When trying to work out if a material can resist pressure, copious wear, transport, and storage, manufacturers often conduct a burst strength test. This helps them choose materials that are durable, efficient, and, above all, safe. Let’s learn more about this useful test.
What is Burst Strength?
A material’s burst strength is the maximum pressure it can withstand before rupturing. It’s measured in PSI (pound-force per square inch) or kPa (kilopascals), depending on the standard used. When we say “bursting,” we mean rupturing to the extent of failure. The reason it’s called bursting and not, let’s say, breaking is because pressure is involved, so when these parts do fail, they tend to produce a bit (sometimes a lot!) of an explosion. Think of an over-inflated balloon or a full soda can if dropped on the floor.
Benefits and Challenges
A burst strength test ensures that a material is in compliance with and up to the required standards (certain industries have regulations that specify the minimum burst strength requirements). The test helps manufacturers to weed out defective or non-suitable materials, and ultimately find the perfect one for their needs. They’ll also be able to avoid subjecting the final product to pressures that exceed the burst strength limit. Ultimately, knowing this measure can help save money, time, and the company’s reputation in the long run by avoiding product failure.
Although it’s undoubtedly a useful test, it’s not done by all manufacturing companies. This could be due to the associated challenges. For instance, the samples need to be prepared consistently to ensure the most accurate results, which can be tricky. The testing equipment (which we’ll go over a bit further down) needs to be regularly calibrated and maintained—something that adds to the budget, and might be unfeasible for smaller companies. Performing the test also requires a certain level of technical expertise to do correctly, meaning extra staff training.
Applications
That said, there are a few industries in particular that should prioritize this test over others and set aside a budget for it (or would do well to). These include the manufacturing of products that are subject to internal pressures, like packaging materials, textiles, and containers. When it comes to packaging, manufacturers need to make sure that their products, whether plastic or paper, can remain durable and keep the contents of the packages protected during transportation, use, and storage. This is especially important for medical packaging, where the products inside need to stay sterile and safe to use and is conducted on pharmaceutical blister packs and sterile pouches, too.
For textiles, the burst strength is useful to know when making furniture upholstery, and clothes like jeans or weather-resistant and heavy-duty items. It’s also used to test the strength and durability of plastic films, bottles, and containers, and both metal and plastic pipes. For pipes, there’s a special version of the test that adds pressure until the sample ruptures or leaks. It comes in handy for the oil and gas and chemical industries.
Testing Burst Strength
To test a material’s burst strength, hydrostatic pressure is applied to a sample of it until it bursts. There are different types of pressure depending on what’s being tested. These are:
- Hydraulic: Uses liquid, like oil or water, to apply force to a material externally
- Pneumatic: Similar to hydraulic pressure but uses compressed air or gas
- Internal pressurization: Uses fluid or gas inside packaging
- Internal air pressure: Similar to internal pressurization but just uses air
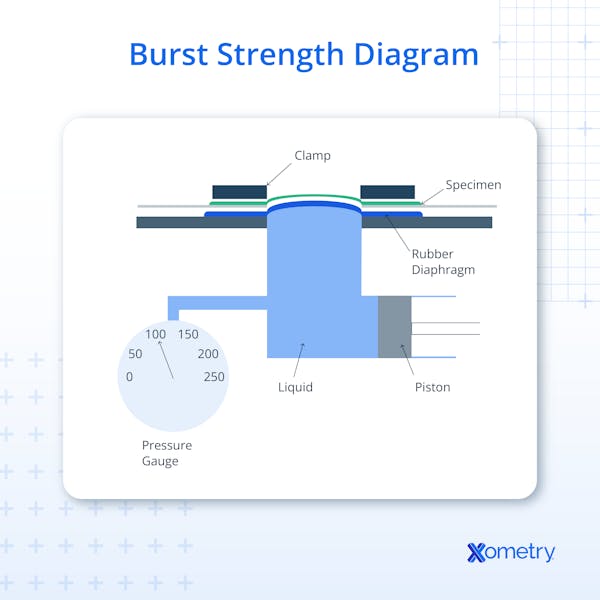
For paper, a version of the test, known as a Mullen test (after its inventor, J.M. Mullen), is used, which entails applying hydraulic pressure to a rubber diaphragm, which then transfers the force to the sample until it bursts.
The specific machine used to test this is simply yet aptly named a burst strength tester. These devices are widely available and have everything needed to do the test, but they must be properly calibrated beforehand for an accurate result. The device consists of:
- A sample holder that clamps and holds the material in place
- A plunger used to apply force to the material (often a diaphragm)
- A hydraulic or pneumatic system to provide the pressure
- An analog or digital pressure indicator that shows the amount of pressure put on the sample (can be shown on a computer screen as a graph)
- The controls (buttons and knobs) to operate everything, although some testers nowadays are fully automated and need minimal human intervention
To perform a burst strength test, you’ll need a controlled environment, as temperature and humidity can affect the strength of many materials, like paper. Since there’s some bursting involved (no surprise there), appropriate safety precautions should be taken, i.e., wearing PPE and using shielding. You’ll also need to be fully trained on the method, the equipment, and the relevant standards, some of which can be found in the table below.
| Material | Standard | Pressure Method |
|---|---|---|
Material Paper | Standard ISO 2758:2014 | Pressure Method Hydraulic |
Material Fabrics (industrial, textiles) | Standard ISO 13938-1:2019 | Pressure Method Hydraulic |
Material Fabrics (gentler method) | Standard ISO 13938-2:2019 | Pressure Method Pneumatic |
Material Paperboards (corrugated cardboard) | Standard ISO 2759:2014 | Pressure Method Hydraulic diaphragm system |
Material Flexible packaging seals | Standard ASTM F2054 | Pressure Method Internal pressurization |
Material Packaging materials (whole package test) | Standard ASTM F1140 | Pressure Method Internal air pressure or vacuum |
Material Textiles | Standard ASTM D3786 | Pressure Method Hydraulic |
Burst Strength by Material
The burst strength testing process is fairly straightforward. The sample—typically a circular or rectangular piece of the test material—is prepped and securely clamped into the tester. In the case of paper and paperboard, the sample is put on a rubber diaphragm. Pressure is then gradually applied until the sample bursts. The pressure at which the sample bursts is the material’s burst strength.
FAQs on Burst Strength
What’s the difference between bursting strength and bursting factor?
While they sound alike and are both important measurements for determining the strength and durability of packaging materials, bursting strength and bursting factor are quite different. As we’ve seen, bursting strength is the maximum amount of pressure that a material can handle before tearing or bursting, and it’s typically measured in PSI. The bursting factor is a relative measure of strength, calculated by dividing the sample’s bursting strength by the basis weight. It helps manufacturers compare the durability of materials with different weights.
What’s the difference between bursting strength and other strength types?
Technically speaking, burst strength testing measures the pressure required to rupture a material by applying biaxial stress—meaning stress is applied in multiple directions at the same time—until failure occurs. Tensile strength testing measures how much stress a material can withstand before breaking while being stretched and uses uniaxial (single-direction) stress.
Compression strength testing evaluates how well a material can bear loads that compress it, such as structural metals or items that get stacked on top of each other (e.g., cardboard and plastic boxes). Tear strength testing measures how well a material resists the growth of an existing tear when force is applied in a single direction.
What factors could affect the result of a burst strength test?
There are several things that could alter the outcome, including a material’s composition, thickness, density, and the manufacturing method used to make it. The environment can also play a role, for instance, paper breaks down easier in humidity.
How Xometry Can Help
For any more information or clarification on burst strength, reach out to one of our representatives. We also offer a bunch of manufacturing services, including CNC machining, laser cutting, and 3D printing. You can get started today by uploading your designs to the Xometry Instant Quoting Engine®!
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


