Silicone is a fascinating material that comes in many formats, bends and stays flexible in all kinds of environments, and doesn’t have a melting point in the truest sense of the word. Made up of siloxanes, you can find silicone in oil, rubber, resin, and gel formats (plus others), whether you need a good spatula for flipping food or a sealant to fill gaps in a bathroom or window.
It came to be in the early 1900s after F.S. Kipping combined polydiphenylsiloxane, Ph2SiO (Ph denoting phenyl, C6H5), by analogy with the formula of the ketone benzophenone, Ph2CO. While it was originally called silicoketone, it later received the catchier name silicone, then the more scientifically correct name siloxane down the road. Read on to wrap your head around this interesting and hard-to-define material.
What Is Silicone?
Silicone is one of the many polymers that exist, but it differs because it’s made up of siloxane chains. To create it, you need an oxygen backbone chain with two organic groups attached to each silicon center. The organic group in its composition almost always includes methyl, and the materials can be cyclic or polymeric. When you adjust the chain lengths, cross-linking, and side groups, you can get silicones that have different properties.
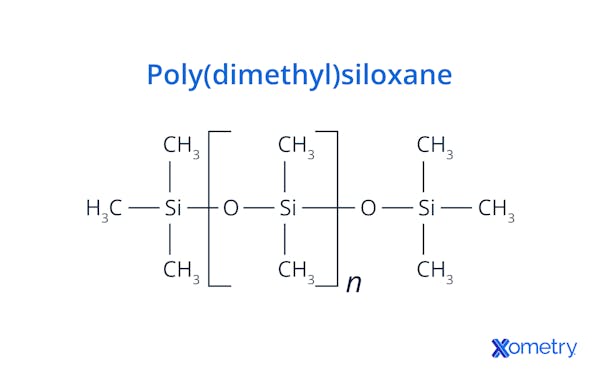
As far as texture and appearance go, you have a wide range of variants with silicones. They can be ultra liquidy substances, rubbery formats, gel-like substances, or hard plastics. Silicone oil is also extremely common and is also known as polydimethylsiloxane or PDMS.
How It’s Made
Silicone is made by pulling silicon from silica and passing it through hydrocarbons. It is then combined with other chemicals to create silicone. The rubber version of silicone has an inorganic Si-O structure that has organic functional groups attached. The bond between silicon and oxygen gives it great resistance to high temperatures and its ability to remain flexible at many different temperatures.
Once you have the silicone polymer, it gets blended with fillers and aids to create a stiff gum. Then, it’ll get crosslinked at a high temperature with the help of peroxides or polyaddition curing. After this is done, you have silicone, a solid elastomeric material.
Silicone vs. Silicon
Let’s clear one thing up first. Silicone and silicon often get confused with one another, but they are different substances. Silicone is a material that actually contains silicon (among other components), and silicon is a chemical element.
Properties
Silicone comes carrying quite a few specific physical and chemical properties. It’s resistant to hot and cold temperatures (think between -150°F and 550°F before turning brittle or melting, and it has fantastic flexibility. As for tensile strength? You’re looking at a PSI between 200 and 1500. Silicone’s maximum elongation also rings in at around 700%.
Silicone is great at compressing and rebounding, and it’s resistant to heat and flames. It also bonds well with metals (hello, adhesives, and sealants). It’s a great choice for outdoor products as it won’t crumble in the face of bad weather and has serious resistance to UV rays, water, and ozone.
It’s gas permeable, nonstick, and doesn’t stain, meaning you’ll undoubtedly find it in the food and beverage industry as well as the medical sector.
While it might sound like a wonder material, it has some downsides too. It’s not resistant to oil after long periods of time (though some varieties offer a little more resistance) and it’s not resistant to abrasion and wear and tear after a while.
Types of Silicone
There are many different types of silicone to choose from, and each offers its own perks:
- Methyl groups: These get grouped under the name MQ and are some of the first basic silicone rubbers that were created.
- Methyl vinyl groups: Look to methyl vinyl silicones or VMQs for materials that can compress impeccably well. They’re super common, and the vinyl mixed into this silicone makes vulcanization easier.
- Methyl phenyl (MPQ) and methyl phenyl vinyl (PVMQ) groups: What makes this type of silicone stand out from others is that it boosts its properties and retains those capabilities in cold temperatures.
- Flouro, vinyl, and methyl (FVMQ) groups: Meet the silicones that can better handle oils, solvents, and fuels.
- Silicone rubbers: There are three major subtypes under this group, including liquid, room temperature vulcanized, and high temperature vulcanized. Liquid has the smallest molecular chains making it a great choice for extrusion or injection molding. It’s also great for products that need to be weather-resistant.
- RTV (room temperature vulcanized) silicone rubber: This kind of silicone stays solid when it hits room temperature, and it’s a standard choice for the likes of sealants, potting, or molds.
- Solid or HTV (high temperature vulcanized) silicone rubber: These are long-chained polymers with the heaviest molecular weights. It usually comes as an unprocessed material and needs to be vulcanized at the same temperature as more traditional types of rubber.
Applications
Silicone has so many uses, and although we’ve put together a list, it’s just a small sampling of all the ways it can be worked into manufacturing:
- Spacesuit fabrics
- Aerospace gaskets and seals
- Adhesives, sealants, and coatings
- Cookware and cooking utensils
- Toys
- Weather-resistant parts and coatings and varnishes
- Medical defoamers and adhesives
- Tubing
- Jewelry
- Food containers
- Cosmetic surgery components
- Cosmetic ingredients for deodorants, laundry soap, shampoo, and more
- Insulating tape and varnish
- Keyboards and housings
FAQs on Silicone
Is Silicone Rubber or Plastic?
Silicone is a funny one in that it sits in somewhat of a gray area, but it’s usually categorized as a rubber. That said, it has both plastic and rubber properties and can be turned into liquids, solids, and more flexible materials.
How Xometry Can Help
You can work with our manufacturing team in many ways at Xometry. Get a free quote for services such as liquid silicone rubber molding, plastic injection molding, plastic 3D printing, and more on our website.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


