molding besides CNC Machining?
Another alternative to Plastic Injection Molding is:
- Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming: In thermoforming, heated and stretched sheets of plastic are pressed over a one-sided mold to create parts. While thermoforming is slower than injection molding and limited to simpler, single-sided geometries, it remains a cost-effective alternative for large plastic components with moderate precision requirements.
How Xometry Can Help
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including CNC machining, 3D printing, and other services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Get started on your injection molding services or CNC machining quote with us today.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


