One of the most familiar plastic families out there—especially when it comes to manufacturing—is nylon. This group of thermoplastics is pretty versatile, and they can be worked into fibers, films, and molded shapes. There are plenty of nylon types to choose from, so we’ve broken down five of the most common ones below for an understanding of how they’re made and used.
1. Nylon 1,6
This nylon isn’t a go-to for fabrics, but it’s a top selection if you’re after moisture absorbency. It’s made with three ingredients—adiponitrile, formaldehyde, and water—and then formed through a reaction called acid catalysis.
2. Nylon 4,6
This type was made with the intention of getting a nylon that could handle much higher temperatures. Because of this helpful property, it’s normally found in engine components (like transmissions), brakes, and cooling systems as it won’t melt as quickly as others.
3. Nylon 510
You’ll find 510 is grouped under the same patent as 6,6 (which we’ll get to), but it’s made of pentamethylene diamine and sebacic acid. It’s on the spendier side when it comes to production, so you won’t see it getting made in mass quantities. However, small batches will be created for the scientific and industrial industries, which rely on it for its strength and durability.
FREE Product Development E-Book
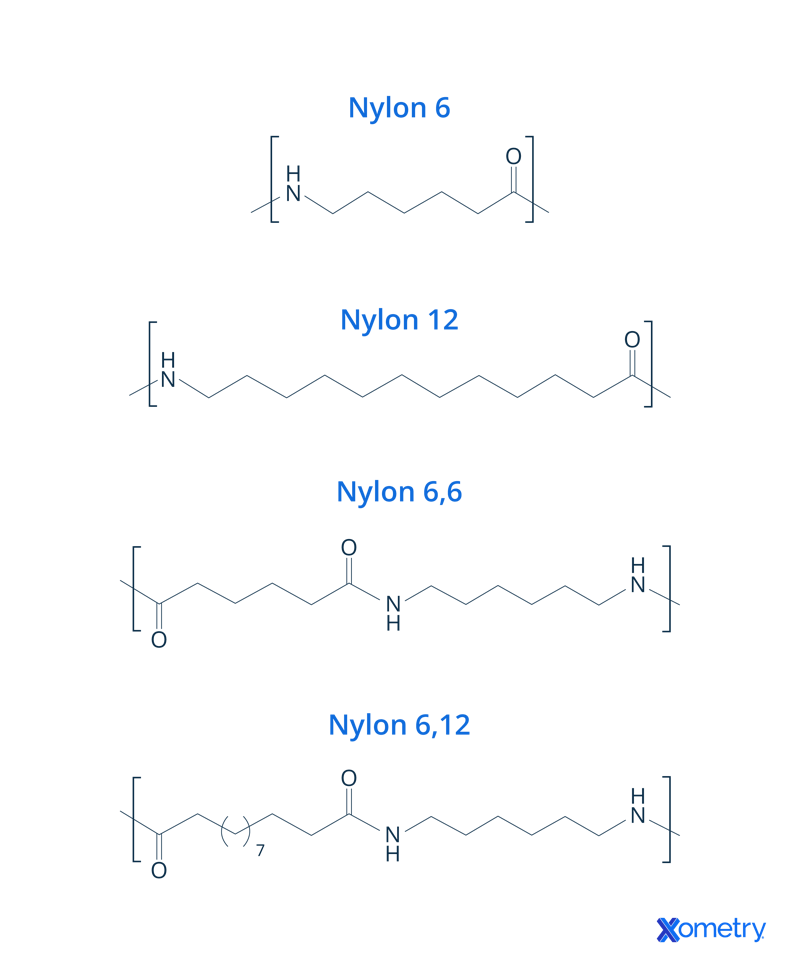
4. Nylon 6
If you need something that’s stretchy, strong, and shiny, no. 6 is the one to go for—plus, it absorbs a good amount of water. It's an easy one to dye different colors, and it’s capable of dealing with high temperatures of up to 150 ℃ before it becomes a molten liquid. It’s a top pick for many different industries, getting mixed into construction materials, medical and electronic products, and fabrics found in the clothing industry.
5. Nylon 6,6
Aside from this name, you can also find this nylon categorized under polyamide 66 (or PA 66). It was developed in order to give manufacturers a little more temperature resistance and a lot less moisture absorbency. Because of its higher yield strength and toughness, it’s a good choice for making wear pads, slide bearings, and materials that will be exposed to oils and chemicals.
How Nylon Is Made
After a reaction between adipic and diamine acids, the formula used to make nylon (which varies based on the type you’re using) will then get forced through an extruder with numerous small holes, turning it into usable fibers. These fibers are then placed onto bobbins and through an industrial-scale process. Then they’re wound onto spools and eventually woven into materials, fabrics, and garments.
Usually during these processes, nylon will be dyed in different colors, depending on function and aesthetics, and it’ll get mixed with other textiles before it becomes the final product.
Quality
Different nylon types will be tested for a wide range of characteristics under standardized processes, and this will help you tell whether or not nylon is of a good quality. However, some characteristics that might be viewed as negative in specific situations (like moisture absorption) can actually be positive perks when it comes to other applications. It all depends what physical, chemical, and mechanical properties you need for the use in question, and then you can choose based on which nylon can offer those to you.
Cost
When you put it up against other comparable materials, you’ll find that nylon is pretty inexpensive. It may be a surprise to learn that it was actually more expensive than silk when it was first made, but nowadays it’s far more cost effective, even more so when it’s mixed with other textiles. Every type of nylon—on this list and otherwise—can be used in a manufacturing setting. So not only is it fairly cheap, but it’s reliable and versatile.
Environmental Impact
Although nylon is infinitely recyclable, it is, after all, a plastic. It’s one type of material that gets broken down into microplastics, which are found everywhere—from the seas to the air we breathe. Not only that, but the production and recycling processes both release greenhouse gasses. It’s a useful material with many different positive characteristics, but that doesn’t hide the fact that it’s not great for the environment.

How Xometry Can Help
At Xometry, we’re experts in working with plenty of materials, whether it’s nylon, another thermoplastic, or various metals and textiles. Our services can help you manufacture and process these materials with ease, and you can get a free quote today for nylon 3D printing, nylon 66 CNC machining, nylon injection molding, plastic 3D printing, and plastic extrusion as well as explore many other options on our website.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


