Compression molding is used across many industries and is a popular choice among Xometry customers. Although it came onto the scene in 1905, it has held its ground over the years through all of our technological advances. There are still plenty of reasons why companies and manufacturers turn to it over other methods. It has proven to be a solid and reliable choice for making everything from dental devices to video game controllers. Up ahead, we’ll go into detail about how compression molding works, what it’s used for, and both its advantages and disadvantages.
What Is Compression Molding?
Compression molding is a manufacturing process used to create plastic and composite parts. Through a mixture of heat and high pressure, it squeezes materials—like thermosetting polymers or thermoplastic compounds—into set shapes. It’s the heat and pressure that allows solid materials to soften and reform into new structures that are wholly even and cured. During the process, curing triggers a chemical reaction, which helps give the final product strength and durability.
What Is the Importance of Compression Molding?
This is one process that’s helpful when it comes to turning pre-impregnated intermediate products into semi-structural and structural composite components. It’s also key for developing fibrous materials that have been impregnated with thermoset and thermoplastic matrices. Not only that, but compression molding is a great process for companies looking to cut costs, minimize waste, and make numerous products. Compression molding is also better suited for manufacturing certain part geometries, such as thick walls.
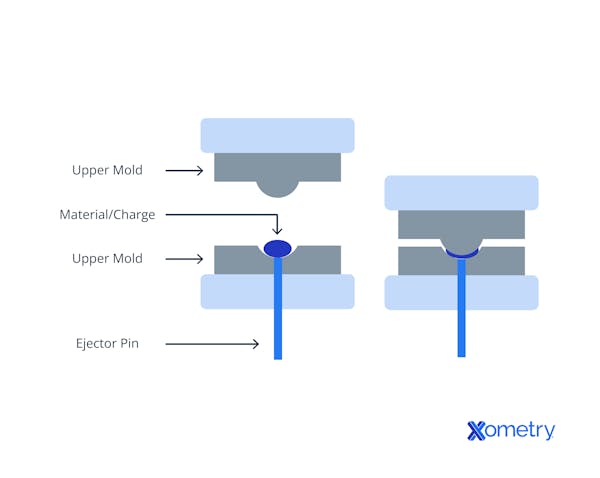
Compression molding diagram
How Does Compression Molding Work?
There are a few steps in the compression molding process. Here’s how it works, according to our engineers:
Step 1: The first step in compression molding is creating the molds, which are responsible for shaping the end product. These are usually made of steel or aluminum and, once they’re put together, have a cavity, an upper mold, and a lower mold.
Step 2: After the mold is created, the machine is set up for the process. Users will clean the mold, input the settings, and turn on the heat. Keeping the temperature controlled is essential for preventing defects and warping.
Step 3: For thermosets, the next step involves placing a charge made of fiber-reinforced resin, silicone, or rubber into the cavity. The mold is then closed while heat, pressure, and speed settings are locked in to begin the molding process.
It’s slightly different for thermoplastics. For these materials, temperature-controlled cooling molds are used instead.
Step 4: Once the shapes are complete, they cool and any extra edges or excess material are removed. Altogether, the process can take 1 to 5 minutes, but it largely depends on how thick the parts are.
Learn more about Xometry's Molding Services
How Long Does the Compression Molding Process Take?
Molding cycle times in compression molding are typically influenced by the thickness of the part being molded. However, they generally fall within the range of 60-300 seconds, making compression molding a fairly fast molding process for thermoset materials.
What Is the Equipment Used for Compression Molding?
These are the main components of a compression molding machine and the tools needed to fulfill the process:
- Large tonnage press. This is usually 150 tons to 2,500 tons.
- Heated mold. As mentioned earlier, the mold will have an upper and lower portion as well as an inner cavity. They’re designed to control the flow of material as it melts and reshapes into the new desired object.
- Heating chamber. This or an oven will be used to heat materials and get them to their molten state.
- Heating lines. These long and cylindrical electrical resistors are the primary heating elements.
- Shop air. This helps clean the cavity and gets rid of debris, particles, and contaminants from different parts of the machine.
- Cutting tools. These are used to manually cut away any leftover materials.
How Is Deformation Utilized in Compression Molding?
Compression molding relies on the deformation of a softened raw material pre-form under pressure and heat to force the material into the desired shape. It involves applying pressure or squeezing a malleable material charge between two halves of a heated mold. The material is then transformed into a molded part as it cools or undergoes curing.
What Are the Materials Used in Compression Molding?
These are the most common materials used for compression molding and why they’re popular:
1. Epoxy
These thermosetting resins have superb mechanical properties, high heat resistance, and dimensional stability. Epoxy is often combined with reinforcing materials like glass or carbon fiber to form high-performance composites. Because of this, the material is usually used for aerospace parts, electrical insulation, and structural composites.
2. Silicone
Known for its top-notch heat resistance, silicone is also flexible and ideal for electrical insulation. Silicone easily flows into the cavity and can be molded into intricate shapes, making it a great material for precision seals, gaskets, medical devices, and automotive components. At Xometry, we offer different durometers to fit your needs precisely.
3. Melamine
Melamine resins offer outstanding heat resistance, hardness, and chemical resistance, making them suitable for compression molding. Melamine molds easily and produces finished parts with excellent surface finishes and dimensional stability. Melamine is commonly used in compression molding for manufacturing kitchenware, decorative laminates, electrical components, and heat-resistant utensils.
4. Urethane
Urethane, or polyurethane, materials are favored in compression molding for their exceptional toughness, abrasion resistance, and impact strength. They can be formulated to exhibit a wide range of physical properties, making them versatile for various applications. Urethane flows well during compression molding, allowing for intricate mold designs and the production of items such as automotive parts, rollers, wheels, and industrial seals.
5. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
This type of plastic is perfect for melting and molding. It offers fantastic chemical resistance, strength, and rigidity. On top of this, it’s capable of handling major impacts, which is why it’s used for automotive components and industrial parts.
6. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS)
For electrical components, industrial equipment, and some automotive parts, manufacturers will often use PPS. This is because it flows well once it’s melted down but cools into a stiff but strong finish.
7. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
You’ll likely recognize this material in the kitchen as it’s used to create non-stick surfaces. In compression molding it offers much of the same benefits—stability in high temperatures, chemical resistance, and a slick surface.
Compression molding works really well for rubber products that have thicker or uneven walls--think insoles, phone cases, or silicone kitchen gadgets.Greg PaulsenDirector, Applications Engineering
What Are the Applications of Compression Molding?
Thanks to its customizable parts and settings and its flexibility with materials, compression molding spans many different industries. It has a lot of different uses, with just a small chunk of those listed below.
1. Kitchenware
The staples in your cooking space may exist thanks to compression molding. This process can make products like bowls, cups, plates, and utensils and create versions that are resistant to heat and breaks.The ever-popular melamine plates used for eating outdoors are often made this way.
2. Automobile Parts
Both small and large components for vehicles like cars, trucks, and tractors can be made through compression molding. As examples, you can get door panels, dashboards, and parts for engines.
3. Parts of Electricity
With the previous materials listed, it’s no surprise that compression molding can be used to make electrical components. Manufacturers can get precise shapes, reliable functionality, and consistency across the board.
4. Video Games and Computers Devices
The devices we spend hours on wouldn’t function the same without the help of compression molding. This process can produce keypads for computers, video game controllers, and parts that provide electrical insulation.
5. Components for Medical and Dental Equipment
You could probably name quite a few tools and devices your doctor and dentist rely on, but without some finer details and tiny components, they wouldn’t be usable! Compression molding can create plastic and silicone parts like syringe stoppers and pieces for respirator masks.
Case Study: Combating COVID-19 with a Contactless, AI-Based Thermal Imaging Device
What Is the Quality of Parts Produced Through Compression Molding?
Compression molding is known to produce high-quality parts. It is a manufacturing process that enables the production of high-volume parts with good dimensional precision, strength, temperature resistance, and surface quality. While no manufacturing process is entirely free from defects, compression molding typically yields parts with lower defect levels compared to other molding processes such as injection molding and transfer molding. Common defects that can occur in compression molding include flash, voids and porosity, uneven curing, and delamination. However, these defects can be minimized through proper mold design, precise temperature and pressure control, and material selection.
Are Compression Molding Products Durable?
Yes. Compression molding produces durable products due to several key factors. First, the selection of thermosetting polymers in compression molding offers exceptional strength, rigidity, and chemical resistance. These materials undergo a chemical reaction during curing, forming a crosslinked network that enhances durability and stability. Additionally, the ability to include high fiber content, such as glass or carbon fibers, further improves mechanical properties like strength, stiffness, and impact resistance. The uniform distribution of material within the mold cavity ensures consistent mechanical properties throughout the part, minimizing weak points and potential failure areas.
Is Compression Molding Safe To Use?
Yes, compression molding is generally considered a safe manufacturing process when proper safety measures are followed. Some key procedures to follow include: wearing appropriate protective gear, including safety glasses, gloves, and heat-resistant clothing, performing regular maintenance and inspection of the compression molding machine, handling and storing raw materials according to the supplier’s instructions, furnishing good ventilation in the work area, and providing adequate training and education of personnel and operators.
Is Compression Molding in Demand?
Yes, not only is the demand for compression molding currently strong, but the global compression molding market is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. The compression molding machine market is expected to experience substantial revenue growth. The market is being fueled by increased investments in the manufacturing, infrastructure, and automotive sectors by both private and public entities on a global scale. These investments have led to a surge in demand for compression molding machines. As a result, the forecast period presents lucrative opportunities in the global compression molding machine market.
What Is the Lifespan of Compression Molding Products?
The lifespan of compression molding products can vary depending on several factors, including: the specific material used, the intended application, and the level of maintenance and care provided to the product. However, compression molding products are generally designed to be durable and long-lasting.
What Is the Future of Compression Molding?
At Xometry, we have only seen demand for compression-molded products increase over time. The need for products that are produced through this method is increasing thanks to specific industries seeing a boom in growth—whether that’s new medical and dental developments or an influx of new car parts.
Machine learning, AI, and automated systems is also making compression molding simpler to execute. While the demand for compression molded products is growing, so are the available materials that can be used in these types of machines. With how easy it is to manufacture everyday items like dishes and more advanced components for a computer to function, it’s hard to see this manufacturing process winding down in the near future.
What Are the Advantages of Compression Molding?
Here are some of the advantages that Xometry makes their customers aware of when considering the process:
Advantages include:
- Ultra-strong parts that last through immense wear and tear and heavy-duty use.
- Molds are highly customizable and can be created for intricate designs or more basic styles.
- Compression molding can handle various materials, including highly viscious materials, and therefore make a wide range of different products.
- Molds are efficient when it comes to using material, which saves money in the long run.
- The parts made from compression molds have excellent finishes.
- Batch production is possible and users can create settings and cycles for maximum efficiency.
- Compression molding machines can use recycled and eco-friendly materials—a perk for sustainably-minded companies.
What Are the Disadvantages of Compression Molding?
The disadvantages of compression molding include:
- Complex parts are no problem, but intricate components with thin walls is a no-go.
- Pressure range limits make it difficult to create detailed shapes
- While it only takes a few minutes, compression molding is slower than other processes like injection molding.
- The heat, pressure, and cooling process can lead to longer production times, too.
- Flash can happen and create imperfect parts, wasting material, time, and resources.
The Future of Compression Molding
At Xometry, we have only seen demand for compression-molded products increase over time. The need for products that are produced through this method is increasing thanks to specific industries seeing a boom in growth—whether that’s new medical and dental developments or an influx of new car parts.
Machine learning, AI, and automated systems is also making compression molding simpler to execute. While the demand for compression molded products is growing, so are the available materials that can be used in these types of machines. With how easy it is to manufacture everyday items like dishes and more advanced components for a computer to function, it’s hard to see this manufacturing process winding down in the near future.
What Is the Difference Between Compression Molding and Injection Molding?
Compression and injection molding are similar but have a few key differences. These can influence your decision when it comes to selecting the best process for the job. Compression molding uses heat and pressure to form a shape within the mold. Injection molding, as its name suggests, funnels or injects hot material into a closed mold.
Injection molding is better for objects that require intricate details (like threading or ribbing), thin walls, or complex parts. Compression molding wins out when it comes to thicker products needed for their strength, robustness, and durability. Overall, Injection molding processes tend to be quicker than compression processes.
How Xometry Can Help
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including injection molding and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Get an instant quote today.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


