Steel is undeniably one of the best manufacturing materials out there. But it’s safe to say that the number of grades and types to choose from makes it hard to find the perfect option. If toughness and resistance to things like corrosion and wear are all important, you’ll probably come across 52100 steel as an option, and for good reason. Thanks to its composition (which is high in carbon), you get all these properties and more. Here’s what to know about it, how it’s made, and what pros and cons you can expect from using it.
What Is 52100 Steel?
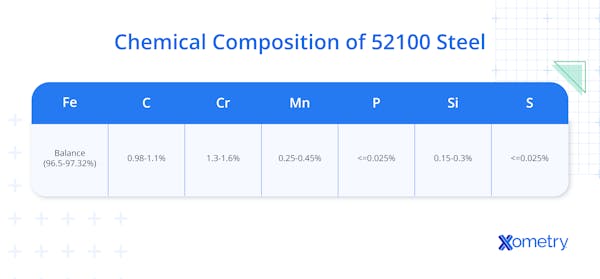
While it has many names, 52100 steel is chromium-alloy steel with a high carbon content that gets praised for its ability to put up with taxing situations—whether that’s corrosive environments or an expectation to go through serious wear and use. Composition-wise, it has 0.98-1.10% carbon, 1.30-1.60% chromium, 0.15-0.30% silicon, 0.25-0.45% manganese, and trace amounts of other elements like phosphorus (<= 0.025%) and sulfur (<= 0.025%).
What Is 52100 Steel Used For?
This kind of steel is made for putting up with heavy loads and a good dose of friction. That’s why 52100 is often used for bearings or components for machines, especially in the world of aerospace and automotive.
How Is 52100 Steel Made?
Making 52100 steel is very similar to concocting other types of steel. It’s just a matter of getting the composition right. Here are the steps of the process you can usually expect:
- First, all the raw materials (like carbon, iron, and chromium) in their specific quantities are added to an electric arc or induction furnace.
- Once it’s molten, it’s refined with argon oxygen decarburization or vacuum degassing, as this ditches any impurities that can impact the end product.
- Then, the molten steel will be cast into the intended shape, whether that’s sheets, billets, ingots, or something different.
- After casting it will be heated again, then shaped and processed in order to lock in those top qualities and ensure the grain structure is how it should be.
- Then, annealing takes place, which reduces internal stresses and refines the steel’s microstructure.
- Hot working will usually be followed by heat treatments to harden and temper the steel.
- Now, it’s ready for finishing, like grinding, polishing, and machining.
What Is the Chemical Composition of 52100 Steel?
The chemical composition of 52100 steel is outlined in Table 1:
What Is the Carbon Content of 52100 Steel?
The carbon content of 52100 steel typically ranges between 0.98% and 1.10%. This high percentage contributes to the steel's hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain its shape under high-stress conditions. The precise carbon content may vary slightly depending on the specific manufacturing process and steel supplier, but it generally falls within this range.
What Are the Properties of 52100 Steel?
The mechanical properties of 52100 steel are given in Table 2:
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
Property Machinability (spheroidized, cold drawn, and annealed. Based on AISI 1212 steel as reference with a 100% machinability) | Metric 40% | Imperial 40% |
Property Hardness, Knoop (converted from Rockwell C hardness) | Metric $875 | Imperial $875 |
Property Bulk Modulus | Metric 140 GPa | Imperial 20300 ksi |
Property Density | Metric 7.81 g/cm3 | Imperial 0.282 lb/in³ |
Property Fracture Toughness | Metric 15.4-18.7 MPa•m½ | Imperial 14.0 - 17.0 ksi•in½ |
Property Poisson’s ratio | Metric 0.27-0.30 | Imperial 0.27-0.30 |
Property Modulus of Elasticity | Metric 190-210 GPa | Imperial 27557-30458 ksi |
Property Shear Modulus | Metric 80 GPa | Imperial 11600 ksi |
52100 Steel Properties Table Credit: https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=6704
Machinability Rating of 52100 Steel
The machinability rating of 52100 steel is 40%. AISI 52100 alloy steel can be cut and shaped using standard metal machining techniques. However, it can also benefit from a spheroidizing annealing process to make it more machinable. This involves subjecting the steel to a steady temperature of 649°C (1200°F) for a designated duration, followed by a gradual cooling process. The spheroidizing annealing procedure helps improve the machinability of the steel by refining its microstructure and reducing its hardness.
What Are the Thermal Properties of 52100 Steel?
The thermal properties of 52100 alloy steel can be found in Table 3 below:
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
Property Melting point | Metric 1424°C | Imperial 2595°F |
Property Thermal expansion coefficient (@ 23-280°C/73.4- 36°F, annealed) | Metric 11.9 µm/m•°C | Imperial 6.61 µin/in•°F |
Property Thermal conductivity | Metric 46.6 W/m•K | Imperial 323 BTU•in/hr•ft²•°F |
52100 Steel Thermal Properties. Table Credit: https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=6704
51200 Steel Heat Treatment
Heat treating 52100 steel helps improve the hardness of your material. For this kind specifically, you’ll likely be looking at a divorced eutectoid transformation (DET) anneal before you jump right into heat treating. Annealing it in this way involves getting the steel to 1460°F and leaving it for 30 minutes, then cooling it to 1260°F, followed by air cooling.
Then, you’ll austenitize the steel at 1500 to 1525°F for anywhere from 10 to 30 minutes. This is followed by oil quenching and tempering at a temperature between 300 and 500°F. Remember that higher austenitizing temperatures can lead to higher hardness, but using cryogenic processes can take this hardness even further.
What Are the Common Forms of 52100 Steel Material?
Here is what you can expect when it comes to the shapes, formats, and finishes you can find 52100 steel in:
Sheet
These are flat pieces of steel, and you can find them in numerous thicknesses and sizes, perfect for custom cuts.
Bar
The format you need for things like bearings, gears, and other mechanical products. They’ve got excellent strength and are shaped like cylinders.
Plate
These look like sheets but tend to be thicker, making them perfect for times when you need serious strength and durability.
Hot Rolled
These bars are made by heating 52100 to high temperatures then rolling them into the shape you’re after.
Annealed
This heat treatment gives steel better machinability and helps alleviate any internal stresses that crop up when it’s being made.
Cold Drawn
These bars are pulled through a die, which gives them a better finish and much more accurate dimensions.
What Are the Equivalents of 52100 Steel?
To stay on top of the steel type you’re using across the world, these are the global name equivalents for 52100.
| Country/Governing Body | Equivalent Grade/Name |
|---|---|
Country/Governing Body USA | Equivalent Grade/Name $52,199 |
Country/Governing Body China (GB) | Equivalent Grade/Name Cr2; GCr15 |
Country/Governing Body EU (EN) | Equivalent Grade/Name 102Cr6 (1.2067) |
Country/Governing Body France (AFNOR) | Equivalent Grade/Name 100Cr6; 100Cr6RR |
Country/Governing Body Germany (DIN, WNr) | Equivalent Grade/Name 100Cr6 |
Country/Governing Body Japan (JIS) | Equivalent Grade/Name SUJ2 |
Country/Governing Body England (BS) | Equivalent Grade/Name 534A99; 535A99 |
Country/Governing Body Italy (UNI) | Equivalent Grade/Name 100Cr6 |
Country/Governing Body Sweden (SS) | Equivalent Grade/Name 2258 |
Country/Governing Body Poland (PN) | Equivalent Grade/Name LH15 |
Country/Governing Body Russia (GOST) | Equivalent Grade/Name KH; ShKh15 |
52100 Steel Global Name Equivalents Table Credit: Steel Numbers
What Are the Advantages of Using 52100 Steel?
Here are some of the perks you can expect from 52100 steel:
- With tempering, heat treating, or quenching, you get a very hard steel.
- Because of the carbon content, it’s super resistant to wear.
- It’s also highly resistant to fatigue and can handle multiple loads and stresses without failing.
- Even in tough conditions, it will hang onto its shape.
- After heat treating, you’ll have a steel material that’s great for machining.
52100 steel is a high-carbon, chromium-alloy steel known for its extreme hardness (60-67 HRC), excellent wear resistance, and superior fatigue strength, making it ideal for bearings, high-precision shafts, gears, tooling, and industrial cutting applications. Its fine carbide distribution provides exceptional durability, but its hardness makes machining difficult, requiring carbide or cubic boron nitride (CBN) tooling. It also has low weldability and can be brittle if not properly heat-treated. While it offers good dimensional stability and some corrosion resistance, careful handling is needed during heat treatment to prevent warping. Pre-hardening machining or alternative materials may be preferable for easier workability.Kurt PokopacSolutions Engineer
What Are the Disadvantages of Using 52100 Steel?
There are also some downsides to be aware of with this particular steel:
- It is corrosion-resistant, but not nearly as much as other types of stainless steel.
- Welding with 52100 can be tricky and requires specific preheating processes to do it successfully.
- This type of steel can be much more brittle than other types.
- It also tends to be a slightly more expensive steel compared to others.
- In its fully hardened state, it can be much more difficult to machine.
What Is the Difference Between 52100 Steel and D2 Steel?
52100 steel and D2 steel are two types of tool steels that have distinct compositions, properties, and applications. 52100 steel is a high-carbon chromium alloy steel. It is renowned for its exceptional hardness, reaching up to 60-65 HRC when properly heat treated. It offers excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for bearings that must carry high loads and rolling friction. This steel also has good toughness and fatigue resistance.
On the other hand, D2 steel is a high-carbon, high-chromium tool steel. It is also very hard, typically ranging from 58-62 HRC after heat treatment. It provides excellent wear resistance, good toughness, and moderate corrosion resistance. D2 steel is commonly used in cutting tools, punches, dies, and forming tools.
What Is the Difference Between 52100 Steel and S30V Steel?
52100 steel and S30V steel are two different types of steel that have notable differences in their composition, properties, and applications. 52100 steel is a high-carbon chromium alloy steel renowned for its exceptional hardness, reaching up to 60-65 HRC when properly heat treated. It offers excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for bearings that must support high loads and rolling friction. This steel also possesses good toughness and fatigue resistance
S30V steel, on the other hand, is a high-performance stainless steel specifically designed for knife blades. It is known for its excellent edge retention, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. It can be hardened to around 58-60 HRC, providing a balance between hardness and toughness that is well-suited for knife blades. However, 52100 alloy steel is tougher and easier to sharpen than S30V steel.
How Xometry Can Help
We offer many different services at Xometry that involve steels like 52100, including CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, and stainless steel 3D printing—all of which you can get free quotes for.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


