"Plastic fabrication" is the step in the design and manufacturing process when a selected shaping or molding method turns raw polymer materials into finished products. The ultimate goal in the plastic manufacturing business is to select the most suitable fabrication method for the economical production of a diverse range of goods suitable for various applications, from simple household items to sophisticated industrial components. The fabrication process typically entails some combination of cutting, molding, welding, and assembly steps to achieve the desired plastic shapes and sizes.
Plastic materials are generally adaptable to various fabrication methods, allowing manufacturers to produce affordable and lightweight plastic parts. However, plastic fabrication also has its drawbacks, including the potential toxicity of the raw materials, sensitivity to UV light, and a lack of high-temperature strength compared to metals.
This article presents an overview of plastic fabrication, explaining its definition, purpose, methods, materials, advantages, and typical applications.
What Is Plastic Fabrication?
The term "plastic fabrication" refers to the process of designing, producing, and assembling custom or mass-produced components made from plastic or composite materials. This field encompasses a wide range of manufacturing techniques used to form raw plastic into functional parts for various industries, including automotive, medical, aerospace, and consumer goods.
- Plastic extrusion
- Plastic pultrusion
- Plastic welding
- Thermoforming
- Injection molding
- Rotational molding
- Blow molding
- Plastic CNC machining
- Vacuum casting
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM)
- Selective laser sintering (SLS)
Each of these methods involves a distinct set of processes. Plastic’s adaptability, cost-effectiveness, and low weight make it a highly versatile material, which is why it is widely used across numerous industries.
What Is Plastic Fabrication Also Known As?
“Plastic processing” and “plastic manufacturing” are other terms for plastic fabrication. This phrase can refer to any or all of the steps that go into shaping and molding plastic materials into finished goods.
What Is the Purpose of Plastic Fabrication in Manufacturing?
Plastic fabrication is used in manufacturing to create finished goods with specific forms and functions from raw plastic materials. Due to plastic's flexible nature and affordability, this process enables the production of a wide range of items used in various industries, including consumer goods, automotive components, medical devices, and electronics.
What Are the Industries That Use Plastic Fabrication?
The automotive, food, aerospace, electronics, medical, packaging, and consumer goods industries utilize one or more plastic fabrication methods to produce finished products. The adaptability of plastic fabrication enables it to serve a variety of applications in these industries. Injection molding is a widely used plastic fabrication method in various sectors. The process starts with molten plastic material injected into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies to form the desired shape. Additionally, the medical field utilizes injection molding to produce items such as syringes, IV components, and sterile medical equipment.
How Does Plastic Fabrication Work?
Plastic fabrication involves multiple processes, starting with design and planning, material selection, material preparation, forming and shaping, finishing, assembly, and concluding with quality control and inspection. There are several plastic fabrication methods, each with its unique processes. Listed and discussed below are three common methods:
- 3D Printing: 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, constructs parts layer by layer from a digital 3D model. It is particularly effective for producing complex geometries and rapid prototypes. The process begins with designing the model using CAD software, followed by selecting a compatible thermoplastic filament or resin, particularly important for FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers. The chosen material is loaded into the printer, where it is extruded or cured layer by layer onto a build platform. After printing is complete, the object is finished through support removal or surface smoothing, and then inspected for dimensional accuracy and defects.
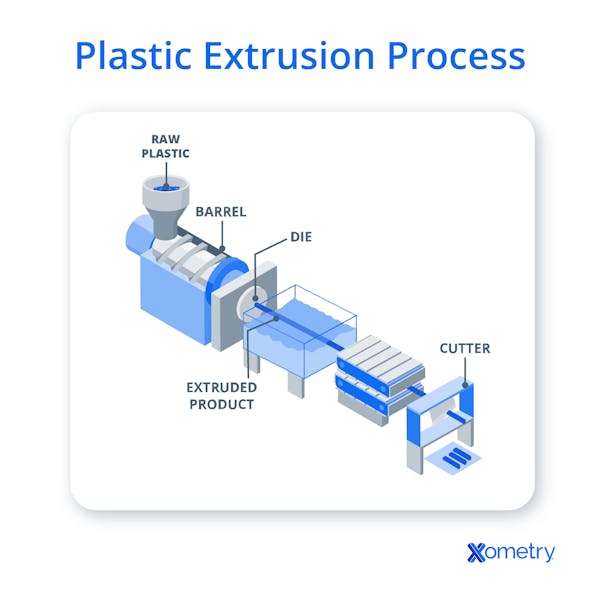
- Extrusion: Extrusion is a popular method for shaping plastic pellets into continuous objects such as sheets and pipes. Fundamental procedures include designing the required die form, selecting appropriate plastic pellets based on their properties, melting the pellets, and then extruding the molten plastic through the die to shape it. The operation is finished by cutting the continuous shape to the necessary lengths and checking for uniformity and flaws.
- Plastic Injection Molding: The plastic injection molding process creates intricate pieces by pouring molten plastic into a mold. After choosing the right material and designing the mold, plastic pellets are heated and injected into the mold. There, they cool and solidify inside the mold's shape. After this, the object is removed from the mold and thoroughly inspected for flaws, dimensions, and overall quality.
What Is the Step-by-Step Process of Plastic Fabrication?
Each step of the plastic manufacturing process, from design to delivery, is essential for economically transforming raw polymeric materials into usable products.
1. Design and Planning
The first step in manufacturing a successful product is to understand the product requirements, including (but not limited to) size, dimensional tolerances, mechanical properties, and chemical and temperature resistance. A preliminary design, usually a 3D computer model, can then be created.
2. Material Selection
Choose the appropriate plastic (e.g., ABS, PVC, polyethylene, polycarbonate) based on the functional needs of the product. Consider factors like strength, flexibility, cost, and environmental conditions.
3. Material Preparation
Prepare the selected materials by extruding, molding, or cutting them into usable shapes.
4. Forming and Shaping
Shape the plastic materials into the desired product using methods like injection molding, thermoforming, or CNC machining.
5. Finishing and Assembly
Assemble subcomponents into final parts if necessary and add any necessary features. Other finishing processes that may be needed include burr or flash removal, surface smoothing, painting, sealing, or curing.
6. Quality Control and Inspection
Verify that the part meets all customer specifications by using statistical process control and inspection.
7. Packaging and Delivery
Deliver the finished products to the intended recipients in packaging that adequately protects the product from damage during transport.
Skipping any of the steps listed above may result in the production of plastic parts that are defective or incomplete. Each step is crucial to achieving success and meeting customer expectations.
Can Fabricated Plastic Parts Be Polished Using Acetone Vapor Smoothing?
Acetone vapor smoothing is a technique used to reduce surface roughness and achieve a polished appearance on fabricated plastic parts. The plastic product is exposed to acetone vapor, which dissolves the rough surface layer of the polymer, leaving behind a smoother surface. Acetone vapor smoothing works by thoroughly dissolving the plastic's outer layer and removing any surface flaws, with a particular focus on the high surface energy associated with asperities.
To learn more, see our full guide on Acetone Vapor Smoothing.
What Are the Materials That Can Be Used in Plastic Fabrication?
All plastics can be manufactured into final products using suitable fabrication techniques. The following materials are some of the ones that are commonly employed in the manufacture of plastics:
1. Acrylic (PMMA)
PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate, or simply acrylic) is a transparent thermoplastic that resists UV light and has excellent optical clarity. Its lightweight and weather resistance make it a popular choice for displays, signage, and lenses. Acrylic (PMMA) fabrication is best accomplished through techniques like CNC machining, laser cutting, and heat bending. Thermoforming works well, too. These methods utilize acrylic's clarity, lightness, and adaptability for various applications, including displays, signage, and lenses.
2. Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is particularly well-suited for production techniques such as injection molding, where its impact resistance is leveraged to create sophisticated safety gear, eyewear, and electronic components. This technology offers critical transparency and durability, surpassing alternatives like vacuum forming and machining in terms of speed.
3. Polyethylene (PE)
The versatile plastic polyethylene is available in a variety of densities, including high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE). Due to its chemical resistance, flexibility, and affordability, it is used in pipes, household goods, and packaging. Extrusion, blow molding, and injection molding are optimal fabrication methods for harnessing the potential of Polyethylene (PE), encompassing diverse densities such as HDPE and LDPE.
4. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE is rigid and offers a high strength-to-weight ratio. It is widely used in bottles, toys, and pipes. Its resistance to chemicals and impact makes it suitable for demanding environments.
5. Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene, renowned for its chemical resistance and toughness, is often used in textiles, food containers, and automotive parts. It strikes a balance between toughness and affordability. Injection molding and thermoforming are both excellent methods for fabrication. While thermoforming is efficient for producing larger, less complex parts, injection molding is more suitable for making intricate, smaller components.
6. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC is a flexible plastic that is widely used in medical equipment, vinyl flooring, and pipes. PVC decking is an application of PVC, offering numerous advantages due to its composition of synthetic polyvinyl chloride rather than organic materials like wood pulp. Because it is synthetic, it is extremely resilient to water and can tolerate a variety of weather situations. It requires less upkeep than conventional wood decking, thus yearly sealing is not necessary. Additionally, it has a lifespan of at least 50 years.

7. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
PET's optical clarity and good mechanical properties make it a top choice for beverage bottles and food containers. Its recyclability adds to its popularity as a sustainable packaging material.
8. Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Also known as acetal, POM is used in precision parts such as gears and bearings. This is due to its excellent mechanical properties and resistance to wear and chemicals. Blow molding is suitable for certain plastic materials, including POM. It's commonly used for producing hollow parts like bottles, containers, and certain types of POM components.
9. Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene is derived from the monomer styrene and is a versatile polymer widely employed for its rigidity. Found in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation, PS is used in various applications. As a thermoplastic, it's solid at room temperature but can be melted for molding or extrusion at higher temperatures, after which it's resolidified. This adaptability stems from its liquid hydrocarbon origin, derived commercially from petroleum.
“Plastic fabrication plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing by enabling the cost-effective production of durable, lightweight components across diverse industries. Its versatility allows for innovative design solutions, supporting everything from rapid prototyping to large-scale production.”
How Much Does Plastic Fabrication Cost?
The cost of manufacturing plastic products depends on the size of the part, the material it is made from, and the fabrication method used. Simple molds cost between $3,000 and $6,000, while more complex, large-scale, or high-volume molds can run between $25,000 and $50,000 or more. For exceptionally complex projects, costs may exceed $100,000. Plastic fabrication encompasses a range of methods beyond molding. Hobbyists can buy entry-level 3D printers for $200 to $500. For individuals with some experience, midrange solutions between $500 and $2,000 are suitable. Professionals wanting top-notch quality can purchase high-end 3D printers for $2,000 to $10,000. Industrial variants, priced between $10,000 and $100,000, are excellent for use in the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries.
What Are the Advantages of Plastic Fabrication?
Advantages of fabricating products from plastics include:
- Plastics can be molded into various shapes and sizes for a wide range of applications.
- Plastic components are lightweight, reducing transportation costs.
- Polymers are resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and weather.
- It is easy to create complex designs and features using plastics.
What Are the Disadvantages of Plastic Fabrication?
Disadvantages of fabricating products from plastics include:
- Many plastics are not biodegradable, leading to pollution.
- Certain plastics melt at relatively low temperatures, limiting their use in high-temperature applications.
- Certain plastic formulations can be brittle, making them prone to cracking or breaking under stress or impact.
- Exposure to sunlight can cause color deterioration in the finished plastic part.
What Are Examples of Fabricated Plastic Products?
Here are some examples of products fabricated from plastics:
- Plastic bottles, containers, and bags
- Toys, kitchenware, and electronics casings
- Bumpers, dashboards, and interior components
- Syringes, IV bags, and surgical gloves
- Pipes, insulation, and window frames
Common FAQs About Plastic Fabrication
What Is the Quality Level of Fabricated Plastic Parts?
Products made of plastic can vary in quality depending on the material used, the manufacturing process, and the design. Durability, resistance to the elements, and precise dimensions are all features of high-quality plastics. However, issues like brittleness, warping, or a shorter lifespan may result from the use of poor-quality materials or poorly controlled production techniques.
Are Fabricated Plastic Products Durable?
Yes, depending on factors like material choice, design, and manufacturing techniques, fabricated plastic products can be durable. High-quality plastics, sound engineering, and the right finishing processes can enhance a product's durability, making it more resistant to abrasion, impact, and environmental elements. Less durable products may be the result of using inferior materials, poor manufacturing practices, or the misapplication of materials when designing the product in the first place.
What Is the Difference Between Plastic Fabrication and Plastic Extrusion?
Plastic extrusion is a particular technique within the field of plastic fabrication, whereas plastic fabrication encompasses a broader range of techniques, including shaping, molding, cutting, welding, and assembly of plastic components into finished goods. Plastic extrusion involves melting plastic and forcing it through a die to form continuous profiles with uniform cross-sections. This process is often used for items like pipes, tubes, and window frames.
To learn more, see our full guide on Plastic Extrusion.
What Is the Difference Between Plastic Fabrication and Sheet Metal Bending?
Plastic fabrication refers to making products from plastics using any of a number of different manufacturing methods. One of the possible methods for producing plastic parts is bending sheet plastic. Some examples of parts made by bending plastic sheets are signage, displays, covers, enclosures, and light diffusers.
Sheet metal bending is a specialized manufacturing process used to work with thin metals. In particular, in sectors like consumer goods and automotive, it offers versatility for producing intricate designs and one-of-a-kind items.
Sheet metal bending is used to reshape metal sheets to create desired shapes and angles. The construction and manufacturing sectors often employ this method to produce components such as brackets, enclosures, and panels. Sheet metal bending, as opposed to plastic fabrication methods, involves working with metal materials, which offer improved strength, rigidity, and durability compared to plastics.
To learn more, see our full guide on Sheet Metal Bending.
Summary
This article presented plastic fabrication, explained it, and discussed how it works and its advantages. To learn more about plastic fabrication, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including fabrication and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


