Materials
Information about common materials used in manufacturing processes.










Coefficient of Friction Testing: Procedure, Application, Benefits, and Challenges
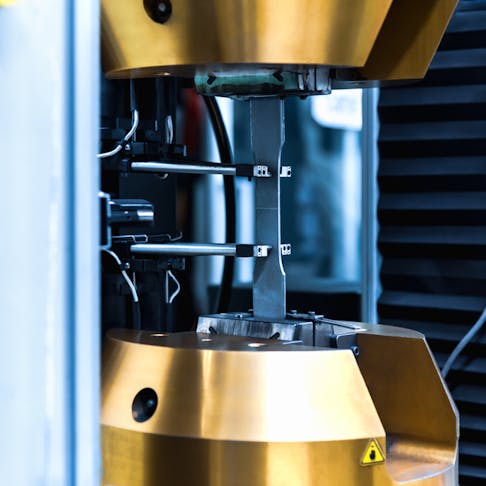







Lap Shear: How It Is Conducted, Applications, and How It Is Calculated










What Is Elastic Limit? Definition, Importance, How It Works, and Examples









Martensitic Stainless Steel: Definition, Composition, Types, Properties, and Applications




All About Titanium Alloy 6-4: Definition, History, Properties, and Applications



Copper: Definition, Composition, Properties, and Industrial Applications











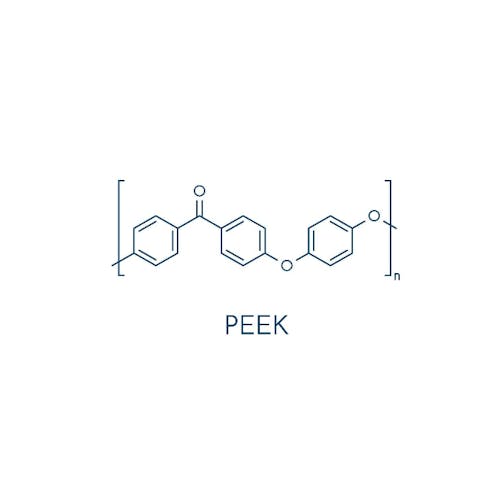
Engineered Thermoplastic Polyurethane (ETPU): What do You Need to Know About This Material?






























4140 Pre-Hardened Steel: Properties, Industry, Advantages, and Disadvantages

Peel Tester: How Does It Work, How To Test, and Technical Requirements

Manganese Bronze: Definition, Composition, Properties, and Applications













Aluminum Bronze: Definition, Composition, Types, Properties, and Applications

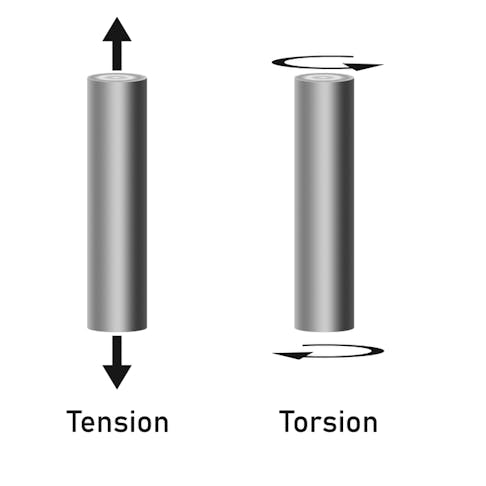

Bending Stress: Definition, How it Works, Calculation, Types, and Examples

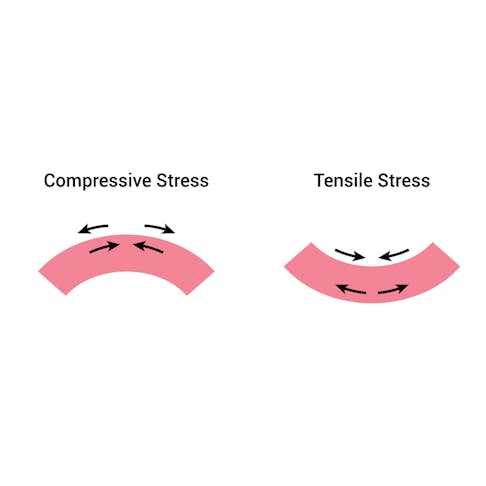









Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel: What Is It, How It Works, Process, and Advantages









ABS Plastic (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Definition, Properties, and Uses
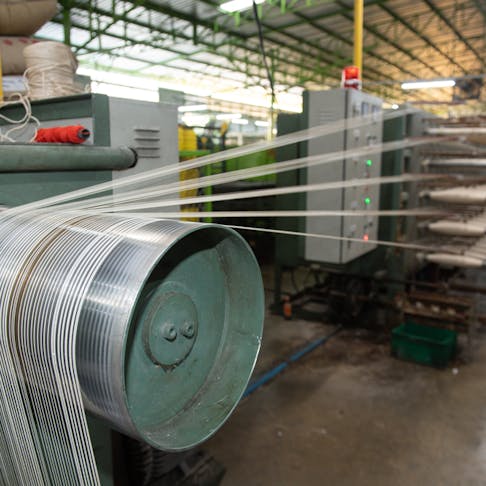
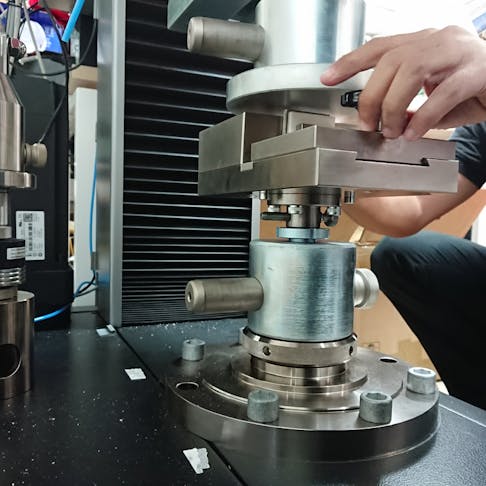


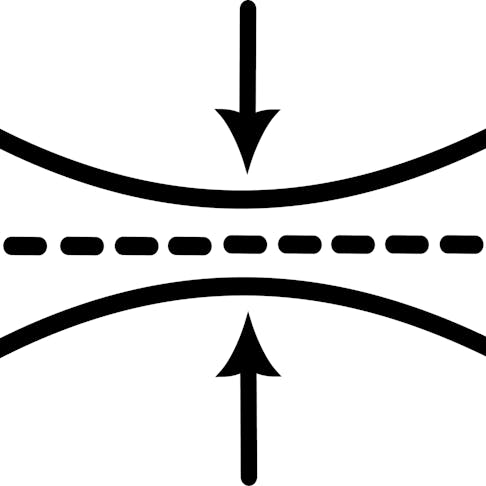



Flexure/Bend: How Is It Tested, What are the Standards and Why Is It Necessary
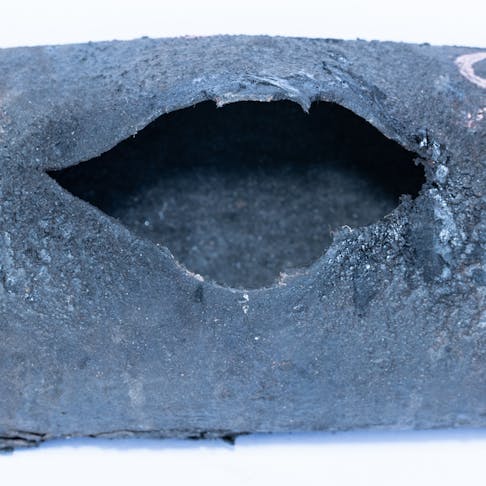
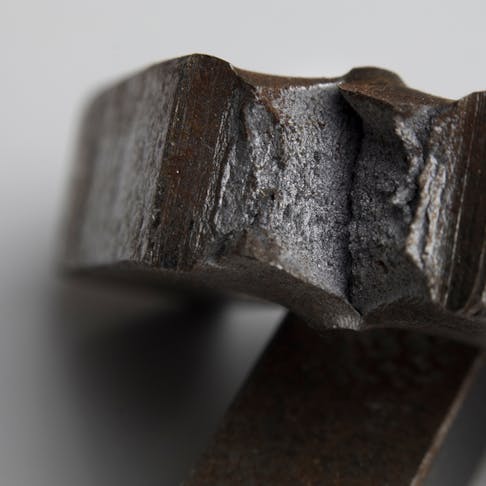


Fracture or Breaking Point: Definition, Implications, Tests, Types, and Benefits
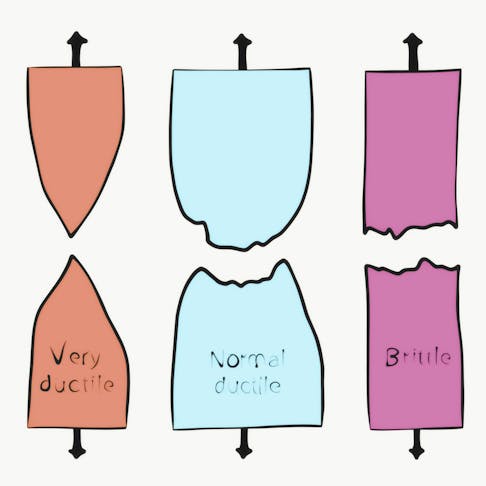



Metallurgical Degradation: Definition, What Occurs, Factors, and How It Affects Metals

Copper Nickel Alloys (CuNi): Definition, Applications, Advantages, and Disadvantages

Superalloys: Definition, Properties, Applications, Types, and Advantages




Modulus of Resilience: Definition, How It Works, Importance, Examples, and Advantages

Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS): Definition, How It Works, Calculation, and Example



Glass Transition Temperature: Definition, How It Works, Factors, and Advantages

Thermal Resistance: Definition, How It Works, Importance, Calculations, and Factors


Elongation at Break: Definition, Calculation, Benefits, Limitations, and Examples


Thermal Conductivity: Definition, How It Works, Importance, Calculations, and Factors






Aluminum Alloy: Definition, Characteristics, Types, Properties, and Applications
Plastic: Definition, Types, Properties, Applications, Advantages, and Disadvantages








Teflon® (Polytetrafluoroethylene): Definition, Properties, Types, and Applications
















Fracture Toughness Tests: Definition, Purpose, Standards, Process, and Benefits


What is Polybutylene Terephthalate: Characteristics, Advantages, and Disadvantages























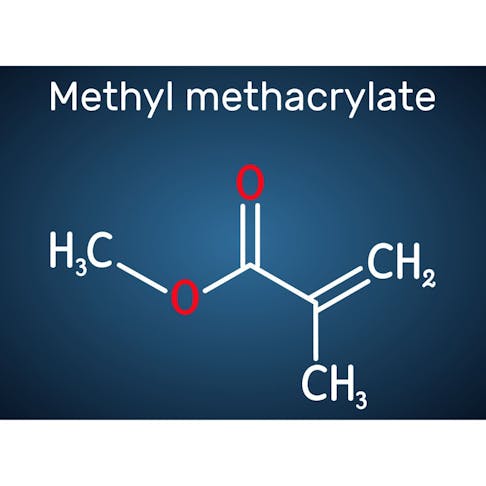



Thermoplastic Polyolefin (TPO): What It Is, Properties, and Advantages
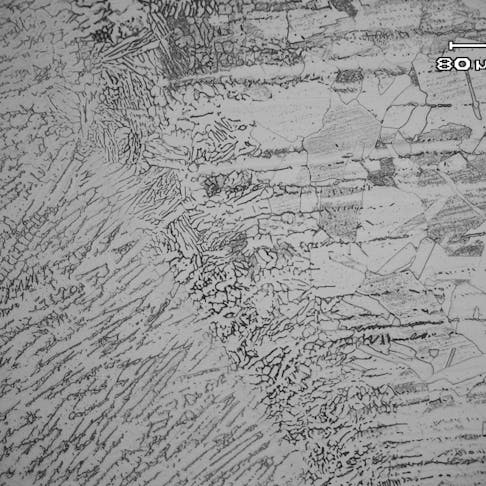



Pearlitic Stainless Steel: Composition, Uses, Performance, and Benefits in Manufacturing




Harper–Dorn Creep: Definition, Factors, Importance, and How To Reduce It



Martindale Test: Purpose, Types of Materials Tested, and Standards Used

Nabarro-Herring Creep: Definition, How It Occurs, Factors, and Importance in Manufacturing










Ferritic Stainless Steel: Definition, Composition, Types, Properties, and Applications

Hastelloy® Metals: Definitions, Composition, Properties, and Applications

Phosphor Bronze: Definition, Composition, Properties, and Applications
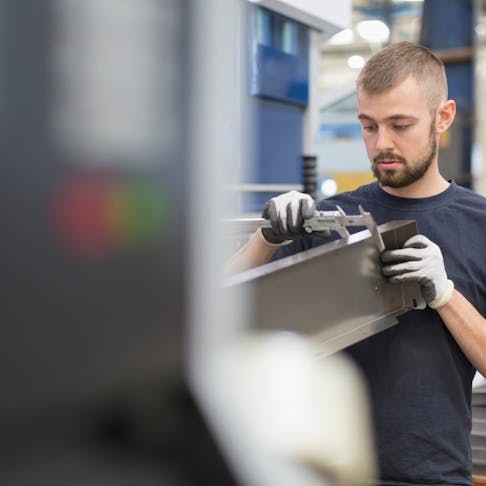
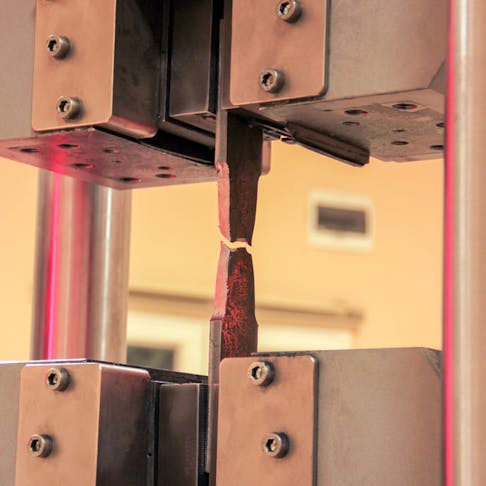




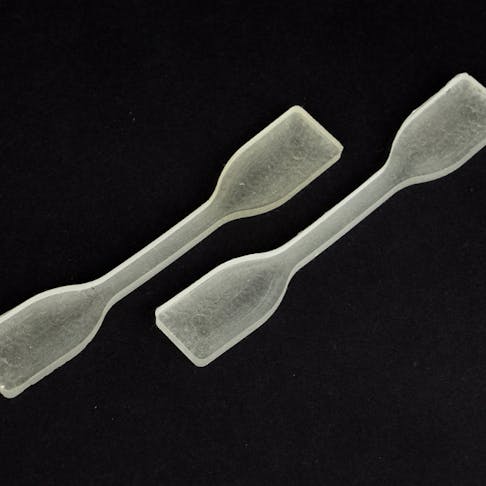



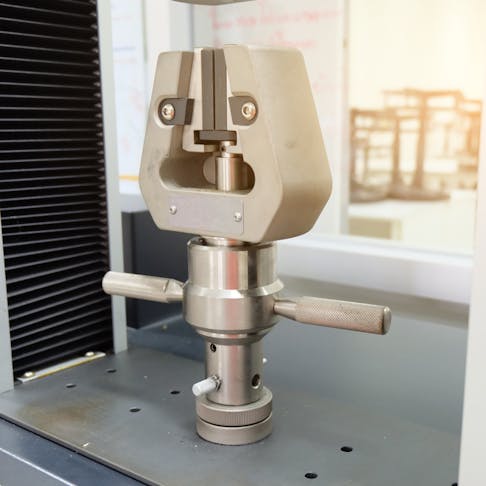
Tensile Testing Machine: Definition, How It Works, Types, Components, and Examples


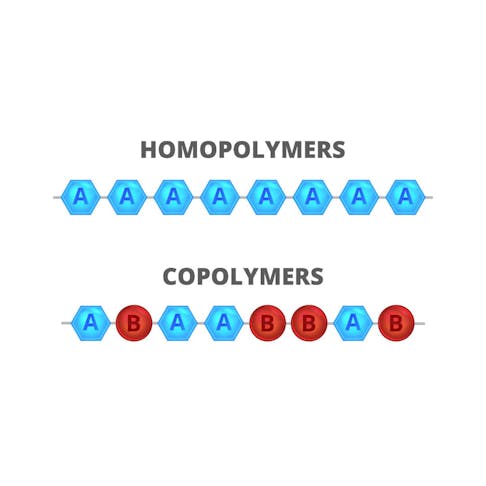



Compressibility: Definition, How It Works, Calculation, and Applications


Austenitic Stainless Steel: Definition, Composition, Types, Grades, Properties, and Applications


All About Engineering Plastics: Definition, Importance, Uses, Properties, and Types

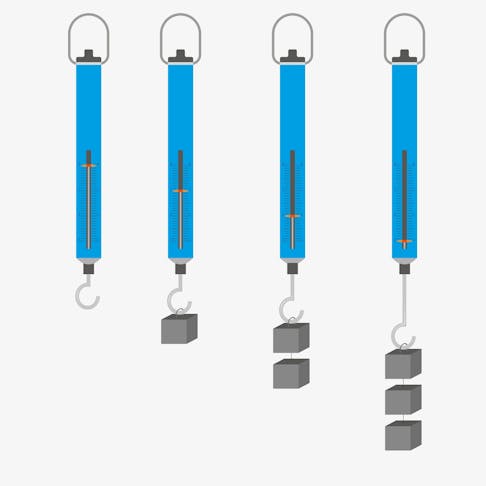
Force-Measurement Devices: Types, Devices, Characteristics, and Purpose









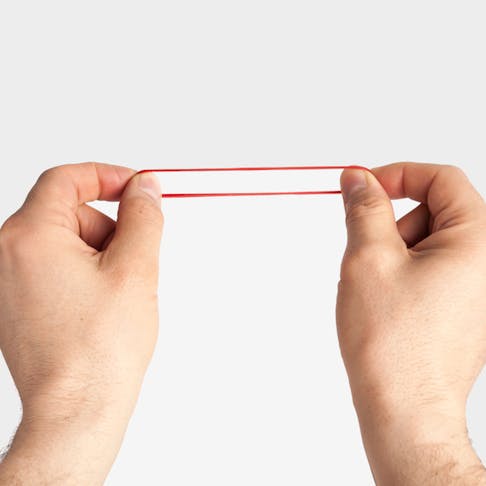
Proportional Limit: Definition, Concept, Characteristics, and Significance














