Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding
Manufacture custom silicone prototypes and end-use production parts in 15 days or less in a range of durometers and grades of LSR materials. Subject to availability. Xometry doesn't guarantee that we can provide this service at any given time.
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection Molding (LSR molding) is a manufacturing process that utilizes liquid silicone rubber to produce exact and durable parts, benefiting from the material's properties and the advanced injection molding technology. LSR is known for its flexibility, heat resistance, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for applications where elasticity and long-term performance are essential. The process involves preparing the liquid silicone rubber, injecting it into preheated molds, and curing the material at elevated temperatures to solidify the silicone within the mold, followed by part removal once cured.
LSR molding is used across various industries, such as automotive, to create seals, gaskets, and vibration-damping components. Medical devices (implants or tubing) utilize LSR molding for its biocompatibility. Consumer products (baby goods and kitchenware) and electronics use it to manufacture durable components that withstand high temperatures. Liquid silicone rubber injection molding offers versatility and reliability, ensuring that components meet stringent performance and safety standards (biocompatibility, high-temperature resistance, and dimensional accuracy). LSR injection molding enables the creation of complex shapes and fine details, leveraging the material's unique flow characteristics to maintain consistent quality across high-volume production runs.
How Does Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding Work?
Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding works by injecting a two-part liquid silicone rubber compound into a closed, heated mold cavity, where it undergoes a thermal curing process that converts the liquid material into a solid, flexible part. The process begins with mixing two components: a base silicone containing vinyl groups and a crosslinker (typically containing hydride groups), combined with a platinum catalyst. The catalyst initiates crosslinking under heat, forming a solid elastomer. The mixed liquid silicone is metered and injected into the mold under controlled pressure, ensuring even flow through the mold channels and complete filling of the cavity. The silicone cures into the precise shape of the mold, producing parts that are highly flexible, durable, and resistant to extreme temperatures and chemical exposure. The curing step ensures that the finished components maintain dimensional accuracy and a smooth surface finish, which is essential for high-performance industrial and consumer products.
Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding is widely used in industries that require precision and material reliability. It produces seals, gaskets, and connector covers that withstand extreme temperatures and vibration in automotive manufacturing. Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding is used in medical and consumer health applications to produce respiratory masks, medical tubing, and baby bottle nipples that require biocompatibility, flexibility, and softness. LSR is used in electronics to produce keypads, protective gaskets, and waterproof seals with excellent electrical insulation and flexibility. The process supports large-scale production while maintaining consistency and high quality, making it valuable for products that demand durability and precise engineering.
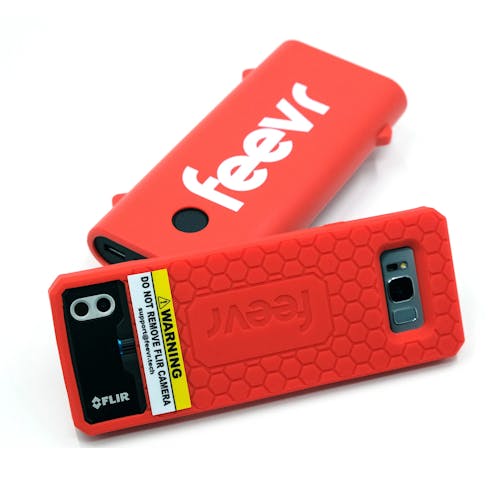

Xometry Injection Molding Capabilities
| Service | Details |
|---|---|
Service Lead Time | Details Starts at 15 business days, including 24-hour quote responses with design-for-manufacturing (DFM) feedback |
Service Production Options | Details Domestic and international |
Service Machines Available | Details Single, multi-cavity, and family molds; 50 to 3,700+ press tonnage; side actions including hand-loaded cores |
Service Inspection and Certification Options | Details Includes FAI and PPAP. ISO 9001, AS9100, ISO 13485, UL, ITAR, and ISO 7 and 8 Medical Clean Room molding. |
Service Tool Ownership | Details Customer-owned with mold maintenance |
Service Mold Cavity Tolerances | Details +/- 0.005" when machining the mold and an additional +/- 0.002" per inch when calculating for shrink rate |
Service Part to Part Repeatability | Details +/- 0.004" or less |
Service Critical Feature Tolerances | Details Tighter tolerances can be requested and may increase the cost of tooling because of additional sampling and grooming. Xometry will mill to a steel-safe condition on critical features. |
Service Available Mold Types | Details Steel and aluminum; Production grades range from Class 105, a prototype mold, to Class 101, an extremely high production mold. Xometry typically produces Class 104, 103, and 102 tools. |
This table depicts the general tolerances for Xometry’s injection molding services and accounts for adequate draft, radii, and coring for manufacturability. Learn more about our injection molding manufacturing standards.
Additional Molding Options Available at Xometry

Insert Molding Service

Overmolding Service
Custom Plastic Injection Molding Service
What are the Materials Used in Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding?
The materials used in Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding are listed below. They include different curing systems (platinum- or peroxide-cured), silicone variants (fluorosilicone, high- or low-consistency rubbers), and blends (TPE or colorable silicones), each suited to specific applications.
- Platinum-Cured Silicone (PCS): PCS is a durable, flexible, and biocompatible material valued for its heat, chemical, and aging resistance. The material is used in medical, food-grade, electrical, and consumer applications requiring purity, stability, and long-lasting performance.
- Peroxide-Cured Silicone (PVS): Peroxide-Cured Silicone (PVS) is a strong and flexible material known for its heat, tear, and weather resistance. It offers good adhesion to metals and plastics but is less biocompatible and has lower chemical stability than platinum-cured silicone. It is commonly used in automotive, industrial, and electrical applications, but it is unsuitable for medical or food products.
- Fluorosilicone (FVMQ): Fluorosilicone (FVMQ) is a durable and flexible material resistant to fuels, oils, extreme temperatures, and chemicals. It is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications where long-lasting performance under harsh conditions is essential. However, it has reduced flexibility at lower temperatures than other silicone variants.
- High Consistency Rubber (HCR): High Consistency Rubber (HCR) is a strong and flexible material known for its heat resistance, durability, and stability under pressure. Used in medical, automotive, and electrical applications that require long-lasting performance and safety.
- Low Consistency Silicone (LCS): Low Consistency Silicone (Liquid Silicone Rubber or LSR) delivers flexibility, precision, and resilience for parts requiring smooth finishes and detailed designs. It is used for medical seals, industrial components, and consumer grips.
- Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Silicone Blends: Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Silicone Blends combine the rubber-like flexibility of silicone with the thermoplastic processability of TPEs, offering durability, soft-touch comfort, and ease of molding. These blends are used for applications requiring flexibility and processing efficiency (medical devices and industrial seals).
- Medical-Grade Silicone (MGS): Medical-Grade Silicone (MGS) offers high purity, flexibility, and biocompatibility, ensuring safe and reliable performance in healthcare applications. It must meet stringent regulatory standards (FDA approval or ISO 10993) for use in medical devices and implantable components.
- Food-Grade Silicone (FGS): Food-Grade Silicone (FGS) is a safe, non-toxic, and flexible material for direct food contact. It offers odor-free performance and must comply with relevant regulatory standards (FDA 21 CFR 177.2600) for food contact materials.
- High-Temperature Silicone (HTS): High-Temperature Silicone (HTS) provides excellent heat resistance, ranging from -60°C to 250°C, while maintaining flexibility under extreme thermal and mechanical stress. It is used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications where durability and thermal stability are essential.
- Colorable Silicone (CS): Colorable Silicone (CS) is a flexible and durable material that allows precise color customization while maintaining heat and chemical resistance. It is used in consumer products, medical devices, and food-grade applications requiring visual appeal and reliable performance.
Platinum-Cured Silicone (PCS)
Description
Platinum-Cured Silicone (PCS) provides excellent flexibility, durability, and biocompatibility. Material selection is essential in achieving the desired performance of molded products, influencing strength, elasticity, and resistance to environmental factors. PCS is used in medical, food-grade, and high-performance industrial applications due to its purity, stability, and ability to maintain shape under stress. The non-toxic composition and resistance to heat, chemicals, and aging make Platinum-Cured Silicone (PCS) a preferred material for demanding environments.
Key Properties
Density: 1.10 to 1.25 g/cm³
Cure/Processing Temperature (typical): 160 to 200 °C.
Tensile Strength: 8 to 15 MPa
Flexural Modulus: 2.0 to 3.0 MPa
Key Advantages
- Excellent flexibility and elasticity
- Superior heat and chemical resistance
- Long-term stability and biocompatibility
- Non-yellowing and odorless performance
Common Applications
- Medical tubing and implants
- Food-grade seals and molds
- Electrical insulation parts
- Consumer and baby care products
Peroxide-Cured Silicone (PVS)
Description
Peroxide-cured silicone (PVS) provides strong tear strength, flexibility, and resistance to high temperatures, making it suitable for applications requiring excellent adhesion and durability under harsh conditions. Selecting the right material is essential for achieving product performance, durability, and cost efficiency. PVS is valued for its strong adhesion and suitability for parts that require firmness and stable shape retention. It performs well in demanding environments where exposure to heat, oil, or weathering is common. The Peroxide-cured silicone (PVS) offers higher tear strength than platinum-cured types, making it suitable for applications where tear resistance is critical. It is generally unsuitable for medical or food-contact applications due to residual byproducts from the peroxide curing process that affect material purity.
Key Properties
Density: 1.10 to 1.25 g/cm³
Service Temperature: Ranges from -50 °C to 200 °C, with a curing/processing temperature range of about 160 °C to 220 °C.
Tensile Strength: 6 to 12 MPa, depending on formulation and curing conditions.
Flexural Modulus: 1.5 to 2.5 MPa
Key Advantages
- Strong tear and compression resistance, making it ideal for applications with frequent mechanical stress.
- Good thermal and weathering stability, though perhaps less stable than platinum-cured silicone in extreme environments.
- Excellent adhesion to metals and plastics, making it ideal for bonding in automotive and industrial applications.
- Cost-effective compared to platinum-cured silicone, making it suitable for applications where cost efficiency is a priority.
Common Applications
- Automotive gaskets and seals, including engine components that require high heat resistance.
- Industrial hoses and rollers, where flexibility and durability under mechanical stress are critical.
- Electrical insulation components (cable coatings and electrical seals) are used due to their excellent dielectric properties.
- Consumer-grade molds and kitchenware (excluding direct food contact), where cost-effective performance is prioritized.
Fluorosilicone (FVMQ)
Description
Fluorosilicone provides a balance of flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance. Choosing the right material is essential for meeting the performance needs of specific applications, as it determines properties (strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness). FVMQ is valued for its resistance to fuels, oils, and extreme temperatures, making it suitable for demanding environments where other elastomers lose performance. The stability of Fluorosilicone (FVMQ) under harsh conditions ensures long service life and consistent product quality.
Key Properties
Density: 1.35 to 1.45 g/cm³
Cure/Processing Temperature (typical): -50°C to 250°C
Tensile Strength: 7 to 12 MPa
Flexural Modulus: 1.0 to 2.5 MPa
Key Advantages
- Excellent resistance to fuels and oils, ensuring reliable performance in harsh environments.
- Strong performance in extreme temperature ranges, from -60°C to 230°C, maintaining flexibility and stability under thermal stress.
- Long-term flexibility and resilience, even under prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures.
- Reliable resistance to weathering and ozone, making it ideal for outdoor, automotive, and industrial applications.
Common Applications
- Aerospace and automotive seals (gaskets, O-rings, and other critical sealing components).
- Fuel system gaskets and seals, offering superior resistance to gasoline, diesel, and other fuels.
- Chemical processing components (seals, gaskets, and O-rings) are exposed to aggressive chemicals, which is common.
- Industrial O-rings and diaphragms, used in various applications where chemical and temperature resistance are critical.
High Consistency Rubber (HCR)
Description
High Consistency Rubber (HCR) offers excellent strength, durability, and moderate flexibility, making it ideal for applications that require high firmness and resistance to wear. Selecting the right material, such as High Consistency Rubber (HCR), ensures the final product meets required performance characteristics (high resistance to wear, environmental conditions, and chemical exposure) in demanding applications. Material selection impacts the longevity and functionality of the molded parts, influencing cost-effectiveness, production speed, and quality. HCR (High Consistency Rubber) is a high-viscosity silicone rubber typically processed by compression or transfer molding and extrusion, though specialized systems also allow for injection molding of HCR compounds. It differs from thermoplastics (ABS and polypropylene), which are melted and remolded during processing. High Consistency Rubber (HCR) is valued for its resilience and high-performance capabilities in specialized applications, requiring durability under high temperatures and mechanical stress.
Key Properties
Density: 1.10 to 1.25 g/cm³
Cure Temperature Range: typically 170 °C to 220 °C, depending on the formulation.
Tensile Strength: 8 to 12 MPa (depending on formulation)
Flexural Modulus: 2.0 to 3.0 MPa
Key Advantages
- High tear and tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to mechanical stress
- Excellent resistance to heat, aging, and oxidative degradation, ensuring long-term durability in harsh conditions.
- Strong dimensional stability under load, making it reliable for applications requiring consistent performance over time.
Common Applications
- Seals and gaskets in automotive, industrial, and high-performance applications.
- Industrial-grade tubing and stoppers are used in applications where high temperature and chemical resistance are required.
- Electrical insulators, offering high dielectric strength and thermal stability in demanding electrical applications.
- Automotive engine components (gaskets, seals) are exposed to high temperatures and mechanical stress.
Low Consistency Silicone (LCS)
Description
Low-consistency silicone (Liquid Silicone Rubber, LSR) combines flexibility with high precision, making it suitable for products that require smooth finishes and detailed shapes. Material choice is crucial in molding processes, as it determines the product’s strength, elasticity, flow characteristics, and cost efficiency. The Low-consistency silicone offers a balance of softness and resilience, making it suitable for applications exposed to temperature shifts or repeated mechanical stress, while maintaining high performance over time. The stable chemical structure of low-consistency silicone ensures reliable performance under pressure, heat, and mechanical stress, making it a dependable option for industrial, medical, and consumer-grade components.
Key Properties
Density: 1.10 to 1.20 g/cm³
Cure Temperature Range: typically 150°C to 200°C, depending on the formulation and application.
Tensile Strength: 6 to 10 MPa (depending on formulation)
Flexural Modulus: 1.2 to 1.8 MPa
Key Advantages
- Excellent flexibility and compression recovery, allowing it to retain shape and function in dynamic applications.
- Stable performance across a wide temperature range, from -50°C to 250°C, ensuring reliability under extreme thermal conditions.
- High resistance to aging, UV radiation, and environmental stress, ensuring long-term durability in challenging environments.
- Excellent surface finish and easy mold release, making it ideal for high-precision and complex molded parts.
Common Applications
- Medical seals, diaphragms, and other medical components require biocompatibility and flexibility.
- Soft-touch industrial parts (grips, gaskets, and seals) are where flexibility and comfort are essential.
- Consumer product grips, handles, and soft-touch components, providing both comfort and durability.
- Electrical insulation, gaskets, and seals, offering excellent dielectric properties and reliability in demanding applications.
Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Silicone Blends
Description
Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Silicone Blends combine the elasticity of rubber with the processability of thermoplastics, offering a versatile material for injection molding. These blends are made by combining silicone with other thermoplastic elastomers. Selecting the right Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Silicone Blends is crucial to achieving the desired balance between flexibility, strength, durability, and production efficiency, depending on the application. TPE Silicone Blends provide soft-touch surfaces, excellent flexibility, and good heat resistance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications (consumer, medical, and industrial products) that require tactile comfort, flexibility, and thermal performance. The material delivers consistent performance in parts requiring elasticity, impact resistance, and resilience under repeated bending and mechanical stress without permanent deformation.
Key Properties
Density: 0.90 to 1.20 g/cm³
Softening Point: 200°C to 250°C, depending on the specific blend and formulation.
Tensile Strength: 5 to 15 MPa, depending on formulation and processing conditions.
Flexural Modulus: 5 to 15 MPa, depending on the specific blend and application.
Key Advantages
- High flexibility and elasticity make them ideal for applications that require dynamic performance and comfort.
- Good heat and chemical resistance, although the exact resistance varies depending on the formulation and the specific blend used.
- Excellent grip and soft-touch feel, making them ideal for consumer products (grips, handles, and soft-touch components).
- Recyclable and cost-effective for high-volume production, providing efficient solutions for large-scale manufacturing.
Common Applications
- Medical device components, including non-implantable parts that require flexibility, biocompatibility, and sterilization resistance.
- Consumer product grips, handles, and soft-touch components, providing durability and comfort.
- Seals and gaskets, providing excellent sealing performance in automotive, industrial, and consumer products
- Electrical cable insulation offering flexibility, heat resistance, and reliable performance in demanding electrical applications.
Medical-Grade Silicone (MGS)
Description
Medical-grade silicone meets strict regulatory standards, ensuring precision, safety, and reliability in healthcare applications. Choosing the right material (medical-grade silicone) is vital for achieving desired properties (flexibility, strength, durability, biocompatibility, and cost efficiency). The Medical-grade silicone (MGS) is used in medical manufacturing due to its purity, biocompatibility, and excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and sterilization. Medical-grade silicone maintains stability under repeated sterilization and long-term use, making it ideal for products requiring consistent performance, patient safety, and durability.
Key Properties
Density: 1.10 to 1.20 g/cm³
Cure/Processing Temperature: typically 150°C to 200°C, depending on the formulation.
Tensile Strength: 7 to 12 MPa
Flexural Modulus: 1.5 to 3.0 MPa
Key Advantages
- High biocompatibility and safety, meeting stringent regulatory standards for medical use.
- Strong resistance to heat, aging, and chemicals, ensuring long-term stability and reliability in medical applications.
- Excellent flexibility and tear strength, providing reliable performance in medical devices that require durability and flexibility.
- Maintains shape, clarity, and mechanical properties under repeated sterilization cycles, ensuring consistent performance.
Common Applications
- Catheters, medical tubing, and flexible components require biocompatibility and sterilization resistance.
- Seals, gaskets, and critical components for medical devices require secure, sterile seals.
- Implantable components (breast implants and pacemaker components) require long-term biocompatibility and durability and are limited to specific implant-grade silicones validated for long- or short-term implantation.
- Respiratory masks, valves, and other components require flexibility, comfort, and sterilization resistance.
Food-Grade Silicone (FGS)
Description
Food-Grade Silicone delivers flexibility, safety, and durability for products in direct contact with food, meeting stringent regulatory standards (FDA 21 CFR 177.2600) for food-contact materials. Material selection is crucial in molding, as it determines the performance and quality of the final product (non-toxicity, flexibility, strength, and resistance to wear), which are essential for food-safe applications. The Food-Grade Silicone (FGS) is valued for its non-toxic, odorless nature, making it ideal for hygienic applications that require strict cleanliness standards. It withstands high and low temperatures, resists aging, and maintains its shape over time, ensuring long-lasting reliability and performance in demanding food-contact applications.
Key Properties
Density: 1.10 to 1.20 g/cm³
Softening Point: Ranges from 180°C to 220°C, depending on the specific formulation.
Tensile Strength: 6 to 10 MPa
Flexural Modulus: 1.0 to 2.0 MPa
Key Advantages
- Non-toxic and food-safe composition, meeting regulatory standards for direct food contact.
- High flexibility and tear resistance, ensuring durability in food-grade applications.
- Excellent heat and cold resistance, maintaining performance in both high-temperature and freezing conditions.
- Long-lasting and odor-free performance, ensuring hygienic use over time.
Common Applications
- Baking molds, kitchen utensils, and bakeware, offering non-stick properties and heat resistance.
- Food storage seals, gaskets, and lids provide secure, non-toxic sealing properties.
- Beverage dispenser components, offering flexibility and durability in food-safe applications.
- Baby bottle nipples, pacifiers, and feeding accessories, offering non-toxic, hypoallergenic, and durable performance for infant care.
High-Temperature Silicone (HTS)
Description
High-Temperature Silicone (HTS) plays a key role in injection molding, where materials must withstand extreme heat and maintain flexibility under pressure, making it ideal for high-performance applications. HTS is used in environments that require resistance to heat, oxidation, compression, and mechanical stress, making it suitable for harsh applications. The stability, elasticity, and heat resistance of High-Temperature Silicone (HTS) make it ideal for demanding automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications where consistent performance is essential.
Key Properties
Density: 1.18 to 1.25 g/cm³
Cure/Processing Temperature (typical): 200 to 300°C
Tensile Strength: 7 to 12 MPa
Flexural Modulus: 2.0 to 2.8 MPa
Key Advantages
- Excellent heat and oxidation resistance
- Strong flexibility and compression recovery
- Long service life under thermal stress
- Resistant to weathering and aging
Common Applications
- Automotive gaskets and seals
- Aerospace components
- Industrial oven and furnace parts
- Electrical insulation materials
Colorable Silicone (CS)
Description
Colorable Silicone (CS) is an adaptable material in injection molding that allows manufacturers to combine high functionality with aesthetic design, offering precise color customization without compromising performance. Material selection in molding is essential for achieving desired product performance, influencing elasticity, strength, flexibility, durability, and cost-efficiency, especially for materials like Colorable Silicone (CS). Colorable Silicone (CS) is valued for its ability to accept pigments while maintaining excellent elasticity, thermal resistance, and chemical stability, ensuring both functional and aesthetic performance. CS provides consistent color distribution, smooth surface quality, and long-term durability, making it ideal for applications in consumer goods, medical products, and wearable accessories, where both appearance and reliability are critical.
Key Properties
Density: 1.10 to 1.20 g/cm³
Cure/Processing Temperature: typically 150 to 200°C, depending on the specific formulation and application.
Tensile Strength: 6 to 10 MPa
Flexural Modulus: 1.0 to 2.0 MPa
Key Advantages
- Wide color customization with stable pigment dispersion, enabling manufacturers to achieve precise and consistent colors.
- Excellent flexibility and tear resistance, providing durability and performance in applications requiring frequent movement or mechanical stress.
- Strong thermal and chemical stability, allowing it to perform reliably in demanding conditions, including exposure to heat, chemicals, and UV radiation.
- Long-lasting surface quality and non-fading color, ensuring aesthetic appeal and performance over extended use in various environments.
Common Applications
- Consumer products, wearable accessories, and personal items require visual appeal and functional durability.
- Medical devices, seals, and gaskets require biocompatibility and color customization for easy identification.
- Kitchenware, food-contact components, and kitchen tools require high-heat resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Electrical components, lighting parts, and seals where color customization and electrical insulation are needed.
Which Material Is Best for Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding?
Platinum-Cured Silicone (PCS) is the most commonly used material for Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding (medical, food-grade, and high-performance applications) due to its excellent flowability, biocompatibility, and thermal stability. The best material choice depends on specific application needs and performance requirements. PCS provides excellent flowability, thermal stability, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for applications that demand precision and long-term performance. The smooth flow characteristics of PCS allow the silicone to fill intricate mold cavities without air pockets or weak spots. Mold design and injection conditions contribute to the final result. PCS maintains superior temperature resistance, flexibility, and strength under pressure compared to other silicone materials, making it ideal for demanding applications.
PCS offers superior thermal stability and elasticity in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments compared with common thermoplastics such as polypropylene, polycarbonate, and ABS. Its non-toxic, chemically stable composition makes it well-suited for medical, food-grade, and industrial uses where safety, biocompatibility, and durability are essential. The combination of consistent curing, high elasticity, and clean molding results makes Platinum-Cured Silicone (PCS) the preferred choice for many Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding applications, requiring high performance and precision.
LSR Injection Molding Design Guidelines
| Feature | Tip |
|---|---|
Feature Undercuts | Tip Reduce undercuts, which will increase the complexity and cost of the tool ejection mechanisms, by adding in pass-thru coring. |
Feature Wall Thickness | Tip Prevent wall sink and voids by maintaining an even wall thickness. Thinner walls reduce cycle time and reduce costs. |
Feature Drafts | Tip Ensure liquid injection molding parts are designed with a minimum draft angle of 0.5°, or up to 5°, for faces with medium textures. |
Feature Ribs/Gussets | Tip Ribs should be 40-60% the thickness of outer walls and should still maintain draft. |
Feature Bosses | Tip Bosses should be designed at a depth of 30% the wall thickness and with a 30% edge groove. Attach them to side walls or ribs for structural integrity. |
To see these design-for-manufacturing recommendations in detail, view our Injection Molding Design Guide.
Ready to Get an LSR Injection Molding Quote?
What Are the Applications of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding?

Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding is suitable for producing small to medium-sized parts, and larger parts, provided that mold design, injection speed, and pressure are appropriately adjusted to ensure fine details and smooth finishes. The process works best for flexible components (seals, valves, and medical-grade items) that require precise dimensions and reliable performance under stress. Large or rigid parts are rarely produced with LSR due to the material’s softness and specific curing requirements, but certain formulations and molding adjustments accommodate the applications.

The success of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding depends on accurate mold design, controlled injection pressure, and proper curing time, ensuring precise cavity filling and part quality. Each of these factors affects how well the silicone fills the cavity, ensuring dimensional accuracy and that the final part maintains its intended shape. Poor temperature control or uneven pressure leads to defects, highlighting the need for precision equipment and stable process conditions to ensure reliable and defect-free output.

Medical products (baby bottle nipples, catheters, and gaskets) must be precisely sized, clean, and have consistent elasticity to meet safety and performance standards. Seals, connectors, and keypads in the automotive industry require precise molding to withstand heat, vibration, and pressure changes, ensuring reliable performance in demanding environments. Each application demands consistent material properties and precise design accuracy to meet rigorous performance and safety standards in industries like medical, automotive, and consumer goods.
What is Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding?
Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding is a precision manufacturing process where liquid silicone rubber is injected into a closed, heated mold under moderate pressure and cured at elevated temperatures, forming flexible, durable, and heat-resistant parts. The process uses a two-part liquid silicone rubber system, consisting of the base silicone and a curing agent, which mix and solidify within a heated mold to create parts with excellent dimensional stability and consistent quality. LSR’s low viscosity allows it to flow easily into complex mold designs, enabling the efficient production of intricate components in large volumes while maintaining excellent strength, elasticity, and fine detail.
The process is suited for products with wall thicknesses typically ranging from 0.25 mm to 10 mm. Thicker sections are possible depending on the material and mold design, ensuring uniform curing and minimizing defects (air bubbles or uneven surfaces). The range allows manufacturers to produce small precision parts and larger components, with accuracy maintained across different part sizes, though the precision varies depending on the complexity and dimensions of the mold design. Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding is used across multiple industries, including automotive (seals and gaskets), medical (surgical tools and implants), electronics (keypads and connectors), and consumer goods (baby products and kitchenware). Its resistance to heat, chemicals, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and wear makes it ideal for use in environments requiring durability, flexibility, and safety, such as high-temperature or chemically exposed applications.
What Are the Key Benefits of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding?
The key benefits of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding are listed below.
- High Precision: Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding allows the creation of highly detailed and accurate parts with consistent quality. The process maintains precise dimensional tolerances, making it ideal for medical seals, micro-sized valves, and intricate electrical components, depending on part design and mold specifications. The precision reduces the need for extensive post-processing, although some secondary operations remain necessary for highly intricate parts, ensuring uniformity across large production runs.
- Flexibility and Durability: Silicone has natural elasticity and resilience that allow molded parts to withstand stretching and compression without permanent deformation. The resistance to wear, UV radiation, and environmental stress makes silicone reliable for products like automotive seals and wearable device components. The material retains its flexibility over time, even under continuous use or exposure to harsh surroundings.
- Biocompatibility: Liquid silicone is non-toxic, odorless, and generally hypoallergenic, making it safe for medical and food-related uses, provided it meets the necessary regulatory standards. Medical- and food-grade silicones can be formulated to meet regulatory standards, such as Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and International Organization for Standardization (ISO) requirements for medical-grade materials, making it suitable for baby bottle nipples, medical tubing, and prosthetic parts. The chemical stability ensures that the product does not react with bodily fluids or food substances.
- Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness: The injection molding process for liquid silicone reduces production cycle times and minimizes material waste, depending on the part's complexity and mold design. The automated nature allows for efficient continuous manufacturing with minimal supervision, improving productivity, though occasional monitoring and maintenance are required. The consistent molding quality lowers rejection rates and helps control manufacturing costs for large-scale operations.
- Temperature Resistance: Silicone remains stable across a wide temperature range, typically from about -50°C to 230°C, depending on formulation, functioning well in high-heat and freezing environments. The application ranges from engine gaskets to cookware and aerospace seals whose performance requires extreme conditions. The material retains its flexibility and shape even after repeated exposure to temperature fluctuations.
What Are the Limitations of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding?
The limitations of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding are listed below.
- Material Cost: Liquid silicone rubber is generally more expensive than common thermoplastics such as polyethylene or polypropylene, mainly due to its specialized properties and handling requirements. The higher material cost increases the production expense for large-scale manufacturing, particularly for industries with critical durability, flexibility, or biocompatibility. The added cost comes from the material’s purity and specialized handling requirements. Manufacturers reserve LSR for products that require durability, flexibility, biocompatibility, or reliable performance under extreme conditions to justify the higher expense.
- Limited to Specific Applications: Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection molding is typically suited for small to medium-sized parts (seals, gaskets, and medical components), but it has the potential to be used for larger components with the right mold design and process adjustments. The process is less efficient for large or rigid products that require high strength or rigidity, as LSR's flexibility and elasticity make it better suited for more dynamic applications. Its flexibility and softness make LSR ideal for parts that need elasticity, but it is not suited for applications that require high rigidity or structural strength. The material's flexibility limits its use in applications that require high rigidity or impact resistance compared to thermoplastics or metals.
- Mold Complexity: The molds used for LSR molding require precise design, temperature control, and specialized heating and cooling systems to maintain product quality. Any deviation in mold temperature, injection speed, or curing conditions affects the part's final shape, consistency, and quality. Specialized equipment and technical expertise are required, which increases setup time, complexity, and cost for high-precision or high-volume production runs. The complexity of LSR molding in terms of temperature control and curing makes it more demanding than standard plastic injection molding processes.
- Longer Cure Times: Liquid silicone rubber needs a curing phase to achieve full strength and stability. The step takes longer than the cooling process used in thermoplastic molding. The curing period extends cycle times compared to thermoplastic molding, reducing output per hour. Manufacturers reduce cure time primarily by optimizing mold temperature and catalyst concentration rather than pressure settings, which have a limited effect on curing rate.
What Factors Affect the Performance of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding?
The factors affecting the performance of liquid Silicone Rubber Injection molding are material properties, mold design, and injection conditions. The silicone's viscosity and flow characteristics, including low viscosity and slight shear thinning behavior, affect how easily it fills the mold and the final part's quality, ensuring that detailed areas are filled completely and accurately. Silicone with proper flow properties ensures complete filling of the detailed regions, leading to accurate shapes, strong finished products, and reduced chances of defects (incomplete fills or voids). Mold design elements (heating channels, gate placement, wall thickness, and venting) are key in maintaining uniform temperature, efficient material flow, and the prevention of defects during molding.
A well-structured mold improves product consistency, reduces waste, and shortens cycle times, improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness in production. Injection speed and pressure must be carefully controlled to ensure the silicone flows evenly into every mold cavity. These parameters must be optimized based on the part design, material viscosity, and mold characteristics. Proper adjustment of injection speed and pressure helps prevent defects (air bubbles, surface flaws, or incomplete fills), ensuring smooth surfaces and durable parts with minimal waste. Each factor (material properties, mold design, and injection conditions) works together to ensure consistent quality, efficiency, and reliable performance in silicone rubber injection molding.
What Challenges Do Manufacturers Face When Using Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding?
The challenges that manufacturers face when using Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding are maintaining consistent part thickness, achieving efficient cooling, and ensuring smooth material flow. Maintaining uniform thickness in complex or thin-walled designs is challenging, as uneven cooling times or material distribution lead to weak points, warping, or dimensional inconsistencies. Precision in mold design and injection pressure control is essential to ensure the silicone is evenly distributed throughout the mold, maintaining consistent part quality. Efficient temperature control within the heated mold is another concern, since liquid silicone cures under heat rather than cooling like thermoplastics. Uniform temperature ensures proper crosslinking, dimensional accuracy, and consistent curing. Excessive cooling rates affect material flow and curing uniformity. Uneven cooling results in surface irregularities, internal stresses, or warping, negatively affecting the product’s strength, dimensional stability, and appearance.
Smooth material flow is challenging, as liquid silicone must flow efficiently through tight or intricate mold cavities to ensure complete filling and part integrity. Obstruction or imbalance during injection leads to short shots, trapped air, or poor filling, reducing the quality of the molded part and potentially affecting its curing or material properties. Adjusting injection speed, pressure, and venting is essential to maintain uniform silicone flow, prevent defects, and ensure even curing throughout molding. Addressing these challenges is crucial to achieving consistent, durable, high-quality results in Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding.
How Do Material Properties Affect the Cost and Performance of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding?
Material properties affect the cost and performance of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding by determining how efficiently the material processes and how well the final product performs under stress. Higher-durometer silicones within a given formulation increase durability and resistance to mechanical stress, but at the expense of softness and elastic recovery.
Materials with higher flowability, typically platinum-cured LSR grades, reduce cycle times by filling mold cavities faster and requiring less injection pressure. It reduces production energy costs and improves productivity, but Liquid Silicone Rubber has lower flowability compared to thermoplastics (polypropylene or ABS). Heat resistance and thermal stability are crucial for how well molded parts perform in demanding environments (automotive or medical equipment) exposed to high temperatures. Materials like high-temperature silicone (HTS) and fluorosilicone (FVMQ) are preferred in these environments due to their superior thermal resistance. Higher-performing materials (Platinum-Cured Silicone) are more expensive but deliver longer service life, reduce maintenance costs, and result in better long-term value and consistent quality in molded products in demanding applications.
How Does Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding differ from Other Types of Injection Molding
Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding differs from traditional thermoplastic injection molding by using a two-part liquid silicone compound that is mixed, metered, and cured in the mold rather than melting and cooling solid plastic pellets. The silicone material is injected in liquid form and cured inside the mold under heat and pressure, resulting in flexible and durable components. Traditional injection molding uses melted thermoplastics (ABS and Polycarbonate), which harden upon cooling. Most thermoplastics have lower flexibility and heat resistance than LSR, though thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) can approximate silicone’s softness but not its temperature stability. Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding produces parts with superior elasticity, temperature tolerance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for demanding applications. The biocompatibility and long-term resilience of LSR provide manufacturers with an advantage in creating safe, high-quality products that maintain performance under extreme conditions.
How Do Production Speeds in Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding Compare to Other Molding Methods?
Production speeds in Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding are comparable to or slightly faster than other molding methods for small to medium-sized parts once molds are optimized, though curing still limits overall throughput compared to thermoplastic molding. The process uses LSR, which flows effortlessly into molds, allowing for quick filling and consistent curing under controlled heat and pressure, though precise temperature control is crucial for ensuring proper curing. Shorter cycle times are achievable because Liquid Silicone Rubber cures rapidly once injected, reducing waiting periods between production runs. Curing times depend on part size, material formulation, and mold design. The use of specialized molds and temperature control systems is necessary, and these systems ensure consistent quality and uniformity across batches, which is critical for Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding. The combination of precision, reliability, and the ability to produce high-quality, biocompatible parts makes Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding an efficient choice for industries requiring consistent product performance (medical, automotive, and consumer goods applications).
Is Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding More Cost-Effective than Thin-Wall Injection Molding?
No, Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding is not always more cost-effective than Thin-Wall Injection Molding, as each method serves different purposes and production goals. Each technique serves different purposes and production goals, with LSR molding having higher material costs and more complex processing. Thin-Wall Injection Molding is better suited for high-volume, low-cost applications. Liquid silicone molding delivers higher durability, flexibility, and temperature resistance, which makes it ideal for medical, electrical, and high-performance parts. The material cost and curing process increase production expenses. Thin-Wall Injection Molding focuses on lightweight designs and faster cycle times, reducing material usage and energy consumption. It is more economical for high-volume production of packaging, consumer goods, or disposable components. The choice between Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding and Thin-Wall Injection Molding depends on whether the priority is long-term performance and durability (as in silicone molding) or cost efficiency and speed (which defines thin-wall manufacturing).
Is Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding More Suitable for Mass Production than Structural Foam Injection Molding?
Yes, Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding can be more suitable for mass production than Foam Injection Molding due to its faster cycle times, precision, and ability to produce consistent high-quality parts. The process uses liquid silicone rubber that cures quickly, reducing downtime between production runs and supporting large-scale manufacturing. It is cost-efficient for industries that require flexible, durable, and heat-resistant products such as medical devices, automotive seals, and consumer goods. Foam Injection Molding is used to reduce material weight and improve the strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for structural or large components where rigidity is essential. The use of foam injection molding saves material and energy. It requires longer cooling times and more complex gas flow control, which limit production speed compared to other molding processes. Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding delivers superior performance in high-volume applications requiring accuracy, efficiency, and repeatable quality, particularly in industries such as medical devices, automotive, and electronics.
To learn more, see our full guide on Foam Injection Molding.
Is Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding More Energy-Efficient than Metal Injection Molding?
Yes, Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding is generally more energy-efficient than Metal Injection Molding because it operates at lower processing temperatures and requires less energy for material melting and curing. The liquid silicone process uses precise temperature and pressure control, allowing faster cycle times and reduced material waste during production. Metal Injection Molding involves high heat for sintering and debinding metal powders, which increases energy use and production costs. Silicone molding produces flexible, heat-resistant parts with better efficiency, lower operational costs, and consistent quality for applications that do not require the strength and rigidity offered by metal injection molding. The trade-off lies in performance goals as metal molding favors strength and rigidity. Silicone molding supports lightweight, energy-saving, and cost-effective production for flexible components in different industries (medical, automotive, and consumer goods).
Does Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding Provide a Higher Strength-to-Weight Ratio than Gas Assisted Injection Molding?
No, Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding does not provide a higher strength-to-weight ratio than Gas Assisted Injection Molding, which creates lightweight and rigid parts by incorporating hollow sections within components. Gas-assisted molding creates hollow sections within parts by injecting pressurized gas during the molding process, reducing material usage and producing lightweight yet rigid components. It results in a better strength-to-weight balance, ideal for large structural or automotive parts that require stiffness with minimal mass. Liquid silicone molding focuses on flexibility, temperature resistance, and durability rather than structural rigidity. The material provides excellent elasticity and long-term performance, but LSR molding is not used for applications where maximizing lightweight strength is the primary goal. Each method serves different production goals, as Gas Assisted Injection Molding for weight reduction and stiffness, and Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding for elasticity and heat stability.
Can Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding Be Used for Multi-Component Parts?
Yes, Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding can be used for multi-component parts through multi-shot or overmolding techniques that bond silicone with thermoplastics or metals. The process allows the combination of liquid silicone with other materials (thermoplastics or metals) through multi-shot molding, producing components with integrated functions in a single cycle. The approach is used in manufacturing medical seals bonded to rigid housings or soft-touch grips over hard plastic bases. However, multi-component designs increase mold complexity and require precise alignment to ensure accurate bonding between materials. Differences in thermal expansion and curing behavior lead to defects or weak adhesion if not correctly managed. Careful material selection and process control are essential to achieve strong, consistent bonds and maintain production efficiency when using LSR molding for multi-component parts.
Is Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding Suitable for Low-Volume Production?
Yes, Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding can be suitable for low-volume prototype production when precision outweighs tooling cost, although mold fabrication remains a significant upfront investment. The process supports shorter production runs due to its relatively quick cycle times, precise material control, and reduced waste during molding. However, mold fabrication involves an initial investment, which makes LSR molding more cost-effective for low-to-medium production volumes. Mold fabrication requires an initial investment, but LSR molding is cost-effective for producing small quantities of detailed components when high precision is needed. Medical devices and consumer products use LSR molding for prototypes and specialty parts that demand precision, flexibility, and durability. The ability to produce consistent, high-quality items without excessive rework makes LSR molding practical for low-volume manufacturing where accuracy and material efficiency are priorities.
Why Use Xometry Injection Molding Services?

Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.

Easy to Use
Get your parts delivered right to your door without the hassle of sourcing, project management, logistics, or shipping.

Vetted Network
We are ISO 9001:2015 certified and AS9100D compliant. Only the top molders that apply to become Suppliers make it through our qualification process.