High-impact polystyrene (HIPS) refers to a modified form of polystyrene that incorporates rubber additives to improve its resistance to physical impact. HIPS plastic balances strength and ease of fabrication, suitable for thermoforming, injection molding, and scalable production methods. The structural composition of hip plastic allows for greater durability without compromising its rigidity or dimensional stability. The inclusion of rubber particles within the polymer matrix improves impact resistance while maintaining a consistent surface finish, contributing to reliable performance across various manufacturing environments.
HIPS serves as a preferred material in sectors that demand a combination of strength and processability. HIPS plastic supports lightweight, sturdy casings for consumer goods. High-impact polystyrene offers a hygienic, printable surface for branding and labeling in food packaging. It is used in interior trim parts that require precise dimensions and wear resistance in automotive components. The extensive use underscores its ability to meet both functional and aesthetic standards across industries.
What is High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)?
High-impact polystyrene (HIPS) is a modified form of polystyrene that includes rubber to improve its resistance to physical stress. The structure of HIPS combines rigidity with toughness, enabling it to withstand impacts without breaking. The addition of rubber particles into the polymer matrix boosts durability while maintaining a smooth surface suitable for various manufacturing processes. HIPS provides reliable performance in applications that require strength and dimensional stability.
The physical properties of HIPS make it ideal for use in packaging and household appliances. HIPS material offers a printable surface and retains its shape during handling and shipping in the packaging industry. HIPS is used for components that require resistance to wear and repeated use in household appliances. Its combination of strength, ease of processing, and impact resistance allows HIPS to meet the functional needs across different product categories.
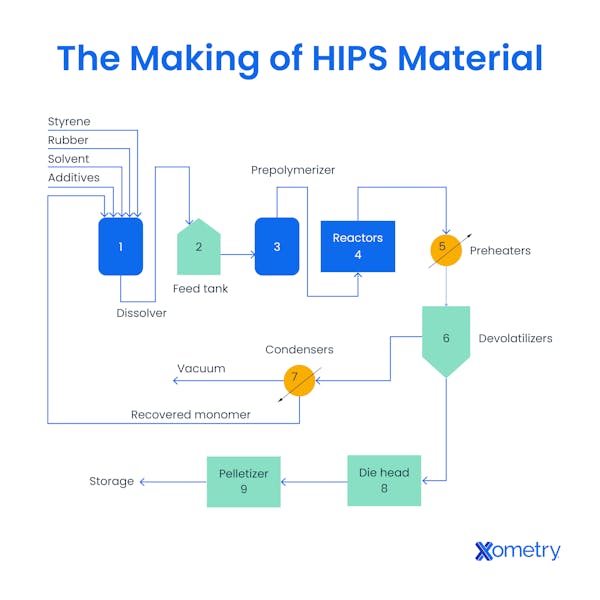
How is HIPS Material Made?
HIPS material is made by blending polystyrene with a rubber modifier, most commonly butadiene rubber, to increase its toughness. The process begins with the polymerization of styrene monomers, which form a rigid backbone that provides structural integrity. Rubber particles are introduced and dispersed throughout the matrix during the reaction, creating a two-phase system that combines stiffness with energy absorption. The resulting molecular structure interrupts crack propagation and distributes mechanical stress more evenly, which increases impact resistance. The integration of rubber into the polystyrene framework transforms the base polymer into HIPS, a material that supports applications requiring durability, form stability, and efficient processing.
What is the Full Form of HIPS Material?
HIPS material full form refers to High-Impact Polystyrene. The thermoplastic is derived from standard polystyrene that has been structurally modified with rubber to improve its mechanical performance. The inclusion of rubber particles in the polymer matrix enhances toughness and reduces brittleness, thereby improving its ability to withstand physical stress without fracturing. The modification process yields a dual-phase system that combines rigidity with impact resistance, rendering HIPS material suitable for applications that require durability and consistent form. The balance between strength and processability contributes to its widespread use in packaging, consumer products, and structural components.
How does HIPS Material Affect the Quality of the Product?
HIPS material affects product quality by providing a favorable balance of strength, impact resistance, and ease of processing. HIPS’ structural properties enable the production of durable yet lightweight products, which is crucial in industries that demand reliability and efficiency in their manufacturing processes. The inclusion of rubber additives within the polymer matrix improves its toughness, providing resistance to physical impacts without compromising its rigidity or dimensional stability. The characteristic makes HIPS a preferred choice for applications requiring a material that withstands wear and tear while maintaining its form.
HIPS ensures durability and safety in food packaging. The ability to be easily molded into precise shapes provides a consistent surface for labeling and branding, making it ideal for packaging that must meet aesthetic and functional standards. The material's hygienic properties are vital in maintaining the integrity of packaged goods, particularly in environments where sanitation is paramount. HIPS' combination of impact resistance and ease of fabrication enables the creation of high-quality, high-performance products for consumer goods. Its widespread use reflects its effectiveness in meeting the stringent demands of industries requiring durable, high-performance materials.
What Are the Properties of High-Impact Polystyrene?
The properties of High-Impact Polystyrene are listed below.
- High Impact Strength: High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) excels at absorbing shocks without cracking, making it ideal for durable consumer products. Its toughness comes from its rubber-modified structure, which boosts resilience to stress.
- Rigidity: HIPS retains a firm and stable shape, enabling precise control of dimensions despite its impact resistance. The rigidity helps ensure structural integrity in molded parts and enclosures.
- Ease of Processing: HIPS's key advantage is its compatibility with methods such as injection molding and thermoforming. Its low melting point and predictable flow are HIPS properties that ease manufacturing workflows.
- Good Surface Quality: HIPS provides a smooth, uniform finish that readily accepts paints, adhesives, and printing inks. It makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring aesthetic appeal or branding.
- Clarity (in Certain Grades): Standard HIPS is opaque, but specialized grades offer translucency or gloss for visual applications (such as packaging or displays) where visibility is important.
- Moderate Chemical Resistance: HIPS resists diluted acids and bases but isn't suitable for harsh chemicals, allowing safe use in consumer goods without compromising safety performance.
- Moisture Resistance: HIPS exhibits moderate water resistance, which aids in maintaining mechanical stability in humid environments. It supports the properties of HIPS in household items and packaging exposed to moisture.
HIPS is a polystyrene matrix reinforced by finely dispersed rubber domains, forming a dual-phase structure that absorbs impact while maintaining dimensional stability. It exhibits predictable thermal behavior and a smooth surface, enabling consistent performance in molding, thermoforming, and high-volume fabrication. It also has moderate density and rigidity, supports lightweight yet sturdy components, allowing reliable structural integrity in consumer goods, packaging, and automotive interiors. Its limitations in chemical and thermal resistance shape its role toward controlled environments rather than extreme operating conditions. The overall profile reflects a material engineered to balance durability, manufacturability, and cost efficiency across diverse industrial applications, an equilibrium that defines its widespread adoption.
What is the Density of High-Impact Polystyrene?
The density of high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) ranges between 1.04 and 1.06 g/cm³. The density supports a balance between structural rigidity and manageable weight, which contributes to its widespread use in manufacturing. The material maintains form during shaping processes, which supports consistent results in molding and extrusion. The moderate density allows HIPS to retain stiffness without becoming brittle, supporting its role in applications that require impact resistance and dimensional stability. Processing efficiency improves with increasing density, as the material flows evenly and cools predictably during fabrication. The combination of rigidity and ease of shaping positions HIPS as a practical choice for components that require durability and visual consistency.
What is the Melting Point of High-Impact Polystyrene?
The melting point of high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) is approximately 240°C. The thermal property defines the upper limit for processing and shapes the conditions required for molding and extrusion. The material softens predictably under heat, which supports consistent flow and form retention during fabrication. The melting point limits its use in environments with sustained high temperatures, but it remains suitable for applications that demand rigidity and impact resistance without exposure to extreme heat. The balance between thermal behavior and mechanical strength supports its role in consumer products, packaging, and structural components, where moderate temperature stability is sufficient.
What is the Chemical Formula of High-Impact Polystyrene?
The chemical formula of high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) is expressed as (C₈H₈)n. The notation reflects the polymerization of styrene monomers into long chains, where each unit consists of eight carbon atoms and eight hydrogen atoms. The structure forms a rigid backbone that supports the material’s mechanical strength and processability. Rubber particles are introduced during polymerization to improve impact resistance, which modifies the internal structure without altering the base chemical formula. The presence of rubber increases toughness and reduces brittleness, which supports the use of HIPS in applications requiring durability and dimensional stability. The combination of styrene’s rigidity and rubber’s flexibility results in a balanced material suitable for forming, molding, and structural components.
What is the Structure of High-Impact Polystyrene?
The structure of high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) consists of a polystyrene backbone with rubber particles dispersed throughout the polymer matrix. The arrangement creates a dual-phase system in which the rigid polystyrene provides stiffness, while the rubber domains absorb energy during impact. The presence of rubber particles interrupts crack propagation, thereby increasing toughness and reducing brittleness compared to standard polystyrene. The combination of rigidity and energy dissipation enables the material to withstand mechanical stress without fracturing. The structural design contributes to the widespread use of HIPS in applications that require durability, dimensional stability, and resistance to sudden force.
What is High-Impact Polystyrene Used for?
High-Impact Polystyrene is used across manufacturing sectors due to its durability, processability, and cost-efficiency. The uses of HIPS across industries require lightweight, impact-resistant materials. It is ideal for toys, appliance housings, and other consumer goods due to its durability and shape retention. HIPS creates containers, trays, and cups for food packaging, offering a hygienic, moisture-resistant surface that preserves food quality at an affordable cost in large-scale production.
HIPS is selected for interior parts that require rigidity and impact in automotive manufacturing. HIPS plastic uses offer strength with minimal weight, stability under heat and mechanical stress, and a smooth, printable surface ideal for displays, electronic housings, and visual applications needing transparency or gloss. Its ease of processing and dimensional consistency simplify manufacturing, broadening its use in retail and consumer electronics.
The combination of mechanical strength, visual quality, and manufacturing flexibility makes HIPS a preferred choice for high-volume production environments. Its widespread adoption reflects the balance between performance and cost that manufacturers seek when selecting materials for functional and aesthetic components.
Which HIPS Materials Are Used for Medical Applications?
HIPS materials used for medical applications are diagnostic equipment, sterile packaging systems, and disposable medical items. High-Impact Polystyrene is used in medical applications where strength, visual quality, and process reliability are required. Its rigidity supports the structural demands of instrument housings and enclosures that must retain shape under repeated use. The clarity of certain grades enables visual inspection and labeling, contributing to safety and traceability in clinical settings. HIPS plastic is used in packaging, including trays, blister packs, and containers designed to protect sensitive devices and pharmaceuticals from contamination and mechanical damage.
The material’s surface properties allow for consistent sterilization without compromising dimensional stability or appearance. The characteristic supports its role in environments where hygiene and compliance with safety standards are essential. The ease of processing contributes to the efficient production of high-volume items (test kits and single-use accessories). Its balance of mechanical strength and visual appeal makes it suitable for applications that require both durability and presentation quality. The combination of the factors has led to widespread adoption of HIPS in medical manufacturing, where reliability and cost-efficiency are critical.
Can High-Impact Polystyrene be Used in Medical Implants?
No, high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) cannot be used in medical implants. The material provides rigidity and visual clarity, which supports its use in short-term or non-load-bearing components. Its structural properties allow it to be shaped and molded into precise forms, which contribute to its use in temporary medical applications. The absence of reliable biocompatibility limits its use in permanent implants that remain in contact with biological tissue. The risk of adverse reactions and degradation under physiological conditions restricts its role in long-term medical systems. Manufacturers select alternative polymers with proven biocompatibility for implantable devices that require extended performance inside the body.
What Are the Applications of High-Impact Polystyrene?
The applications of High-Impact Polystyrene are listed below.
- Consumer Products: HIPS is used in the manufacture of toys, appliance housings, and storage solutions. Its impact resistance and smooth finish ensure durability and visual appeal in high-volume markets.
- Food Packaging: The material creates trays, containers, and disposable utensils for food service and retail; its moderate moisture resistance and easy forming allow hygienic, cost-effective packaging.
- Automotive Components: HIPS is used in interior automotive parts (trim panels and covers). Its rigidity and stability help maintain structure under stress and temperature changes.
- Medical Devices and Packaging: The material supports the production of diagnostic housings, sterile trays, and disposable medical items, making it suitable for controlled environments due to its clarity and sterilization compatibility.
- Point-of-Purchase Displays: HIPS is used in signage, display stands, and retail fixtures. Its print-friendly surface and ease of fabrication allow vibrant, customized branding.
- Electronic Housings: The material is chosen for enclosures of small electronic devices and accessories. Its insulation and consistent molding ensure safe, reliable product designs.
- Modeling and Prototyping: HIPS is used for models, prototypes, and educational tools due to its machinability and low cost, making it suitable for iterative design and demos.
What Role Does HIPS Plastic Play in Automotive Safety Features?
High-Impact Polystyrene contributes to automotive safety features by offering a balance of structural reliability and cost-efficiency. The material is used in dashboards, interior panels, and trim components where impact resistance and dimensional stability are required. Its ability to absorb mechanical stress without fracturing supports occupant protection in minor collisions and routine vehicle use. The rigidity of HIPS allows molded parts to retain their shape under thermal and physical pressure, which helps maintain the integrity of safety-critical zones. Its surface quality supports consistent manufacturing of components that must meet visual and tactile standards without compromising durability.
The cost-effectiveness of HIPS makes it suitable for high-volume production of safety-related parts without sacrificing performance. Its predictable behavior during molding and forming processes reduces waste and supports precise fabrication of complex geometries. The material’s toughness contributes to the longevity of interior components that experience frequent contact, vibration, and temperature shifts. The characteristics support the use of HIPS in automotive environments where safety, reliability, and affordability are essential.
What Are the Advantages of High-Impact Polystyrene?
The advantages of High-Impact Polystyrene are listed below.
- Good Clarity (in Select Grades): Grades of HIPS offer visual transparency or gloss, which supports applications requiring visibility or aesthetic appeal. The characteristic is useful in packaging, displays, and product housings.
- Hardness: HIPS maintains a firm structure that resists deformation under load, supporting dimensional accuracy in finished parts. The property is vital for components that must retain shape during assembly or use.
- Cost-Effectiveness: HIPS offers a lower material cost while maintaining reliable performance compared to other engineering plastics. The balance supports its use in high-volume production across consumer and industrial sectors.
- Surface Printability: The smooth surface of HIPS accepts inks and coatings without extensive preparation, which supports branding and labeling. The feature is valuable in packaging and promotional displays.
What Are the Benefits of HIPS Plastic in Food Packaging?
The benefits of HIPS in food packaging are listed below.
- Provide High Impact Resistance: HIPS provides improved impact resistance compared to general-purpose polystyrene, maintaining structural integrity during typical handling and transport of lightweight items, though it is not suited for heavy-load or high-impact applications.
- Support Clear and Smooth Surface Quality: The surface of HIPS allows excellent printability through techniques (offset and screen printing), enabling precise labeling and strong visual branding for packaging applications.
- Allow Easy Processing into Various Shapes: HIPS adapts well to thermoforming and injection molding, which supports efficient production of trays, cups, and containers. Its formability reduces tooling complexity and shortens cycle times.
- Offer Cost-Effective Material Choice: The affordability of HIPS supports large-scale packaging without compromising basic performance. Its balance of price and utility makes it suitable for high-volume food service operations.
- Suit Single-Use Packaging Applications: Food-grade HIPS formulations meet hygiene and regulatory standards for disposable food packaging, supporting safe contact with consumables and convenient post-use disposal.
What Are the Disadvantages of High-Impact Polystyrene?
The disadvantages of High-Impact Polystyrene are listed below.
- Lower Chemical Resistance: HIPS degrades when exposed to strong acids, bases, and solvents, limiting its use in chemical-prone environments.
- Brittleness at Low Temperatures: The material becomes less flexible and more prone to cracking in cold conditions, impacting its reliability in refrigerated or outdoor storage.
- Limited UV Stability: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can cause HIPS to discolor and weaken due to UV radiation, reducing its outdoor lifespan without protective coatings or additives.
- Relatively Low Heat Resistance: HIPS deforms under moderate heat, limiting its use in high-temperature environments and affecting performance in heat-generating or sterilization applications.
- Poor Weathering Performance: The material does not withstand long-term exposure to moisture, temperature changes, or environmental stress without losing strength, making it unsuitable for outdoor structures unless modified.
What Are the Main Challenges in Manufacturing HIPS Plastic?
The main challenges in manufacturing HIPS plastic are listed below.
- Maintain Uniformity in Rubber-Polystyrene Blend: Achieving uniform dispersion of the rubber phase, polybutadiene, within the polystyrene matrix is essential to maintain consistent impact strength, gloss, and surface quality in HIPS. Uneven distribution creates weak zones and visual defects.
- Control Molecular Weight Distribution: Variations in molecular weight distribution directly influence melt viscosity, flow uniformity, and mechanical balance in HIPS. Controlled polymerization ensures stable flow behavior and predictable mechanical performance during molding.
- Optimize Processing Conditions: Processing parameters (melt temperature, injection pressure, and cooling rate) must be carefully optimized to control internal stress, prevent warping, and preserve the rubber domain morphology that provides impact resistance.
- Prevent Material Degradation During Processing: Excessive heat or shear during extrusion or molding can cause chain scission and oxidative degradation in HIPS, leading to discoloration, loss of gloss, and reduced impact strength.
- Addressing Recycling Difficulties Due to Rubber Content: The rubber content in HIPS complicates recycling because the dispersed elastomer phase impedes separation and melt filtration. The limits reprocessing efficiency and reduce mechanical consistency in recycled products.
What is the Cost of HIPS Material?
The cost of high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) ranges from $1.10 to $1.60 per kilogram, depending on market conditions and supplier location. The pricing places HIPS among the more affordable thermoplastics used in manufacturing. The material offers a balance between mechanical strength and processability, without the higher cost of engineering-grade polymers. HIPS provides cost savings in applications that do not require elevated thermal resistance or advanced impact performance, compared to ABS or polycarbonate. The lower price supports its use in packaging, consumer goods, and structural components where visual consistency and moderate durability are sufficient. Manufacturers select HIPS for projects that demand reliable performance within budget constraints, which contributes to its widespread adoption across multiple industries.
What Are the Different Types of HIPS Products Available in the Market?
The different types of HIPS products available in the market are listed below.
- Virgin HDPE: The pure form is used in food packaging, medical containers, and water tanks. Its chemical resistance and strength support long-term storage and hygiene-sensitive applications.
- Recycled HDPE: The variant is utilized in non-food packaging, piping, and construction materials. Its cost-efficiency supports sustainable manufacturing without compromising basic durability.
- HDPE Pipes: Used for water supply, gas distribution, and drainage systems. Their flexibility and corrosion resistance support underground and industrial fluid transport.
- HDPE Sheets: Used for cutting boards, liners, and industrial surfaces. Their wear resistance and ease of cleaning support repeated use in demanding environments.
- HDPE Bottles and Containers: The products are used in household chemicals, detergents, and personal care items. Their lightweight, leakproof design supports safe, convenient storage.
What is the Difference between HIPS and other Types of Plastic?
The difference between HIPS and other types of plastic is shown in the table below.
| Property | HDPE | LDPE | PMMA | POM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Property Density | HDPE Moderate, supports lightweight structural parts | LDPE Low, suitable for flexible packaging | PMMA High, contributes to rigidity and clarity | POM High, allows precision in machined components |
Property Strength | HDPE Strong, resists impact and stress | LDPE Low, prone to tearing under load | PMMA Moderate, brittle under force | POM High, supports mechanical loads and wear |
Property Flexibility | HDPE Moderate, allows slight bending | LDPE High, used in stretchable applications | PMMA Low, maintains shape with minimal deformation | POM Low, retains form under pressure |
Property Chemical Resistance | HDPE Excellent, resists acids, bases, and solvents | LDPE Good, tolerates mild chemicals | PMMA Poor, vulnerable to solvents and alcohols | POM Excellent, withstands fuels and industrial fluids |
Property Temperature Resistance | HDPE Moderate, softens under heat | LDPE Low, deforms at elevated temperatures | PMMA High, tolerates heat without distortion | POM High, maintains shape across a wide temperature range |
Property Transparency | HDPE Opaque, not suitable for visual applications | LDPE Translucent, limited clarity | PMMA Excellent, used in optical components | POM Opaque, not designed for visual inspection |
Property Common Uses | HDPE Containers, pipes, and industrial packaging | LDPE Film wraps, bags, and squeeze bottles | PMMA Display panels, lenses, and signage | POM Gears, fasteners, and precision parts |
Property Recyclability | HDPE High, widely accepted in recycling systems | LDPE Moderate, less commonly recycled | PMMA Moderate, recycling requires separation | POM Low, recycling is limited due to technical demands |
Property Durability | HDPE Strong, resists wear and environmental stress | LDPE Weak, degrades under mechanical strain | PMMA Moderate, scratches and cracks over time | POM Excellent, long-lasting under mechanical stress |
Property Cost | HDPE Low, supports budget-conscious production | LDPE Low, economical for disposable items | PMMA High priced for specialty applications | POM High, reflects engineering-grade performance |
Is HIPS More Cost-Effective than Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?
Yes, High-Impact Polystyrene is more cost-effective than ABS. The lower cost of raw materials used in HIPS contributes to its affordability in large-scale production. Its manufacturing process requires less energy and fewer additives, which reduces operational expenses during molding and forming. The material supports efficient fabrication with minimal waste, making it suitable for applications where budget constraints are a priority. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers greater impact resistance and thermal stability, which increases its value in demanding environments but raises its production cost. The trade-off between mechanical performance and economic efficiency positions HIPS as a practical choice for non-structural components and disposable goods.
Does High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) Have Better Impact Resistance than High-Density Polyamide (PA)?
No, High-Impact Polystyrene does not have better impact resistance than High-Density Polyamide. Polyamide offers superior mechanical strength and impact resistance, making it well-suited for demanding structural applications. Its molecular structure supports high energy absorption and durability under repeated stress. HIPS offers moderate toughness and rigidity, making it suitable for components that do not require extreme mechanical performance. The balance of cost and ease of processing makes HIPS practical for non-load-bearing parts, while Polyamide (PA) remains the preferred choice for environments requiring long-term resilience and strength.
Is HIPS More Flexible than Polyethylene (PE)?
No, High-Impact Polystyrene is not more flexible than Polyethylene. HIPS maintains a rigid form under mechanical stress, promoting dimensional stability but limiting its flexibility. The stiffness of HIPS contributes to its use in components that require shape retention rather than deformation. The material Polyethylene (PE) exhibits greater flexibility due to its linear molecular arrangement, which allows for more movement between polymer chains. The structural trait enables bending and stretching without fracturing, making it suitable for applications that require pliability. The difference in molecular behavior between the two materials defines their suitability for distinct functional roles in manufacturing.
Does HIPS Offer Better Chemical Resistance than (Acetal POM)?
No, High-Impact Polystyrene does not offer better chemical resistance than Acetal (POM). Acetal exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including solvents, fuels, and weak acids, making it suitable for chemically aggressive environments. Its molecular structure provides stability when exposed to reactive substances, maintaining mechanical integrity over time. HIPS is vulnerable to degradation when exposed to strong acids, bases, and industrial solvents. The limitation restricts its reliability in applications where chemical exposure is frequent or prolonged. The difference in chemical resilience positions Acetal (POM) as a more suitable material for components requiring long-term performance in harsh conditions.
Is HIPS More Commonly Used than Polylactic Acid (PLA)?
Yes, High-Impact Polystyrene is more commonly used than Polylactic Acid. HIPS supports mass production of consumer goods due to its mechanical strength, ease of processing, and cost-efficiency. Its widespread use in packaging, electronics, and household items reflects its compatibility with high-volume manufacturing environments. PLA is selected for applications that prioritize biodegradability and environmental impact. The demand for PLA remains concentrated in packaging and disposable products, where compostability is a key requirement. The broader industrial adoption of HIPS across multiple sectors contributes to its higher usage compared to Polylactic Acid (PLA).
Does HIPS Have a Higher Melting Point than Polystyrene (PS)?
Yes, High-Impact Polystyrene has a higher melting point than standard Polystyrene. The structural modification in HIPS, which includes rubber reinforcement, contributes to its improved thermal behavior compared to unmodified Polystyrene. The adjustment allows HIPS to maintain its form under moderate heat, supporting its use in applications where thermal exposure is a factor. Standard Polystyrene (PS) softens at lower temperatures, which limits its reliability in environments involving heat. The increased thermal resistance of HIPS provides a functional advantage in manufacturing processes that involve elevated temperatures. The distinction supports material selection based on thermal performance requirements.
Is HIPS More Suitable for Food Packaging than Polypropylene (PP)?
No, High-Impact Polystyrene is not more suitable for food packaging than Polypropylene. Polypropylene offers stronger chemical resistance and greater flexibility, making it well-suited for packaging exposed to oils, acids, and physical stress. Its ability to withstand repeated bending and contact with reactive substances contributes to long-term reliability in food storage and transport. HIPS offers rigidity and visual clarity, which support structured packaging and branding visibility. Its lower resistance to chemicals and reduced flexibility limit its performance in demanding food environments. The difference in mechanical and chemical behavior positions Polypropylene (PP) as a more versatile material for food packaging applications requiring durability and safety.
Does HIPS Perform Better than Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) in High-Temperature Applications?
No, High-Impact Polystyrene does not perform better than Polybutylene Terephthalate in high-temperature applications. PBT maintains its mechanical properties under elevated temperatures due to its higher thermal stability and resistance to deformation. Its molecular structure supports consistent performance in environments involving heat exposure, which contributes to its use in electrical and automotive components. HIPS begins to soften at lower temperatures, limiting its reliability in applications that require thermal endurance. The difference in heat tolerance between the two materials defines their suitability for distinct operational conditions, with Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) offering greater resilience in demanding thermal environments.
Is HIPS Stronger than High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)in Terms of Stiffness?
Yes, High-Impact Polystyrene is stiffer than High-Density Polyethylene. HIPS maintains a rigid structure under mechanical stress, making it suitable for applications requiring dimensional stability and shape retention. Its stiffness contributes to consistent performance in molded parts and packaging that must resist bending or warping. HDPE exhibits greater flexibility due to its molecular arrangement, which allows it to absorb strain without fracturing. The difference in structural behavior between the two materials defines their suitability for distinct functional roles, with HIPS favoring rigidity and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) favoring pliability. The contrast influences material selection based on mechanical requirements and environmental conditions.
How is HIPS Plastic Recycled?
HIPS plastic is recycled using the process outlined below.
- Collect waste material. Gather post-consumer and post-industrial HIPS items from packaging, manufacturing, and disposal streams. The step initiates the recycling process by consolidating usable plastic waste.
- Sort by polymer type. Separate HIPS from other plastics using automated systems or manual inspection to ensure material purity. Accurate sorting prevents contamination and supports consistent reprocessing outcomes.
- Clean and remove contaminants. Wash the sorted HIPS to eliminate food residue, labels, and surface debris. Removing contaminants improves the quality of recycled output and reduces processing complications.
- Shred into flakes or pellets. Grind the clean HIPS into small flakes or melt it into pellets for easier handling and reformation. The transformation prepares the material for extrusion or molding into new products.
- Reprocess into new items. Use the recycled HIPS to manufacture trays, containers, or non-food packaging components. The reprocessed material supports cost-effective production while reducing reliance on virgin plastic.
- Address additive challenges. Manage the presence of dyes, fillers, and stabilizers that affect the consistency of recycled HIPS. The additives complicate processing and limit the range of applications for recycled output.
- Evaluate recyclability compared to other plastics. Recognize that HIPS offers better recyclability than some multi-layer or chemically complex plastics. Its single-polymer structure supports repeated use when properly sorted and cleaned.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.

