The ultra-elastic material nylon has comfortably found its place across industries, whether it’s molded into a washer for an airplane or found within the ingredient list of a skincare product. It’s abundant and easy to produce, but not all nylons are exactly the same. They can be broken down into several types based on their amide group, and because of some differences, can be separated out for use in certain applications and manufacturing processes, which could be anything from CNC machining to 3D printing.
Two types you may be familiar with are nylon 6 and nylon 6/12, which have some of the same properties, but also have a few differences. We’ll explain how both are made and what factors make them distinct from one another. You’ll also learn what applications you can incorporate nylon into, some of which are common everyday products and others are more niche items.
What Nylon 6 Is and How It’s Made
Nylon 6 is the same thing as polycaprolactam—which admittedly doesn’t roll off the tongue as easily. It’s a polymer that’s created through the polymerization of caprolactam, which is its biggest building block.
The pipeline from its invention, courtesy of German chemist Paul Schlack, to its use in manufacturing and commerce was a quick on. Even to this day, it’s a popular material that’s still being improved upon. There are seven other types of nylon out there, but the easiest way to remember this specific kind and its structure is through its name, six, which is because it holds six carbon atoms.
Properties
There are a handful of characteristics that make nylon 6 stand out from its fellow nylons and other materials used in similar capacities. To start, it’s extremely elastic and has an impressive tensile strength, too. It’s capable of handling exposure to alkali and acidic substances and it has resistance to different types of abrasion. It can handle up to 220℃ before it melts, but its glass transition temperature sits at 48℃. If you look at a nylon 6 filament, you’ll notice its smoothness and featureless appearance is similar to glass. It’s also impressive at holding water (managing to absorb around 2.4%). Altogether, these properties make it a worthy candidate for automotive, aerospace, cosmetic, and consumer products, and it can serve as a technical nutrient.
It’s easier to visualize nylon 6’s chemical formula and molecular structure by taking a look at the image below.
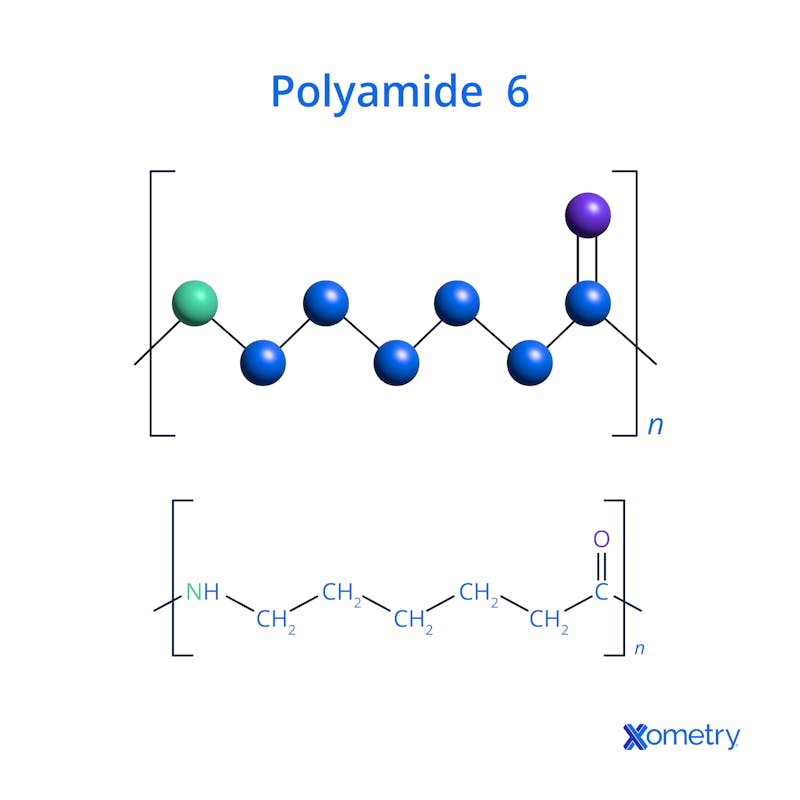
Applications for Nylon 6
Nylon 6 is a popular choice for applications where its durability, toughness, and resistance to wear and tear will come in handy, like the following:
- Fibers
- Toothbrushes
- Guitar strings and picks
- Gears
- Panel catches
- Circuit insulation boards
- Power tool housing
- Medical implants
- Films, wraps, and packaging
Advantages and Disadvantages
The following advantages make nylon 6 a great choice for certain applications:
- Nylon 6 provides excellent stiffness and abrasion resistance
- This material is perfectly fine for use in injection molding
- It’s a great material if you need objects that are resistant to impact and wear and tear
- It has serious elasticity, and even better, it can return to its original shape even after distorting or being subject to tension or pressure
- This type of nylon is a great option if you’re interested in dying it different colors because it holds and shows dye well
On the reverse, there are also a few disadvantages to be aware of with this type of nylon:
- In comparison to other plastics and materials, nylon 6 has a low melting point (220℃)
- Although its water absorption might be a plus, it’s hygroscopic, so it’ll pull water from the air and its surroundings
- When it’s exposed to light and high temperatures, you’ll find that nylon 6 will lose its strength, toughness, and structural integrity
- It’s not UV resistant, and both UV rays and light can discolor it

What Nylon 6/12 Is and How It’s Made
Cousin to nylon 6, nylon 6/12 is also a thermoplastic, but it was created to solve for nylon 6’s moisture absorption—which has proven to be problematic for some applications. It also goes by the name of polyamide 6/12 or PA 612, and is a mix of two different compounds, which gives it its double-number name. The molecular formula is C18H36N2O3, which has quite a few more atoms of each element in place than its precursor.
Properties
To create nylon 6/12, you must polymerize nylon 6 and add in both hexamethylenediamine and dodecanedioic acid, which stretch out the distance between the amide groups. In terms of nylon properties, the result is a material that’s not as strong and has less resistance to chemicals. Its melting point is just a smidge lower than nylon 6, at 218 ℃—for a higher melting point than both, look to nylon 66. That said, it’s a better option if moisture resistance is more important and you need a material that won’t lap up water from the surrounding air.
Applications for Nylon 6/12
Nylon 6/12 is usually a popular material for extruded tubes and several other uses, like the following:
- Electric appliances
- Personal care products, cosmetics, and skincare
- Parts for cars and other vehicles
- Brush bristles
- Fuel systems
Advantages and Disadvantages
These are the main advantages to working with nylon 6/12:
- This type of nylon absorbs much less than its cousin nylon 6, and therefore is less prone to swelling
- It also has great resistance to wear and tear and has a decent level of strength, too
- When you compare it to other similar polyamides, 6/12 provides better electrical insulation and has a lower chance of cracking under stress
- While it’s not as resistant as nylon 6, 6/12 is capable of handling certain levels of heat, and it’s smoother than other polymers
- It’s also a suitable option for injection molding because of its ability to be melted down (without deteriorating) and then cooled and molded
There are also several disadvantages that this type of nylon brings with it:
- Nylon 6/12 has much weaker resistance when it comes into contact with acidic and alkaline solutions
- It’s not as widely available as nylon 6, and, because of its specific purpose, it tends to be more expensive than other types of nylon
- It doesn’t have high crystallinity and therefore also has a lower heat deflection temperature and tends to shrink more within molds than other plastics do
Comparing These Nylon Types
Overall, you’ll find that nylon 6 offers better resistance to chemicals, acids, bases, and impact than its polymerized counterpart nylon 6/12. However, if water absorption is an issue for your particular application, you’ll want to lean on 6/12 for its reduced ability to soak up water that it comes into contact with—in the air or otherwise. Side by side, the two are relatively similar when it comes to strength. Despite nylon 6/12’s lack of resistance to chemicals and acids, it tends to be slightly more expensive because it’s not produced as frequently.
How Xometry Can Help
These types of nylon are popular in various sectors, and to help businesses with these needs, we have numerous services that use nylon 6 and nylon 6/12. These include 3D printing, compression molding, plastic extrusion, and custom plastic fabrication. You can get a free quote today for any of these through our website.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry's network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


