When compared to CNC (computer numerical control) mills, CNC routers are a low-cost option that make creating custom parts easy and accessible. These routers have been designed specifically to carve out complex shapes from soft materials like wood, plastic, foam, sift metals, and sometimes even steel. Let’s have a closer look at how a CNC router works, its various components, what it can and can’t do, and which software to use with it.
What is a CNC Router?
A CNC router can be controlled by a computer—it’s like a traditional router with a modern-day upgrade. To control it, the machine’s servo motors are fed a set of instructions in a language they can understand: G-code. The instructions tell the machine exactly how and where to move and, once it has read them, the router gets to work moving a high-speed rotating cutting tool to make the carvings. The process falls under the subtractive manufacturing category as it removes material to make parts, unlike 3D printing, a.k.a. additive manufacturing, which adds layers.
These routers typically have a gantry-style construction (with a horizontal support beam or structure) where the spindle (the main cutting tool) will move in two directions—left and right along the x-axis, and back and forth on the y-axis—to cut or carve material in the right shape and design. Depending on the material you’re working with and the shape you want the CNC router to carve, there are different cutting tools available. These can be manually swapped out, but some of the more advanced models feature an automatic tool changer so you don’t have to physically get involved.
Unlike standard CNC mills, these routers don’t have much range of motion up and down (along the z-axis), so won’t be able to make deeper cuts or holes on tall parts or very thick materials without struggling or making mistakes. They can be used to engrave lettering onto harder materials like granite, though. In general, CNC routers are best for use on flatter and softer materials (think: MDF, plywood, acrylic, and polyurethane foam/sheet), and metals like brass and aluminum.
CNC routers are used a lot in woodworking to make everything from cupboard doors to 3D sculptures. They can create wooden patterns for sand molds used in metal casting and cut foam into custom shapes to be used in packaging. The advertising industry uses CNC routers to engrave custom signs and lettering on wood or plastic for various promotional products.
How Does a CNC Router Work?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) router works by moving a tool to specific x, y, and z coordinates throughout the machine's available working area. A router or high-speed spindle with a cutting tool then removes material at the desired locations. Different cutting tools can be used depending on the material and the feature being machined. These tools can be manually changed or in the case of a more advanced machine, an ATC (Automatic Tool Changer) can swap out tools.
What Controls a CNC Router?
A CNC router is controlled by a set of servo motors. These motors get their position information from a control-circuit board that converts the user-supplied G-code into precise sets of coordinates for material removal, ultimately resulting in a finished part.
Where Is a CNC Router Used?
CNC wood cutting machines are widely used in the woodworking industry to produce functional and ornamental components for fine furniture.
To What Is a CNC Router Comparable?
A CNC router is comparable to a CNC mill. They both move cutting tools to pre-programmed positions to carve out a part from solid material. However, the key difference is that a CNC mill is able to machine harder materials, like steel, as well as wood and plastic while maintaining higher levels of accuracy. CNC routers also have a larger cutting area and are therefore better suited to large plants or plates.
What is the Main Benefit of a CNC Router?
The main benefit of a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) router is its low cost when compared to a CNC mill. Its affordability makes CNC router’s an accessible technology that can easily be purchased by small businesses and has the potential to dramatically improve a company’s overall productivity.
What Software Is Used in a CNC Router?
To operate a CNC router, both CAD (Computer Aided Design) and CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) software packages are required. The CAD software is used to make a 3D model of the desired part. The CAM software converts the CAD model into a set of machine-readable instructions called G-code.
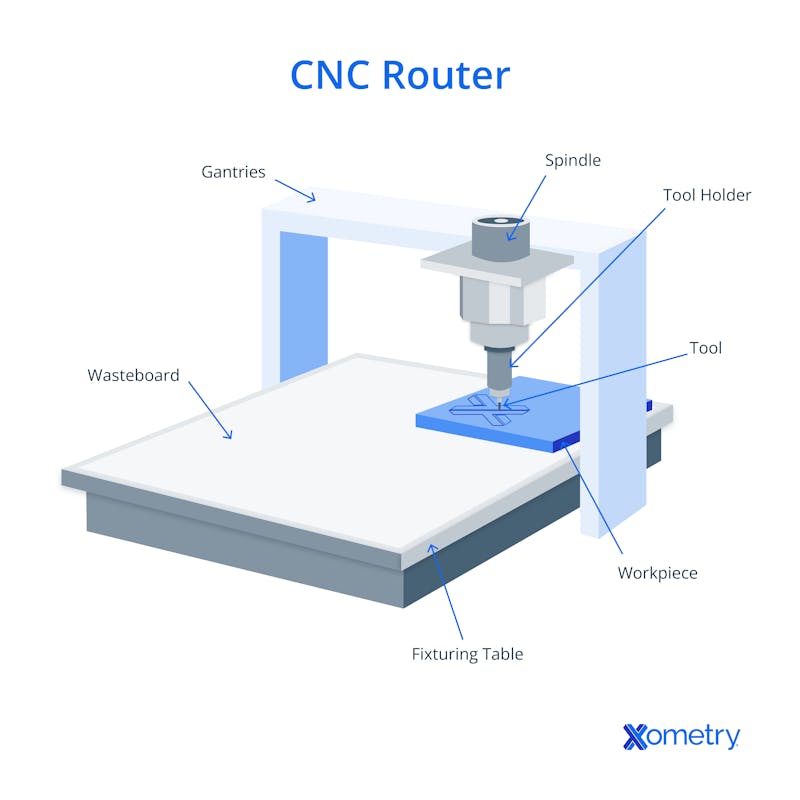
What are the Specific Parts of a CNC Router?
A CNC router machine has four main components that all work together to make the part: the bed, the controller, the motors, and the spindle/router. Below you’ll find a little more information on each of these components.
Bed: This is where you’ll put the material that you want to cut. Some beds have multiple holes or attachment points to make it easier to mount clamping hardware so that the workpiece can stay in place during cutting.
Controller: This part houses all the electronics, including the stepper or servo motors, that control the machine’s speed and how and where it cuts.
Motors: The stepper or servo motors operate each of the three motion axes. Steppers are usually found on cheaper hobbyist routers, whereas servos, which are found on more expensive machines, are used in professional-grade models because they offer more precision. There’s also a separate high-speed motor that rotates the cutting tool.
Spindle/Router: This is what holds and rotates the cutting tool at the set speed. It’s usually mounted on the gantry above the bed and moves as needed along the axes.
The below diagram shows the different parts of a CNC router.
What Materials Can Be Cut on a CNC Router?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) router is primarily limited to cutting non-metallic materials such as MDF (Medium Density Fibreboard), plywood, acrylic, polyurethane foam, and polyethylene sheet. It can also cut softer metals such as brass, aluminum, and in some cases, steel. CNC routers are rarely used to cut harder materials like steel, as the general geometry and construction method of a router makes cutting these types of materials difficult and error-prone. CNC routers can, however, be used to engrave lettering onto harder materials like granite.
Which Industries Make Use of CNC Routers?
CNC routers are a low-cost alternative to CNC mills and are used in a range of industries, some of which are listed below:
- Furniture: CNC routers are used to manufacture a wide range of furniture-related components out of wood or plastic.
- Molding: CNC routers are used to make wooden patterns that are, in turn, used to make sand molds for metal casting. Wooden patterns are low-cost and can be machined quickly on a router.
- Packaging: CNC routers can easily cut foam into custom housings for sensitive or high-value products,
- Advertising: CNC routers can engrave custom lettering for signs and various advertising-related products. These signs can be made from wood or plastic.
Frequently Asked Questions About CNC Routers
Is it Possible To Use a CNC Router in a Carpentry Shop?
Yes, CNC routers are a common feature of most carpentry shops. They have become an indispensable tool for the manufacture of components as simple as cupboard doors and as complex as 3-dimensional artworks.
What Is the Best CNC Router To Buy?
Deciding on which CNC (Computer Numerical Control) router machine is best to buy depends heavily on the type of work that needs to be done as well as the skill level of the operator. For beginners performing small-scale cutting of wood and foam, a Shapeoko is the ideal do-it-yourself CNC router. This model is extensively used in the DIY maker industry and as such, there is a wealth of information available on how to use them optimally. However, if the product mix includes large, industrial-scale components, then a more robust machine is appropriate. The ELECNC 2130, which can automatically load material, change tools and label components, would be an excellent choice. These machines require significant capital investment, so it is important to fully quantify the business case before purchasing such a machine.
What Is the Difference Between a CNC Router and a Spindle?
A spindle is typically the part of a router where the cutting tool is attached. The spindle then rotates the tool at a high rate to allow it to cut a part. In some cases, a CNC router machine has a purpose-built spindle installed whereas for lower-cost machines a standard off-the-shelf router is often installed on the machine's x-axis as a cheaper spindle alternative.
How Xometry Can Help
Need help with CNC routing or any other manufacturing service? Xometry provides a wide range of capabilities including CNC machining, 3D printing, injection molding, laser cutting, and sheet metal fabrication. Get your instant quote — for free and with zero obligation — today.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities including CNC machining, 3D printing, injection molding, laser cutting, and sheet metal fabrication. Get your instant quote today.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


