By now, you’ll likely be aware of how much we love CNC (computer numerical control) machines here at Xometry. They’ve made otherwise arduous manual manufacturing processes, like cutting, drilling, and turning, practically effortless via automation. With CNC machining, almost everything is computerized, so these processes are more accurate than manual methods, resulting in higher-quality parts. Most CNC machines are either 3- or 5-axis, and, in this article, we’ll look at their differences and what they’re each good for.
What Is CNC?
CNC (Computer numerical control) refers to the use of computers to direct the motion of manufacturing machinery. Most CNC machines perform functions that are also found on manual machining devices but depend on a computer program to direct the motion instead. That makes the cutting tool’s movements very precise and generally results in higher-quality parts than those made with manual drill presses, lathes, etc.
What Is a 3-Axis CNC?
A 3-axis CNC machine, such as a lathe, mill, or machine tool center, moves its tool (whether it’s a cutter, drill, or mill) along the X (left to right), Y (front to back), and Z (up and down) axes. More specifically, it can move either horizontally (X-Y axes) or vertically (Z axis) to control the cutting depth. This is what a 3-axis CNC machine looks like:
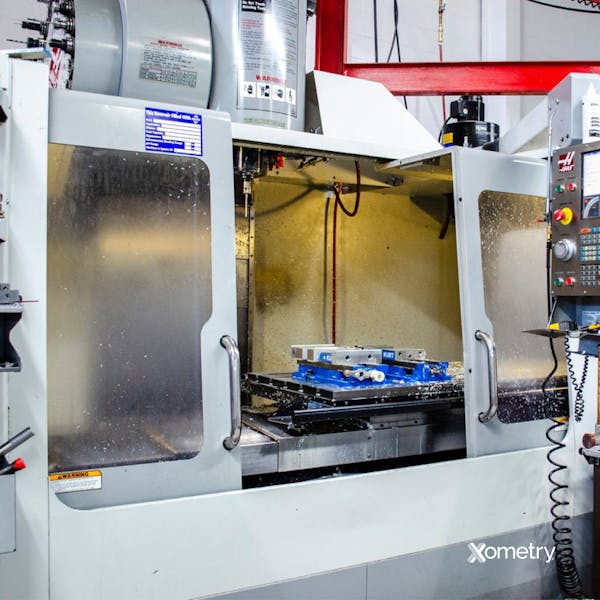

This type of machine can cut and plane to specific depths, depending on the tool used and the material being worked on. Its limited range of motion and the fact that it can’t automatically rotate the workpiece make it best for making simpler parts with straightforward shapes and designs and minimal details. These machines are best for making 2D and 2.5D parts and shorter production runs, and they’re reasonably priced, making them ideal for startups or small to medium-sized businesses.
What Can a 3-Axis CNC Do?
A typical 3-axis CNC machine is capable of carrying out a variety of machining tasks, including: cutting, drilling, and milling. Others are designed as CNC lathes. However, in terms of part complexity, the constraint of those three axes means the machine has some distinct limitations. The best 3-axis machines are used to produce parts with straightforward geometries and minimal design or detail requirements. 2D and 2.5D parts are the best targets for 3-axis CNC machines.
What Are the 3-Axis CNC Examples?
Examples of 3-axis CNC devices are:
- CNC lathes
- CNC milling machines
- CNC machine tool centers
These machines are frequently employed in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
What Are the Advantages of 3-Axis CNC?
The advantages of 3-axis CNC machines are listed below:
- Cost-Effective: 3-axis CNC machines are more reasonably priced than 5-axis machines.
- Easy to Operate: 3-axis CNC machines require minimal training and are simple to use. They are appropriate for small to medium-sized businesses because they are also simple to program.
- Low Maintenance: Compared to 5-axis CNC machines, 3-axis CNC machines have fewer moving parts, making them simpler to maintain and less prone to wear and tear.
- High Accuracy: A variety of applications can benefit from the accurate and precise parts built on a 3-axis CNC machine.
What Are the Disadvantages of 3-Axis CNC?
The disadvantages of 3-axis CNC machines are:
- Limited Capability: Since there’s no way to automatically rotate the workpiece, 3-axis machines can only attack from certain angles. They work best for making parts with simple geometries.
- Limited Efficiency: These are less efficient than 5-axis CNC machines because they require multiple setups to produce complex parts.
Is the 3-Axis CNC Not Capable of Creating 3D Objects?
While 3-axis CNC machines can create 3D objects, there are some restrictions. 3-axis CNC machines can produce 3D parts with clear and simple geometries but not those with complex geometries and finely detailed designs.
What Is a 5-Axis CNC?
As well as left–right, front–back, and up–down, a 5-axis CNC machine has two more movements up its sleeve: it can also rotate its tool around the other two axes (A and B). You can see how the process works in the diagram below.

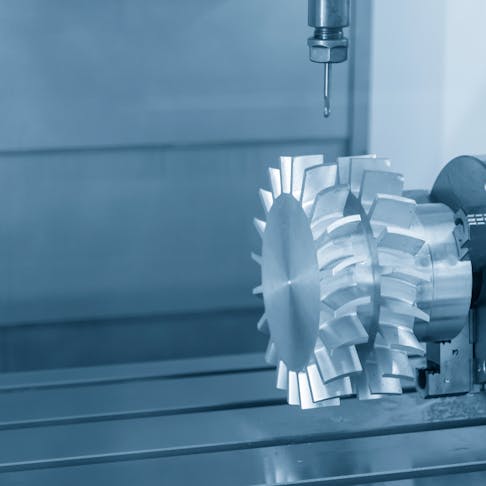
With a full five-axis range of motion, these machines can work at multiple angles to precisely make complex and intricate parts with smooth surfaces, angles, and contours. They can also perform continuous milling, which saves a lot of time, and don’t need any manual intervention as they rotate the workpiece automatically. These high-tech CNC and milling machines or routers can make turbine blades, molds, and impellers, such as the one in the below image.
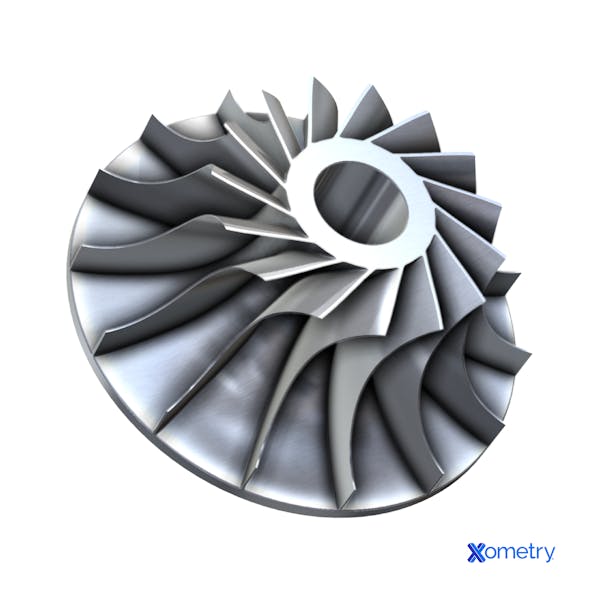

What Can a 5-Axis CNC Do?
A 5-axis CNC can create geometries that demand multiple angles and contours. It can move the cutting tool along five axes, leading to smoother surfaces and more precise parts. A 5-axis CNC machine can also perform continuous milling, which enables the cutting tool to follow the material's curvature and produce fewer marks and steps.
A 5-axis CNC machine can be used to create parts such as: impellers, turbine blades, molds, and aerospace components. For instance, it is used in the aerospace industry to create intricate shapes for aircraft engine components. 5-axis capability is also important for medical implants and prosthetics.
What Are the 5 Axis CNC Examples?
Some examples of 5-axis CNC machines include:
- Continuous 5-axis CNC machines
- 5-Axis CNC milling machines
- 5-Axis CNC routers
What Are the Advantages of 5-Axis CNC?
Listed below are the advantages of 5-axis CNC machines:
- Increased Efficiency: 5-axis machines can speed up production and improve efficiency. They can produce complex shapes and perform continuous milling operations.
- Improved Accuracy: They can create smoother surfaces and more accurate parts because they enable the cutting tool to move along five axes.
- Reduced Tool Changes: Complex geometries are possible thanks to continuous milling operations. That also translates into fewer tool changes. This continuous milling reduces the need for manual intervention and saves time.
- Versatility: 5-axis devices can produce a wide variety of parts and geometries.
What Are the Disadvantages of 5-Axis CNC?
Listed below are the disadvantages of 5-axis CNC machines:
- Cost: 5-axis CNC machines are more expensive than 3-axis CNC machines, making them harder for smaller businesses to afford.
- Training: Due to their complexity, they require more specialized training and expertise to operate and maintain.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is necessary to keep these complex machines running smoothly and to prevent breakdowns.
Does 5-Axis CNC Have No Limitations To Angle?
A 5-axis CNC machine can mill materials at nearly any angle, but it does have some restrictions. The length of the cutting tool, the nature of the material being milled, and the reach of the machine itself all affect the possible angles and dimensions. Additionally, the cutting tool becomes less stable at more extreme angles, which may have an impact on precision.
3-Axis vs. 5-Axis: Pros and Cons
The main difference between these two types of CNC machines is the number of ways they can move their tool: one has three, and one has five. This seemingly small factor, however, makes a world of difference, as you can see in the side-by-side comparison table below.
| Factor | 3-Axis | 5-Axis |
|---|---|---|
Factor Cutting tool movement | 3-Axis Along X, Y, and Z axes | 5-Axis Along X, Y, Z axes, and also along A and B rotational axes |
Factor Efficiency | 3-Axis Good | 5-Axis Excellent, quick |
Factor Tool changes | 3-Axis Need multiple setups for complex parts (re-clamping, repositioning, etc.) | 5-Axis Minimal, can work on part from different angles without repositioning |
Factor Capabilities | 3-Axis Limited, no complex shapes, undercuts, or multi-sided features | 5-Axis Can make deep cuts on all sides of workpiece, intricate shapes and undercuts |
Factor Accuracy | 3-Axis Good | 5-Axis Excellent |
Factor Ease of operation | 3-Axis Minimal training needed, simple to use and program (CNC programming skills needed) | 5-Axis Needs specialized training and expertise and more advanced CAD/CAM programming |
Factor Cost | 3-Axis $25,000 to $50,000 | 5-Axis $80,000 to over $500,000 |
Factor Maintenance/operating costs | 3-Axis Low | 5-Axis Higher |
Factor Cost per part | 3-Axis Lower | 5-Axis Higher, although faster production could lower cost of more complex parts |
Factor Maintenance needs | 3-Axis Low due to fewer moving parts | 5-Axis High, needs regular maintenance to run smoothly |
Factor Wear and tear | 3-Axis Less prone | 5-Axis More prone due to additional moving parts |
Factor Applications | 3-Axis Simpler parts for automotive, aerospace, and electronics (housings, panels, flat surfaces) | 5-Axis Many different sizes and shapes, aircraft engine parts, medical implants and prosthetics |
3-Axis vs. 5-Axis: Pros and Cons
What Is the Difference Between 3-Axis and 5-Axis CNC?
A 3-axis CNC and 5-axis CNC differ in their ability to orient and move the cutting tool along multiple axes. A 3-axis CNC machine is capable of moving its cutting tool along the X, Y, and Z axes. A 5-axis machine, on the other hand, can move the cutting tool along the X, Y, Z, A, and B axes.
The machine’s price is another difference between the two. Of the two, the 3-axis version is far cheaper to buy, program, and operate. The cost per part is thus often lower as well.
Another critical differentiating factor is the ease with which you can create and manipulate complex shapes. Even in complex geometries, deep cuts are possible with 5-axis machines. You can work on all sides of your workpiece without manually rotating it, thus improving productivity. A 3-axis machine, on the other hand, needs numerous adjustments to help the machine cut complex geometry.
How Much Does 5-Axis CNC Cost Compare to 3-Axis CNC?
Prices for 3-axis CNC devices range from $25,000 to $50,000 while 5-axis go from $80,000 to over $500,000. The costs vary depending on whether they are used for entry-level or production-level work.
Frequently Asked Questions About 3-Axis and 5-Axis CNC Machines
How Are 3-Axis CNC and 5-Axis CNC Programmed?
Programming for both 3- and 5-axis CNC work is done manually by professionals. However, programming 3-axis machines is easier than programming 5-axis machines, so the latter will usually warrant a higher-paid programmer.
Is the 3-Axis CNC a Good Starter Investment Than the 5-Axis CNC?
Yes, a 3-axis CNC is a better starter investment than a 5-axis CNC. It is more affordable in terms of purchase, development, and upkeep costs.
Do CNC Machines Use a Lot of Electricity?
Yes, CNC machines draw quite a bit of power. A 20-hp conventional CNC machine with a 7 kw/hr rating can run a monthly power bill of around $1,400. However, some CNC machines are more energy-efficient than others.
How Xometry Can Help
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities including CNC machining, 3D printing, injection molding, laser cutting, and sheet metal fabrication. You can get started today by quickly and easily uploading your designs to the Xometry Instant Quoting Engine®.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.