Titanium alloys are highly significant in modern engineering due to their exceptional blend of properties, including strength, low density, and corrosion resistance. Among these alloys, titanium alloy 6-4 (also called grade 5 or Ti-6Al-4V) stands out as one of the most versatile. It is also the most widely used titanium alloy, making up about 50% of all applications. From use in automotive parts like exhausts and springs to medical components like joint implants, 6Al-4V titanium is used in a broad range of applications across many different industries.
This article will review titanium alloy 6-4, its definition, history, properties, and different applications.
What Is Titanium Alloy 6-4?
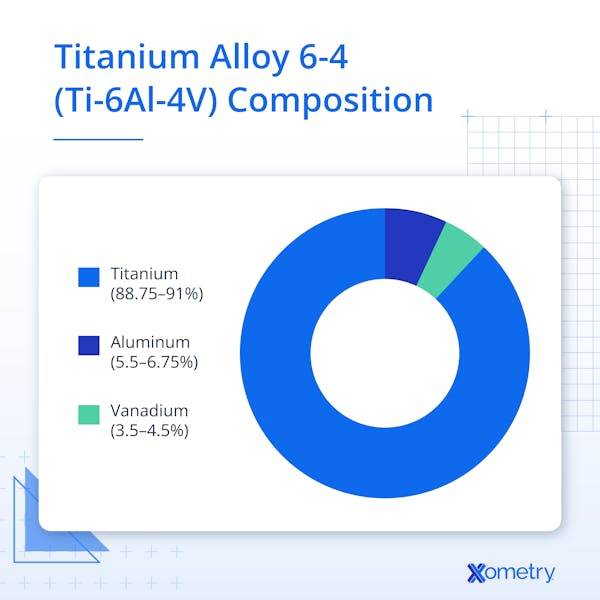
Titanium alloy 6-4, or grade 5 titanium, is often referred to as the workhorse of the titanium industry due to its balanced set of properties. Titanium 6-4, also known as Ti-6Al-4V alloy, is an alpha-beta titanium alloy in which aluminum acts as the alpha stabilizer, and vanadium acts as the beta stabilizer. Ti-6Al-4V composition is 5.5–6.75% aluminum and 3.5–4.5% vanadium, with the remaining percentage being titanium. Titanium alloy 6-4 combines high strength, stiffness, corrosion resistance, and low density, making it useful in aerospace, automotive, and medical applications. Its use in these industries, as well as others, has led to a host of new products that are lighter, more efficient, and safer.
Who Is the Inventor of Titanium Alloy 6-4?
Titanium alloy 6-4 was developed in 1954 at the U.S. Army Watertown Arsenal by Stan Abkowitz, a metallurgist who later became a professor at MIT. It was invented by adding molten aluminum and vanadium to molten pure titanium. The alloy’s first widespread use was for the production of the US military’s U2 high-altitude reconnaissance plane in the 1950s. The invention of the alloy and its use in the production of this aircraft catalyzed the titanium industry. Today, Ti-6Al-4V is the most commonly used titanium alloy in the world.
How Is Ti-6AL-4V Made?
The production of Ti-6Al-4V starts with the Kroll Process. The Kroll process is the most commonly used method to produce commercially pure titanium. In this process, titanium-rich ores such as ilmenite or rutile are chlorinated to form titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), which is a liquid at room temperature. Through a fractional distillation process similar to producing gasoline from crude oil, the TiCl4 liquid is purified. Afterward, magnesium is added to the liquid to produce a sponge-like titanium material and a magnesium-based salt. Next, the sponge is compressed and melted. At this stage, the appropriate ratio of aluminum and vanadium is added to the molten titanium. Once added, the Ti-6Al-4V alloy is cast into ingots and other shapes.
What Are the Properties of Titanium Alloy 6-4?
Titanium alloy 6-4 has many desirable properties that make it great for use in various applications. The different properties of titanium alloy 6-4 are listed below:
1. Low Thermal Conductivity
Titanium 6-4 has a relatively low thermal conductivity of about 6.7 W/mK. This allows it to be used across a broad temperature range without degrading mechanical properties, which is valuable in high-heat applications such as jet engines, landing gear, automotive exhaust systems, and chemical processing equipment.
2. Shear Mechanism
6Al-4V has a shear strength typically reported around 550–760 MPa, which is lower than its tensile strength but comparable to many steels, and higher than aluminum alloys. It is unsuitable for applications in which high shear forces are likely to be applied.
3. High Tensile Strength
Titanium 6-4 has an exceptional tensile strength of 1,170 MPa. Its high tensile strength, combined with a low density of 4.43 g/cm3, makes it ideal where strength and low weight are critical, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and medical applications. For more information, see our guide on Material Tensile Strength.
4. High Modulus of Elasticity
Ti-6Al-4V has an elastic modulus of about 114 GPa, which is lower than steel (~200 GPa) but higher than aluminum (~70 GPa). Its high modulus of elasticity means the material is stiff, rigid, and resistant to deformation. Consequently, the stiffness of 6Al-4V titanium alloy helps to minimize the deformation or bending of critical parts and acts as a vibration damper to reduce the risk of fatigue failure.
What Are the Physical Properties of Titanium Alloy 6-4?
Some physical properties of titanium alloy 6-4 are described in Table 1 below:
| Physical Property | Value |
|---|---|
Physical Property Density | Value 4.43 g/cm3 (0.16 lb/in^3) |
Physical Property Hardness | Value 349 HB (36 HRC) |
Physical Property Melting Temperature | Value 1,604–1,660 °C (2,920–3,020 °F) |
Physical Property Specific Heat Capacity | Value 0.56 J/g°C (0.13 BTU/lb°F) |
Physical Property Thermal Conductivity | Value 6.7 W/mK (46.5 BTU*in/hr-ft2-°F) |
Physical Property Electrical Resistivity | Value 1.71 × 10⁻⁴ Ωcm |
| Mechanical Property | Value |
|---|---|
Mechanical Property Yield Strength | Value 1,100 MPa (160 ksi) if heat-treated |
Mechanical Property Ultimate Tensile Strength | Value 1,170 MPa (170 ksi) if heat-treated |
Mechanical Property Modulus of Elasticity | Value 114 GPa (16,500 ksi) |
Mechanical Property Shear Strength | Value 760 MPa (110 ksi) |
Mechanical Property Shear Modulus | Value 44 GPa (6,380 ksi) |
Mechanical Property Poisson’s Ratio | Value 0.33 |
What Are the Applications of Ti-6Al-4V?
Ti-6Al-4V has many desirable properties that make it preferred for many applications across different industries, such as:
1. Chemical Industry
Corrosion resistance and strength are essential to a properly functioning and safe chemical processing system. Titanium alloy 6-4 has numerous uses within the chemical industry since it exhibits both these properties, reducing maintenance costs and extending the life of chemical equipment. Heat exchangers, reactor vessels, piping systems, and agitators are applications of Ti-6Al-4V in chemical processing, though commercially pure titanium grades (e.g., Grade 2) are more common for corrosive chemical environments.
2. Medical Industry
The medical industry requires parts and components of exceptional quality and tight tolerances for effective, safe, and comfortable use. Due to its biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and high strength, Ti-6Al-4V is widely used in the medical industry for orthopedic and dental implants, surgical instruments, and prostheses.
3. Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is the manufacturing process of creating three-dimensional parts layer-by-layer until the entire object is created. There are many different types of 3D printing; however, each type involves the fusing of subsequent layers to create a rigid part. Each layer of a 3D-printed part is a thin slice of the cross-section of the entire part. Ti-6Al-4V is one of the most widely used alloys in metal additive manufacturing, particularly with powder bed fusion methods such as selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM). It is applied in aerospace, medical, and power generation for both prototypes and production parts.
4. Marine Industry Applications
Two of the most critical material properties in marine applications are corrosion resistance and strength. Ti-6Al-4V alloy is suitable for many marine applications since it has high strength and exhibits great corrosion resistance in seawater. Marine applications of Ti-6Al-4V include seawater piping, heat exchangers, and some propulsion components, though grades with better corrosion resistance (like Ti-6Al-4V ELI or commercially pure titanium) are often preferred.
5. Gas Turbines
Ti-6Al-4V is used in compressor blades, disks, and casings of gas turbines in the aerospace and energy sectors, primarily where moderate temperatures are required. The material is a good choice for these applications due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for a wide operating temperature range. Consequently, titanium 6Al-4V provides reliability, reduced maintenance, and a long-term life for gas turbine assemblies.
6. Firearm Suppressors
Another common use of Ti-6Al-4V (grade 5 titanium) is in firearm suppressors. Ti-6Al-4V is used in firearm suppressors because it is lighter and stronger than stainless steel, although its lower thermal conductivity causes it to retain more heat. The material’s low density and high strength-to-weight ratio mean the weapon will be lighter, but still be able to handle the forces experienced when in use. Additionally, since Ti-6Al-4V has a lower thermal conductivity, the effects of heat are not as severe compared to stainless steel suppressors.
7. Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry is one of the largest users of titanium 6-4 alloys. Low weight and high strength are critical to aircraft performance and efficiency. Ti-6Al-4V is ideal for the aerospace industry due to its lightweight, high strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to be used in a wide operating temperature range. Ti-6Al-4V is used in the aerospace industry for airframe structures, landing gear, and engine compressor components, valued for its strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.
8. Power Generation Industry
The power generation industry is another industry that commonly employs titanium alloy 6-4 in various parts, components, and assemblies. In the power generation industry, materials with high strength and corrosion resistance, as well as materials capable of being used in a wide operating temperature range, are highly desired. Titanium 6-4 checks all three of those boxes. In power generation, Ti-6Al-4V is applied in condenser tubing, heat exchangers, and compressor blades, though commercially pure titanium is often preferred for seawater-facing condenser tubing.
“Ti-6Al-4V shows how carefully balanced alloying can transform a material into the backbone of multiple industries. From aerospace structures to medical implants, I see it as a perfect example of engineering turning raw chemistry into practical performance.”Audrius Zidonis, Principal Engineer at Zidonis EngineeringNote from the Editor
What Are the Advantages of Ti-6Al-4V?
There are many advantages of Ti-6Al-4V alloy that make it valuable across industries, such as:
- It has a high strength-to-weight ratio (tensile strength up to ~1,170 MPa in heat-treated conditions, density 4.43 g/cm3), critical in aerospace, automotive, and other weight-sensitive applications.
- It is corrosion resistant in many environments due to a stable oxide layer, though less so than commercially pure titanium.
- It is biocompatible and widely used in implants, although some studies report low levels of aluminum and vanadium ion release.
- It has good fatigue resistance, which extends service life in demanding applications such as aerospace components, though fatigue strength decreases in corrosive environments.
What Are the Disadvantages of Ti-6Al-4V?
The disadvantages of Ti-6Al-4V are listed and described below:
- Titanium alloys are expensive, and Ti-6Al-4V is no different. The process of refining pure titanium and subsequently producing titanium alloys is extensive and requires advanced processing equipment.
- It is difficult to machine, which increases manufacturing costs. Its low thermal conductivity causes heat to build up at the cutting edge, leading to tool wear.
- Welding Ti-6Al-4V can be challenging and may require specialized equipment and techniques.
- It has relatively poor wear resistance and a tendency to gall under sliding contact, which limits its use in bearing and tribological applications.
- While Ti-6Al-4V is generally corrosion resistant, it is vulnerable to reducing acids such as hydrochloric and sulfuric, as well as high-temperature oxidizing environments. These materials cause the protective oxide layer on the material to break down upon contact.
Frequently Asked Questions About Titanium Alloy 6-4
What Is the Tensile Strength of Ti-6Al-4V?
Ti-6Al-4V has a tensile strength ranging from ~950–1,170 MPa (138–170 ksi), depending on whether it is annealed or heat-treated. The tensile strength of Ti-6Al-4V is determined by conducting a tensile test. In a tensile test, a test specimen is subjected to an increasing tensile load until the specimen ruptures. A stress-strain curve shows the stress applied to the part on the Y-axis and the strain of the part on the X-axis. The stress value at the point of rupture is considered the tensile strength of the material.
What Is the Hardness of Ti-6Al-4V?
Ti-6Al-4V typically has a hardness around 334-349 HB (≈36 HRC) in the annealed state, but can reach higher values (up to ~41 HRC) with heat treatment.
What Is the Density of Ti-6Al-4V?
Ti-6Al-4V has a density of 4.43 g/cm3, roughly half that of stainless steel (≈7.8-8.0 g/cm3).
What Is the Melting Point of Ti-6Al-4V?
Ti-6Al-4V has a melting range of about 1,600–1,660 °C.
How Much Does Ti-6Al-4V Cost?
The cost of Ti-6Al-4V alloy can vary significantly depending on factors such as purity, form (e.g., sheet, bar, or powder), and production techniques. Generally, titanium alloys are more expensive than other common metals like steel or aluminum due to the energy-intensive extraction and processing of titanium ores. The cost of Ti-6Al-4V varies widely depending on form, supplier, and market conditions. For example, as of 2024-2025, market prices list bar stock at several hundred dollars per piece, and powder for additive manufacturing at several hundred dollars per kilogram.
Is Titanium Alloy 6-4 Magnetic?
No, titanium alloy 6-4 is not magnetic. Like other titanium alloys, it is non-ferromagnetic.
Summary
This article presented titanium alloy 6-4, explained it, and discussed its properties and various applications. To learn more about titanium alloy 6-4, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


